First-party data offers e-commerce businesses accurate and reliable insights collected directly from their customers, enabling personalized marketing strategies and improved customer engagement. In contrast, third-party data is aggregated from external sources and may lack precision or relevance, leading to less effective targeting and potential privacy concerns. Prioritizing first-party data enhances trust, compliance with data regulations, and drives higher conversion rates in online retail.
Table of Comparison
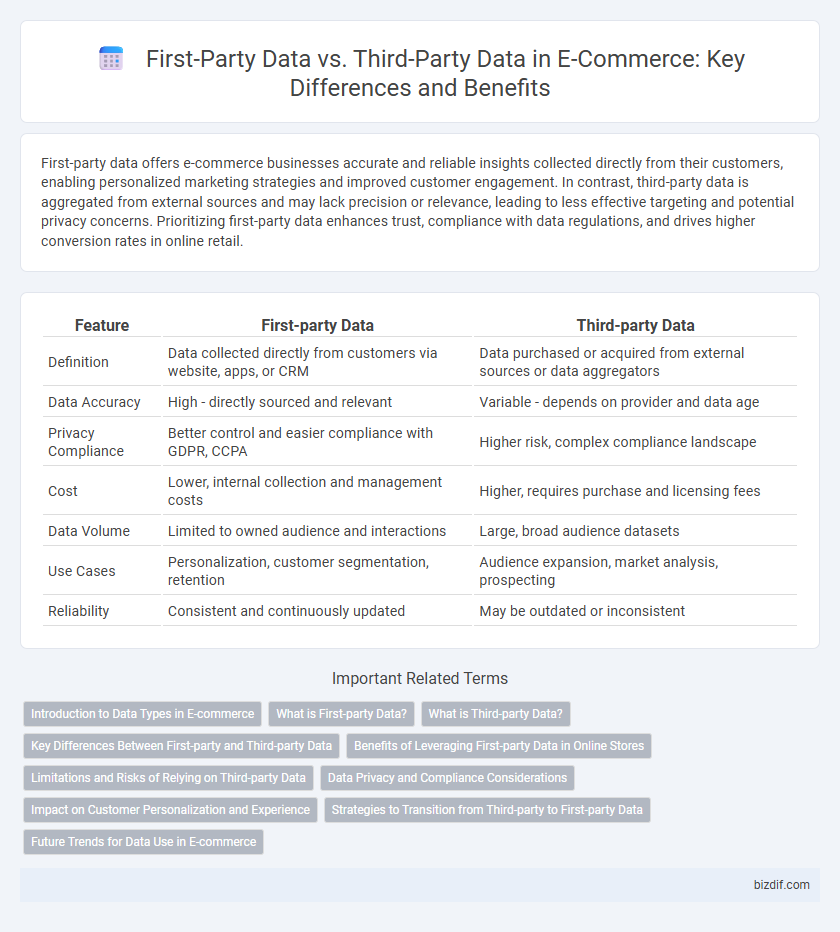
| Feature | First-party Data | Third-party Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data collected directly from customers via website, apps, or CRM | Data purchased or acquired from external sources or data aggregators |
| Data Accuracy | High - directly sourced and relevant | Variable - depends on provider and data age |
| Privacy Compliance | Better control and easier compliance with GDPR, CCPA | Higher risk, complex compliance landscape |
| Cost | Lower, internal collection and management costs | Higher, requires purchase and licensing fees |
| Data Volume | Limited to owned audience and interactions | Large, broad audience datasets |
| Use Cases | Personalization, customer segmentation, retention | Audience expansion, market analysis, prospecting |
| Reliability | Consistent and continuously updated | May be outdated or inconsistent |
Introduction to Data Types in E-commerce
First-party data in e-commerce refers to information collected directly from customers through interactions on websites, apps, or purchase histories, offering highly accurate insights for personalized marketing. Third-party data is aggregated from external sources beyond the direct relationship between the retailer and the customer, often used to reach broader audiences but can lack precision. Understanding these data types enables e-commerce businesses to optimize customer targeting, improve user experiences, and increase conversion rates.
