Cart abandonment rate measures the percentage of shoppers who add items to their online cart but leave before initiating checkout, while checkout abandonment rate refers to users who start the checkout process but fail to complete the purchase. Reducing cart abandonment requires enhancing the overall shopping experience, such as simplifying navigation and providing clear product information. Lowering checkout abandonment focuses on streamlining payment options, minimizing form fields, and offering trust signals to reassure customers during the final purchase steps.
Table of Comparison
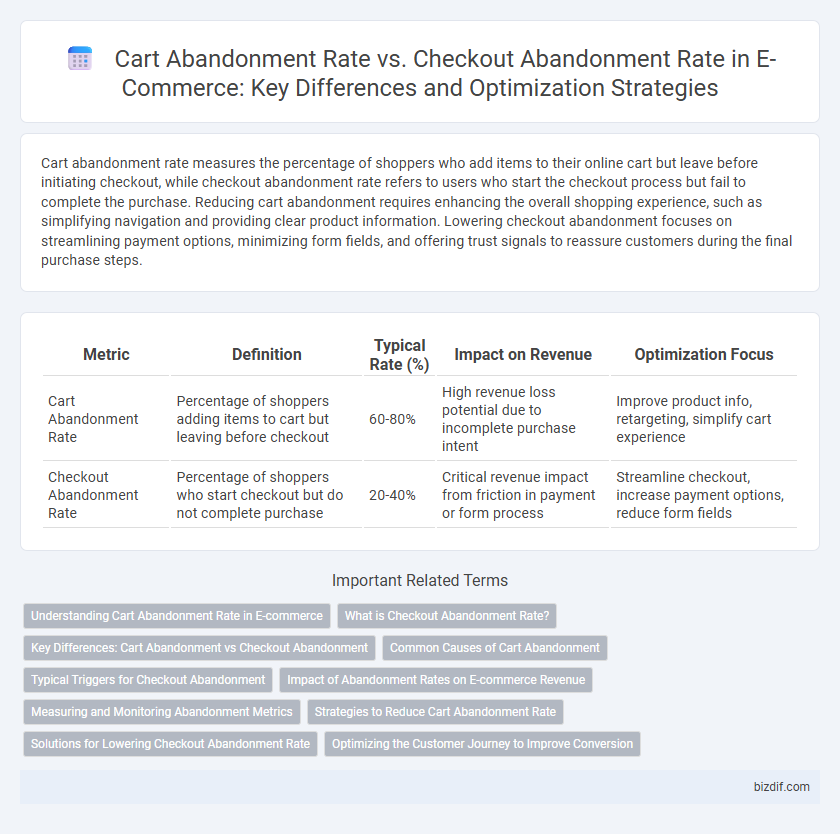
| Metric | Definition | Typical Rate (%) | Impact on Revenue | Optimization Focus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cart Abandonment Rate | Percentage of shoppers adding items to cart but leaving before checkout | 60-80% | High revenue loss potential due to incomplete purchase intent | Improve product info, retargeting, simplify cart experience |
| Checkout Abandonment Rate | Percentage of shoppers who start checkout but do not complete purchase | 20-40% | Critical revenue impact from friction in payment or form process | Streamline checkout, increase payment options, reduce form fields |
Understanding Cart Abandonment Rate in E-commerce
Cart Abandonment Rate in e-commerce measures the percentage of shoppers who add items to their cart but leave before initiating the checkout process, highlighting potential issues in product interest or site navigation. This metric differs from Checkout Abandonment Rate, which tracks customers who begin the checkout process but fail to complete the purchase, indicating possible friction at payment or shipping stages. Analyzing Cart Abandonment Rate helps businesses identify early drop-off points and optimize site usability, product offerings, and marketing strategies to improve conversion rates.
What is Checkout Abandonment Rate?
