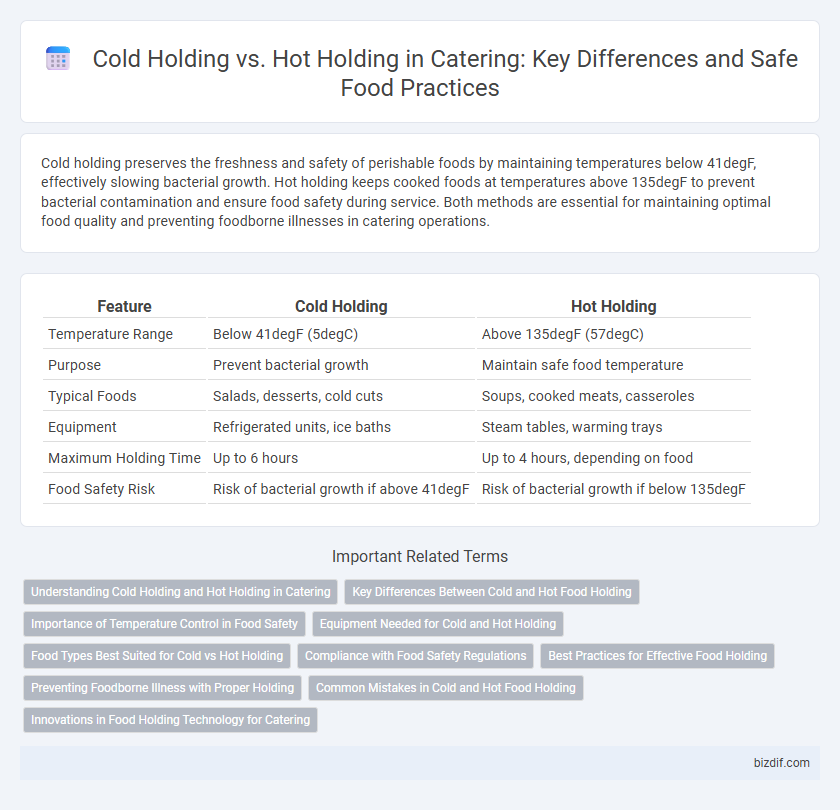
Cold holding preserves the freshness and safety of perishable foods by maintaining temperatures below 41degF, effectively slowing bacterial growth. Hot holding keeps cooked foods at temperatures above 135degF to prevent bacterial contamination and ensure food safety during service. Both methods are essential for maintaining optimal food quality and preventing foodborne illnesses in catering operations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cold Holding | Hot Holding |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Below 41degF (5degC) | Above 135degF (57degC) |
| Purpose | Prevent bacterial growth | Maintain safe food temperature |
| Typical Foods | Salads, desserts, cold cuts | Soups, cooked meats, casseroles |
| Equipment | Refrigerated units, ice baths | Steam tables, warming trays |
| Maximum Holding Time | Up to 6 hours | Up to 4 hours, depending on food |
| Food Safety Risk | Risk of bacterial growth if above 41degF | Risk of bacterial growth if below 135degF |
Understanding Cold Holding and Hot Holding in Catering
Cold holding in catering involves maintaining food at temperatures below 41degF (5degC) to prevent bacterial growth and ensure safety, especially for salads, desserts, and dairy products. Hot holding requires food to be kept at temperatures above 135degF (57degC) to preserve heat, taste, and texture while inhibiting harmful microorganisms, commonly used for cooked meats and soups. Proper temperature control in both cold and hot holding is critical for compliance with food safety regulations and minimizing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Key Differences Between Cold and Hot Food Holding
Cold holding maintains food at temperatures below 41degF (5degC) to inhibit bacterial growth and preserve freshness, while hot holding keeps food above 135degF (57degC) to prevent the proliferation of pathogens. Cold holding typically requires refrigeration or ice-based methods, whereas hot holding relies on steam tables, chafing dishes, or warming trays to sustain safe serving temperatures. Both methods are crucial for food safety but differ significantly in temperature ranges, equipment used, and preservation techniques.
Importance of Temperature Control in Food Safety
Temperature control is critical in catering to prevent bacterial growth and ensure food safety during cold holding (below 41degF or 5degC) and hot holding (above 135degF or 57degC). Maintaining these temperature ranges inhibits pathogens like Salmonella and Listeria, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses. Regular monitoring using calibrated thermometers safeguards proper food preservation and compliance with health regulations.
Equipment Needed for Cold and Hot Holding
Cold holding requires equipment such as refrigerated display cases, ice-filled trays, and refrigerated prep tables to maintain safe temperatures below 41degF and prevent bacterial growth. Hot holding relies on warming trays, steam tables, and insulated food carriers to keep food above 135degF, ensuring safety and maintaining proper texture and flavor. Both types of equipment must meet food safety standards and offer consistent temperature control to preserve food quality during service.
Food Types Best Suited for Cold vs Hot Holding
Cold holding is ideal for foods like salads, deli meats, seafood, and dairy products that require temperatures below 41degF to prevent bacterial growth and maintain freshness. Hot holding suits cooked dishes such as soups, stews, roasted meats, and casseroles, best kept above 135degF to ensure safety and preserve flavor. Proper temperature control tailored to food type optimizes both food safety and quality in catering operations.
Compliance with Food Safety Regulations
Cold holding requires maintaining foods at or below 41degF (5degC) to prevent bacterial growth, ensuring compliance with FDA Food Code standards. Hot holding mandates keeping cooked foods at a minimum of 135degF (57degC) to inhibit pathogen proliferation and meet health department regulations. Both practices are critical for minimizing foodborne illness risks and passing health inspections in catering operations.
Best Practices for Effective Food Holding
Maintaining precise temperature control is essential for effective food holding, with cold holding requiring foods to be kept below 41degF (5degC) to inhibit bacterial growth, while hot holding demands temperatures above 135degF (57degC) to ensure food safety. Using calibrated thermometers to monitor food temperatures regularly and minimizing the time food spends in the danger zone between 41degF and 135degF prevents contamination and preserves quality. Employing insulated containers, proper storage equipment, and adhering to local health regulations further ensures optimal cold and hot holding practices in catering operations.
Preventing Foodborne Illness with Proper Holding
Preventing foodborne illness in catering requires strict adherence to proper cold holding below 40degF (4degC) and hot holding above 135degF (57degC) to inhibit bacterial growth. Maintaining these temperature controls ensures perishable foods remain safe from pathogens like Salmonella and Listeria. Consistent monitoring with calibrated thermometers and rapid cooling or reheating processes are essential best practices for food safety compliance.
Common Mistakes in Cold and Hot Food Holding
Improper temperature control is a common mistake in cold and hot food holding, with cold foods often held above 41degF (5degC), increasing bacterial growth risk, while hot foods dropped below 135degF (57degC) can enter the danger zone. Insufficient monitoring or failure to use calibrated thermometers leads to inaccurate temperature readings, compromising food safety standards. Cross-contamination risks also arise when cold and hot foods are stored or served without proper separation and frequent temperature checks.
Innovations in Food Holding Technology for Catering
Innovations in food holding technology for catering include advanced cold holding systems with precision temperature control using thermoelectric cooling and vacuum insulation to maintain freshness and safety. Hot holding equipment now integrates infrared heating and smart sensors to ensure consistent warmth without drying or overcooking the food. These technologies optimize food quality, extend shelf life, and enhance operational efficiency in high-demand catering environments.
Cold holding vs Hot holding Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com