What is First-party Data?
First-party data in e-commerce refers to information collected directly from customers through channels like websites, mobile apps, and purchase histories, providing highly accurate and relevant insights. This data includes behavioral patterns, preferences, and demographic details, enabling personalized marketing strategies and improved customer experiences. Leveraging first-party data enhances targeting precision while maintaining compliance with privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
What is Third-party Data?
Third-party data in e-commerce refers to information collected by external sources not directly connected to the brand or website, often aggregated from multiple platforms. This data helps businesses understand broader consumer behaviors and demographics but may lack the precision and consent associated with first-party data. Marketers use third-party data for targeted advertising and market analysis to expand customer reach beyond their own user base.
Key Differences Between First-party and Third-party Data
First-party data is collected directly from customers through an e-commerce platform, including purchase history, browsing behavior, and customer feedback, ensuring high accuracy and relevance. Third-party data is aggregated from external sources, often combining multiple datasets to provide broader audience insights but may suffer from lower precision and potential privacy concerns. E-commerce businesses prioritize first-party data for personalized marketing and customer retention, while third-party data is used for expanding reach and targeting new customer segments.
Benefits of Leveraging First-party Data in Online Stores
First-party data in e-commerce offers unparalleled accuracy and customer insight by directly capturing user behavior and preferences on online stores. Leveraging this data enhances personalized marketing campaigns, boosts customer loyalty, and increases conversion rates by delivering relevant product recommendations. Online retailers benefit from improved data privacy compliance and reduced reliance on external sources, strengthening trust and long-term customer relationships.
Limitations and Risks of Relying on Third-party Data
Relying on third-party data in e-commerce introduces significant limitations such as data accuracy issues, reduced relevance, and lack of transparency regarding data collection methods. The risk of privacy violations and regulatory non-compliance increases due to limited control over third-party sources, potentially resulting in data breaches or legal penalties. In contrast, first-party data offers higher reliability, enhanced customer insights, and stronger compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Data Privacy and Compliance Considerations
First-party data in e-commerce is collected directly from customers through owned channels, offering higher accuracy and better compliance with data privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Third-party data aggregates information from external sources, often raising concerns over user consent, data quality, and legal risks under evolving privacy laws. Prioritizing first-party data enables e-commerce businesses to build trust, ensure transparent data practices, and maintain compliance while delivering personalized customer experiences.
Impact on Customer Personalization and Experience
First-party data, collected directly from customers through interactions on an e-commerce platform, enables highly accurate customer personalization by reflecting real behaviors and preferences, leading to enhanced user experiences and increased loyalty. Third-party data, aggregated from external sources, offers broader demographic insights but often lacks the precision needed for deep personalization, potentially resulting in generic recommendations and lower customer engagement. Prioritizing first-party data allows e-commerce businesses to deliver tailored content and dynamic offers, improving customer satisfaction and driving higher conversion rates.
Strategies to Transition from Third-party to First-party Data
E-commerce businesses should prioritize building robust first-party data strategies by leveraging customer interactions on owned channels such as websites, apps, and loyalty programs to create personalized experiences and improve targeting accuracy. Implementing advanced CRM systems and utilizing AI-driven analytics can enhance data collection and real-time insights, reducing reliance on third-party cookies. Fostering direct customer relationships through exclusive offers and transparent privacy policies encourages data sharing, ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and improving long-term data quality.
Future Trends for Data Use in E-commerce
First-party data in e-commerce is becoming increasingly valuable due to rising privacy regulations and the decline of third-party cookies, enabling brands to develop personalized customer experiences through directly collected insights. Advancements in AI and machine learning are enhancing the ability to analyze first-party data, driving more accurate targeting and predictive analytics for customer behavior. Future trends indicate a shift towards data sovereignty and consumer consent frameworks, empowering shoppers with control over their data while allowing retailers to build trust and loyalty through transparent data practices.
First-party Data vs Third-party Data Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com