A payment gateway securely transmits customers' payment information from an e-commerce pet store to the payment processor, ensuring smooth and safe online transactions. The payment processor handles the actual transaction by communicating with the customer's bank and the merchant's bank to authorize and settle payments. Understanding the difference between these two components helps pet retailers optimize their checkout process and enhance customer trust.
Table of Comparison
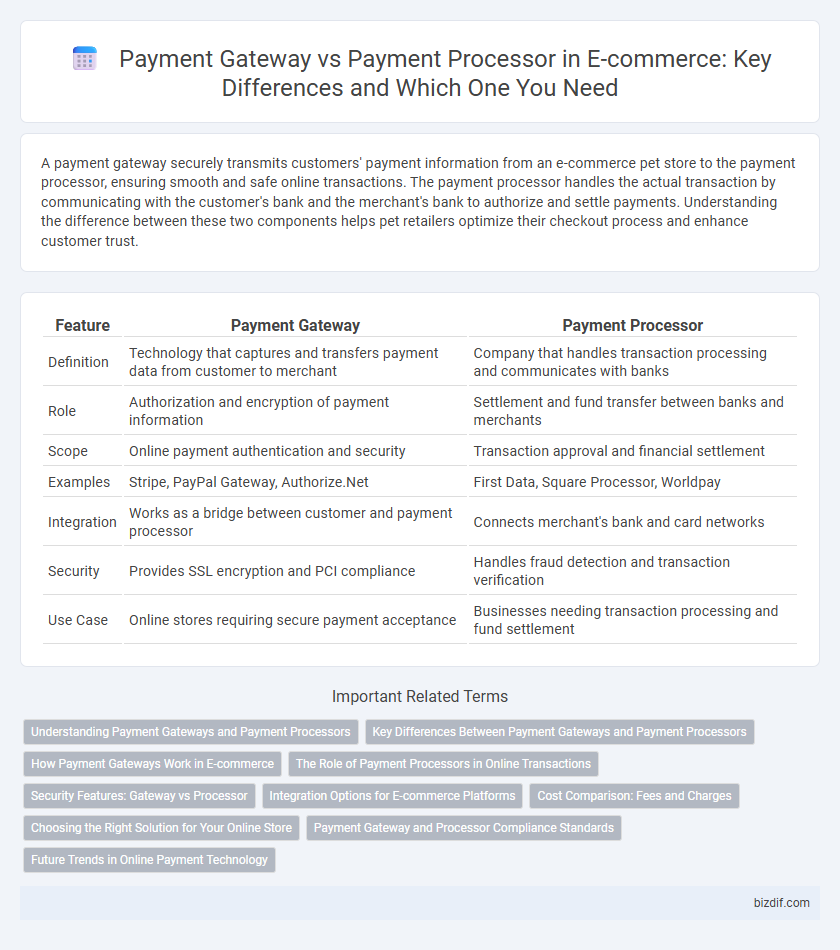
| Feature | Payment Gateway | Payment Processor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technology that captures and transfers payment data from customer to merchant | Company that handles transaction processing and communicates with banks |
| Role | Authorization and encryption of payment information | Settlement and fund transfer between banks and merchants |
| Scope | Online payment authentication and security | Transaction approval and financial settlement |
| Examples | Stripe, PayPal Gateway, Authorize.Net | First Data, Square Processor, Worldpay |
| Integration | Works as a bridge between customer and payment processor | Connects merchant's bank and card networks |
| