The Montessori approach emphasizes self-directed learning through structured activities that promote independence and sensory development, while the play-based approach encourages creativity and social skills through free play and imaginative exploration. Both methods foster cognitive and emotional growth but differ in their balance of guided instruction versus child-led experiences. Choosing between these approaches depends on a child's learning style and the goals of their early education.
Table of Comparison
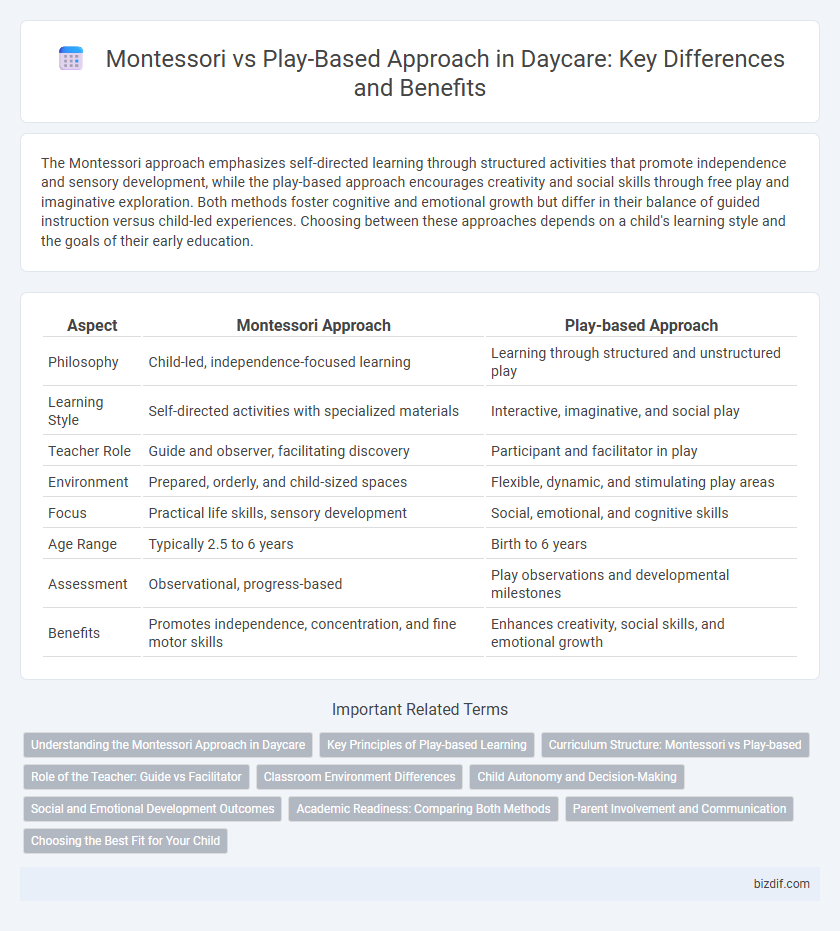
| Aspect | Montessori Approach | Play-based Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophy | Child-led, independence-focused learning | Learning through structured and unstructured play |
| Learning Style | Self-directed activities with specialized materials | Interactive, imaginative, and social play |
| Teacher Role | Guide and observer, facilitating discovery | Participant and facilitator in play |
| Environment | Prepared, orderly, and child-sized spaces | Flexible, dynamic, and stimulating play areas |
| Focus | Practical life skills, sensory development | Social, emotional, and cognitive skills |
| Age Range | Typically 2.5 to 6 years | Birth to 6 years |
| Assessment | Observational, progress-based | Play observations and developmental milestones |
| Benefits | Promotes independence, concentration, and fine motor skills | Enhances creativity, social skills, and emotional growth |
Understanding the Montessori Approach in Daycare
The Montessori approach in daycare emphasizes self-directed learning, hands-on activities, and fostering independence in children aged 2 to 6 years. This method uses specially designed materials that encourage sensory exploration and practical life skills, supporting cognitive and emotional development. Caregivers act as guides, creating a prepared environment that nurtures curiosity and individualized pacing for optimal growth.
