First-party logistics (1PL) involves businesses managing their own warehousing, inventory, and shipping operations, offering greater control and customization over the supply chain. Third-party logistics (3PL) providers handle these tasks on behalf of companies, enabling scalability, reducing overhead costs, and leveraging specialized expertise in transportation and fulfillment. Choosing between 1PL and 3PL depends on factors like business size, complexity, and growth goals, with many e-commerce companies opting for 3PL to streamline operations and improve delivery speed.
Table of Comparison
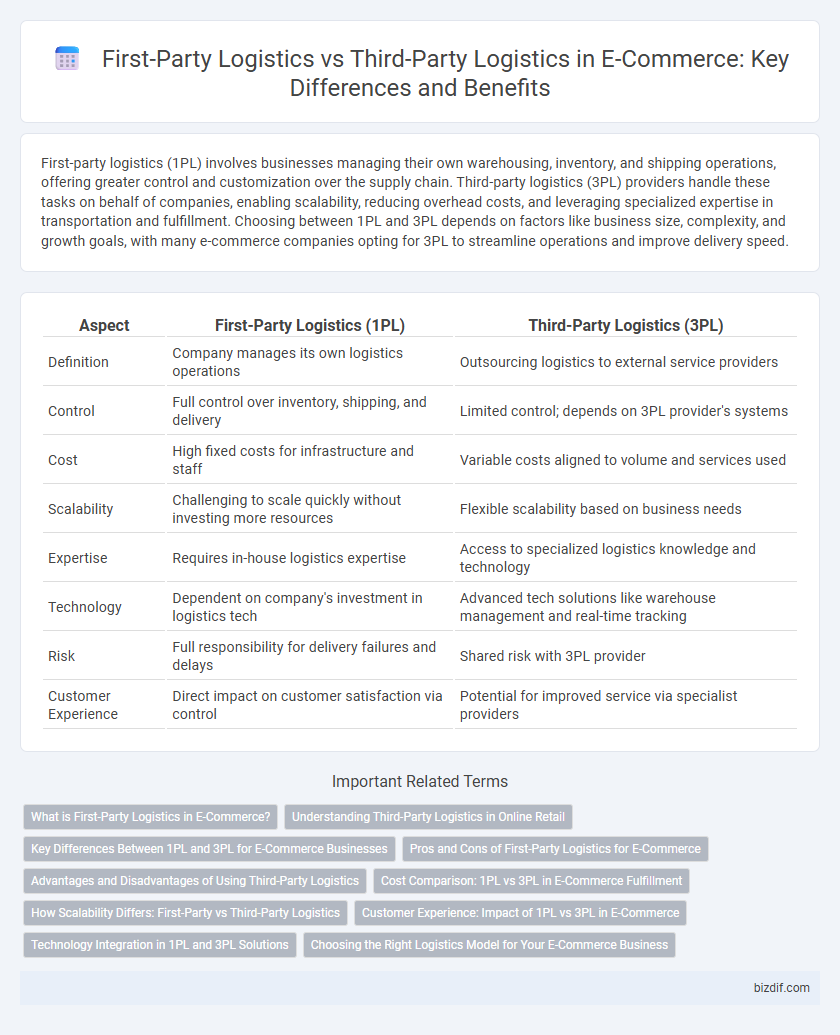
| Aspect | First-Party Logistics (1PL) | Third-Party Logistics (3PL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Company manages its own logistics operations | Outsourcing logistics to external service providers |
| Control | Full control over inventory, shipping, and delivery | Limited control; depends on 3PL provider's systems |
| Cost | High fixed costs for infrastructure and staff | Variable costs aligned to volume and services used |
| Scalability | Challenging to scale quickly without investing more resources | Flexible scalability based on business needs |
| Expertise | Requires in-house logistics expertise | Access to specialized logistics knowledge and technology |
| Technology | Dependent on company's investment in logistics tech | Advanced tech solutions like warehouse management and real-time tracking |
| Risk | Full responsibility for delivery failures and delays | Shared risk with 3PL provider |
| Customer Experience | Direct impact on customer satisfaction via control | Potential for improved service via specialist providers |
What is First-Party Logistics in E-Commerce?
First-party logistics in e-commerce refers to the practice where an online retailer manages its own inventory storage, order fulfillment, and shipping processes internally, without outsourcing to external providers. This approach offers greater control over inventory accuracy, customer service, and delivery timelines, often leading to enhanced brand consistency and cost savings on long-term operations. Companies leveraging first-party logistics rely heavily on in-house warehousing, proprietary transportation networks, and integrated technology systems to optimize the entire supply chain.
Understanding Third-Party Logistics in Online Retail
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers offer specialized supply chain solutions including warehousing, order fulfillment, and shipping services, enabling online retailers to scale operations without investing in infrastructure. Outsourcing logistics to 3PL companies improves delivery speed, reduces shipping costs, and enhances customer experience by leveraging their technology and network expertise. E-commerce businesses gain flexibility and focus on core activities like marketing and product development while third-party logistics partners handle inventory management and last-mile delivery efficiently.
Key Differences Between 1PL and 3PL for E-Commerce Businesses
First-party logistics (1PL) in e-commerce involves the business managing its own inventory storage, packaging, and shipping processes, giving full control over the supply chain but requiring significant resources and infrastructure. Third-party logistics (3PL) providers offer outsourced services including warehousing, order fulfillment, and transportation, allowing e-commerce businesses to scale quickly and reduce operational complexities. Key differences include control over logistics operations, investment requirements, and flexibility in handling peak demand or geographic expansion.
Pros and Cons of First-Party Logistics for E-Commerce
First-party logistics in e-commerce offers greater control over inventory management, fulfillment accuracy, and customer experience, enabling businesses to tailor operations precisely to brand standards. However, it requires significant investment in warehousing, technology, and workforce, potentially increasing fixed costs and operational complexity. Limited scalability compared to third-party logistics can hinder rapid expansion or seasonal demand spikes, posing challenges for growing e-commerce companies.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Third-Party Logistics
Third-party logistics (3PL) offers e-commerce businesses scalable warehousing, advanced technology integration, and access to specialized distribution networks, reducing operational complexities and upfront investment costs. However, reliance on 3PL can lead to less control over order fulfillment processes, potential communication challenges, and variable service quality depending on the provider's capabilities. Outsourcing logistics through 3PL enables faster market expansion but requires careful partner selection to mitigate risks related to inventory accuracy and shipping delays.
Cost Comparison: 1PL vs 3PL in E-Commerce Fulfillment
First-party logistics (1PL) involves brands managing their own fulfillment processes, resulting in higher upfront investments in warehousing, labor, and technology, but offering greater control over inventory and customer experience. Third-party logistics (3PL) providers offer scalable fulfillment solutions with variable costs linked to order volume and shipping, reducing capital expenditure and operational risks for e-commerce businesses. Cost efficiency in e-commerce fulfillment depends on order frequency, product complexity, and growth projections, where 3PL often provides lower marginal costs while 1PL may be more cost-effective for high-volume, stable operations.
How Scalability Differs: First-Party vs Third-Party Logistics
First-party logistics offers greater control but limited scalability due to reliance on in-house resources and infrastructure. Third-party logistics providers leverage extensive networks and advanced technology platforms to rapidly scale operations in response to fluctuating order volumes. E-commerce businesses often choose third-party logistics for flexible expansion during peak seasons and global market reach.
Customer Experience: Impact of 1PL vs 3PL in E-Commerce
First-party logistics (1PL) offers e-commerce businesses direct control over inventory and fulfillment, enabling customized packaging and faster response times that enhance customer satisfaction. Third-party logistics (3PL) providers bring scalability and specialized expertise, improving delivery speed and reliability, which positively influences the overall customer experience. The choice between 1PL and 3PL significantly affects order accuracy, shipping transparency, and return handling, critical factors in customer loyalty and retention.
Technology Integration in 1PL and 3PL Solutions
First-party logistics (1PL) systems often rely on in-house technology platforms tailored to the specific operational needs of the e-commerce business, enabling direct control over inventory management, order processing, and delivery tracking. Third-party logistics (3PL) providers leverage advanced, scalable software solutions such as Transportation Management Systems (TMS) and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) to offer seamless integration with multiple sales channels, real-time shipment visibility, and predictive analytics. Both 1PL and 3PL solutions prioritize technology integration to enhance supply chain efficiency, but 3PLs typically provide more robust, multi-client platforms that support complex logistics networks and enable faster adaptation to market demands.
Choosing the Right Logistics Model for Your E-Commerce Business
Selecting between first-party logistics (1PL) and third-party logistics (3PL) hinges on your e-commerce business size, budget, and scalability needs. First-party logistics offers greater control and customization by managing warehousing, inventory, and shipping internally, ideal for businesses with high order volumes and specialized requirements. Third-party logistics providers streamline operations through outsourced warehousing, fulfillment, and delivery services, offering cost efficiency and flexibility for startups and growing e-commerce brands seeking rapid market entry.
First-party logistics vs Third-party logistics Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com