Wholesale in dropshipping pet products involves purchasing items directly from manufacturers or distributors at bulk prices, ensuring lower costs and consistent supply chains. Retail arbitrage requires sourcing pet supplies from retail stores at discounted prices and reselling them online for profit, but it often comes with limited inventory and price volatility. Comparing the two, wholesale offers scalability and stable margins, while retail arbitrage provides flexibility and quick product turnover.
Table of Comparison
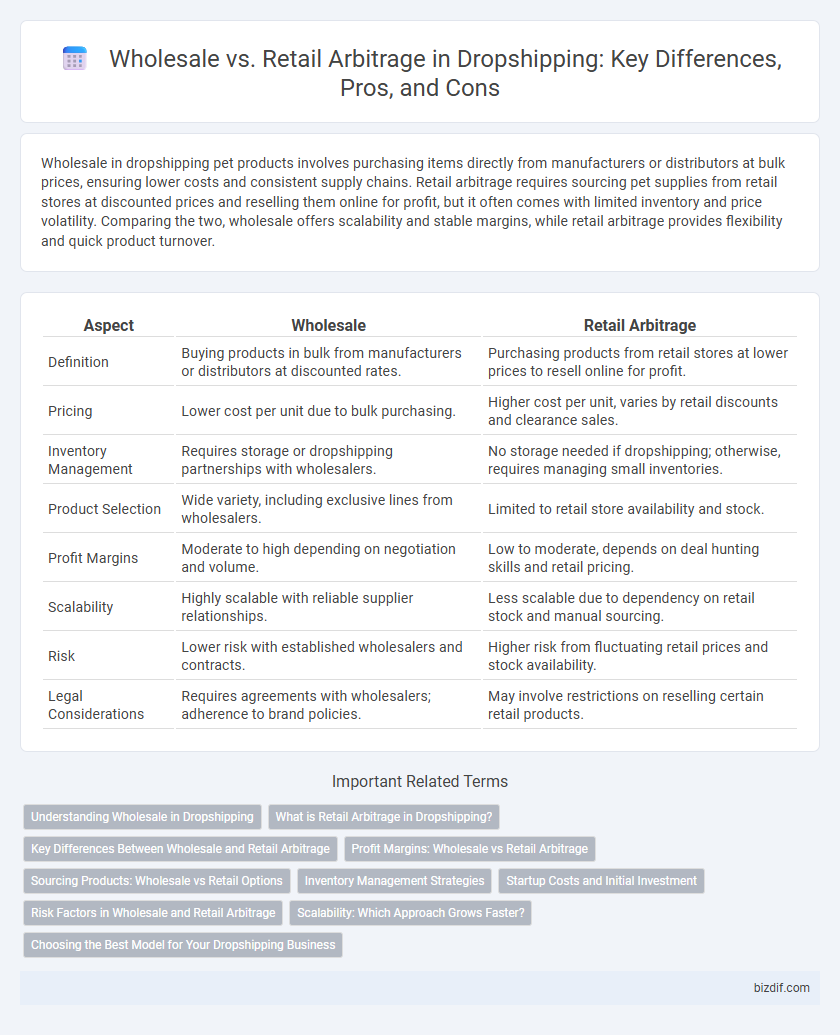
| Aspect | Wholesale | Retail Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying products in bulk from manufacturers or distributors at discounted rates. | Purchasing products from retail stores at lower prices to resell online for profit. |
| Pricing | Lower cost per unit due to bulk purchasing. | Higher cost per unit, varies by retail discounts and clearance sales. |
| Inventory Management | Requires storage or dropshipping partnerships with wholesalers. | No storage needed if dropshipping; otherwise, requires managing small inventories. |
| Product Selection | Wide variety, including exclusive lines from wholesalers. | Limited to retail store availability and stock. |
| Profit Margins | Moderate to high depending on negotiation and volume. | Low to moderate, depends on deal hunting skills and retail pricing. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with reliable supplier relationships. | Less scalable due to dependency on retail stock and manual sourcing. |
| Risk | Lower risk with established wholesalers and contracts. | Higher risk from fluctuating retail prices and stock availability. |
| Legal Considerations | Requires agreements with wholesalers; adherence to brand policies. | May involve restrictions on reselling certain retail products. |
Understanding Wholesale in Dropshipping
Wholesale in dropshipping involves purchasing products in bulk directly from manufacturers or authorized distributors at significantly reduced prices, enabling sellers to maximize profit margins. This model requires establishing reliable supplier relationships and managing inventory indirectly, allowing for scalable business operations without upfront stock investment. Understanding wholesale dynamics is crucial for dropshippers aiming to offer competitive pricing and maintain product quality while minimizing overhead costs.