Key Principles of Play-based Learning
Play-based learning centers on child-led activities where exploration and creativity promote cognitive and social development. This approach emphasizes active engagement, allowing children to develop problem-solving skills and emotional resilience through hands-on play. Key principles include fostering intrinsic motivation, encouraging collaboration, and adapting to individual interests and developmental stages.
Curriculum Structure: Montessori vs Play-based
The Montessori curriculum structure emphasizes individualized, self-paced learning with a focus on hands-on, purposeful activities designed to develop practical life skills and sensory refinement. In contrast, the play-based approach centers around child-led exploration and social interaction, using unstructured play to foster creativity, communication, and emotional development. Montessori classrooms maintain a carefully prepared environment with specific materials, while play-based settings offer diverse, flexible play opportunities to support holistic development.
Role of the Teacher: Guide vs Facilitator
In the Montessori approach, the teacher acts as a guide, carefully observing each child to tailor lessons that promote independence and self-directed learning within a structured environment. Conversely, the play-based approach positions the teacher as a facilitator who encourages creativity and social interaction by providing open-ended materials and supporting children's spontaneous play. Both roles emphasize fostering development, but the Montessori guide directs focused learning, while the play facilitator nurtures exploration and collaboration.
Classroom Environment Differences
Montessori classrooms feature carefully prepared environments with distinct learning areas, natural materials, and child-sized furniture designed to promote independence and self-directed learning. Play-based classrooms emphasize flexible, open spaces with diverse toys and materials that encourage imaginative play, social interaction, and creativity. The Montessori environment fosters order and routine, while play-based settings prioritize spontaneity and exploration.
Child Autonomy and Decision-Making
The Montessori approach emphasizes fostering child autonomy by providing structured environments where children make independent choices within guided activities, supporting self-discipline and decision-making skills. In contrast, the play-based approach encourages autonomy through unstructured, imaginative play that allows children to explore preferences and solve problems organically, promoting creativity and social decision-making. Both methods prioritize empowering children but differ in the balance between adult guidance and free choice in early childhood development.
Social and Emotional Development Outcomes
The Montessori approach fosters social and emotional development by promoting independence, self-regulation, and respectful peer interactions through structured activities and collaborative tasks. In contrast, the play-based approach encourages creativity, empathy, and emotional expression by allowing children to engage freely in imaginative play and social scenarios. Both methods effectively support emotional resilience and social skills, but Montessori emphasizes guided social learning while play-based prioritizes spontaneous interpersonal experiences.
Academic Readiness: Comparing Both Methods
The Montessori approach fosters academic readiness through structured activities that emphasize self-discipline and individualized learning, promoting early literacy and numeracy skills. In contrast, the play-based approach encourages cognitive and social development by allowing children to explore concepts through imaginative and interactive play, which indirectly supports foundational academic skills. Both methods enhance school preparedness but differ in their balance between direct instruction and experiential, child-led discovery.
Parent Involvement and Communication
The Montessori approach emphasizes structured parent involvement through regular updates and detailed progress reports, fostering a collaborative environment focused on individual child development. In contrast, the play-based approach encourages informal communication, offering parents opportunities to observe and participate in spontaneous play activities that stimulate social and emotional growth. Both methods prioritize transparent dialogue, but Montessori relies on systematic feedback while play-based promotes dynamic, interactive engagement.
Choosing the Best Fit for Your Child
The Montessori approach emphasizes structured, self-directed learning with hands-on materials promoting independence and concentration, ideal for children who thrive in orderly environments. In contrast, the play-based approach fosters creativity, social skills, and emotional development through unstructured, imaginative play, suited for children who benefit from flexibility and spontaneous interactions. Evaluating your child's personality, learning style, and developmental needs helps determine whether a Montessori or play-based daycare setting will best support their growth and happiness.
Montessori Approach vs Play-based Approach Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com