Checkout Abandonment Rate measures the percentage of shoppers who add items to their cart and proceed to the checkout page but leave before completing the purchase. This metric highlights friction points in the final steps of the purchase funnel, such as complicated forms, payment issues, or unexpected costs. Reducing checkout abandonment boosts conversion rates and increases revenue in e-commerce platforms.
Key Differences: Cart Abandonment vs Checkout Abandonment
Cart abandonment rate measures the percentage of online shoppers who add items to their cart but leave before initiating the checkout process, while checkout abandonment rate tracks users who start the checkout but do not complete the purchase. Cart abandonment typically reflects browsing behavior or hesitations with product selection, whereas checkout abandonment indicates issues within the payment stage, such as unexpected costs or complicated forms. Understanding these distinctions helps e-commerce businesses tailor strategies to reduce drop-offs at specific funnel points and improve overall conversion rates.
Common Causes of Cart Abandonment
High cart abandonment rates in e-commerce often result from unexpected costs, complicated navigation, and lack of payment options, causing users to leave before proceeding to checkout. Slow website speed and unclear return policies also contribute significantly to shoppers abandoning their carts. Understanding these factors helps businesses optimize user experience and reduce revenue loss.
Typical Triggers for Checkout Abandonment
Checkout abandonment often arises from unexpected costs like high shipping fees or taxes that appear late in the process, deterring customers from finalizing their purchases. Complex or lengthy checkout forms, limited payment options, and lack of trust signals also significantly contribute to users abandoning their carts. Ensuring transparency in pricing, streamlining the checkout process, and providing secure, diverse payment methods can reduce the typical triggers for checkout abandonment effectively.
Impact of Abandonment Rates on E-commerce Revenue
Cart abandonment rate directly reduces potential sales by indicating how many customers add items but leave without proceeding to checkout, while checkout abandonment rate reflects the percentage of users who start the checkout process but fail to complete the purchase. High abandonment rates negatively impact e-commerce revenue by decreasing conversion rates and increasing customer acquisition costs, as businesses spend more to attract shoppers who do not finalize transactions. Optimizing the checkout experience and reducing friction points significantly improves revenue by converting more visitors into paying customers.
Measuring and Monitoring Abandonment Metrics
Measuring cart abandonment rate involves tracking the percentage of shoppers who add items to their cart but leave before initiating the checkout process, while checkout abandonment rate monitors the drop-off during the checkout steps after cart initiation. Effective monitoring requires integrating analytics tools such as Google Analytics and e-commerce platforms to capture precise event tracking, enabling identification of friction points and drop-off stages. Regular analysis of these metrics helps optimize user experience and increase conversion rates by targeting specific abandonment causes.
Strategies to Reduce Cart Abandonment Rate
Reducing cart abandonment rate involves optimizing user experience through streamlined navigation, clear product information, and simplified checkout processes. Implementing targeted email reminders and offering limited-time discounts can effectively re-engage shoppers who leave items in their carts. Utilizing personalized retargeting ads and providing multiple secure payment options also significantly decrease abandonment by building trust and convenience for online customers.
Solutions for Lowering Checkout Abandonment Rate
Reducing checkout abandonment rate requires streamlining the payment process by offering multiple secure payment options and minimizing form fields to enhance user experience. Implementing real-time support through chatbots or live agents addresses customer concerns instantly, significantly lowering drop-offs during checkout. Optimizing site speed and providing transparent shipping costs upfront also build trust, encouraging users to complete their purchases.
Optimizing the Customer Journey to Improve Conversion
Cart Abandonment Rate measures the percentage of shoppers who add items to their cart but leave before initiating checkout, while Checkout Abandonment Rate tracks users who start the checkout process but fail to complete the purchase. Reducing these rates through streamlined navigation, simplified payment options, and personalized reminders enhances the customer journey and drives higher conversion rates. Implementing real-time analytics and A/B testing helps identify friction points, enabling targeted optimizations that improve overall sales performance.
Cart Abandonment Rate vs Checkout Abandonment Rate Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com