What is Retail Arbitrage in Dropshipping?
Retail arbitrage in dropshipping involves purchasing products from retail stores at lower prices and then selling them online at a higher price without holding inventory. This method leverages price discrepancies between physical retail outlets and online marketplaces, enabling dropshippers to generate profit with minimal upfront investment. Successful retail arbitrage requires careful market research, price monitoring, and efficient order fulfillment to maintain competitive margins.
Key Differences Between Wholesale and Retail Arbitrage
Wholesale involves purchasing products in bulk directly from manufacturers or distributors at significantly lower prices, enabling higher profit margins in dropshipping. Retail arbitrage entails buying discounted or clearance items from retail stores to resell online, often with limited stock and fluctuating availability. Key differences include bulk buying versus single-item purchases, consistent supply from wholesalers compared to unpredictable retail inventory, and varying pricing strategies impacting scalability and profit potential.
Profit Margins: Wholesale vs Retail Arbitrage
Wholesale dropshipping typically offers higher profit margins compared to retail arbitrage due to bulk purchasing at lower costs per unit. Retail arbitrage involves buying products at retail prices and reselling them, often resulting in thinner margins after fees and shipping costs. Prioritizing wholesale suppliers can significantly boost overall profitability in dropshipping businesses.
Sourcing Products: Wholesale vs Retail Options
Wholesale sourcing involves purchasing products in bulk directly from manufacturers or authorized distributors, offering lower per-unit costs and consistent inventory availability. Retail arbitrage entails buying discounted or clearance items from retail stores to resell online, often leading to limited stock and higher per-unit prices. Choosing between wholesale and retail options depends on product scalability, profit margins, and supply chain stability in dropshipping operations.
Inventory Management Strategies
Wholesale dropshipping involves purchasing bulk inventory from suppliers, enabling greater control over stock levels and often resulting in better pricing and availability forecasting. Retail arbitrage relies on sourcing products from retail stores or online marketplaces, which can lead to unpredictable stock quantities and frequent restocking challenges. Effective inventory management in wholesale emphasizes demand forecasting and supplier coordination, while retail arbitrage requires agile monitoring of product availability and competitive pricing adjustments.
Startup Costs and Initial Investment
Wholesale dropshipping requires a higher initial investment due to bulk purchasing and inventory storage, often ranging from $1,000 to $5,000. Retail arbitrage has lower startup costs, typically under $500, as it involves buying discounted retail products individually for resale. Understanding the difference in capital commitment helps entrepreneurs choose the most viable dropshipping strategy based on budget constraints.
Risk Factors in Wholesale and Retail Arbitrage
Wholesale arbitrage involves purchasing large quantities of products directly from manufacturers or distributors, reducing per-unit costs but increasing inventory holding risks and potential capital loss if items do not sell. Retail arbitrage carries risks related to sourcing products from retail stores, including stock unavailability, pricing fluctuations, and limited scalability due to fragmented inventory. Both methods face challenges like market demand uncertainty, supplier reliability, and the possibility of obsolete or unsold inventory impacting overall profitability.
Scalability: Which Approach Grows Faster?
Wholesale dropshipping offers greater scalability due to bulk purchasing and consistent supplier relationships, enabling faster inventory expansion and price advantages. Retail arbitrage depends on sourcing limited discounted products from retail stores, which restricts volume and slows growth potential. Therefore, wholesale's streamlined supply chain and predictable stock availability foster quicker business scaling compared to the unpredictable nature of retail arbitrage.
Choosing the Best Model for Your Dropshipping Business
Wholesale dropshipping offers access to bulk products at lower prices, enabling higher profit margins and consistent inventory from trusted suppliers. Retail arbitrage relies on purchasing discounted items from retail stores to resell online at a markup, requiring keen market research and nimble sourcing strategies. Evaluating factors like capital investment, scalability potential, and supplier reliability is crucial to selecting the best dropshipping model for sustainable business growth.
Wholesale vs Retail Arbitrage Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com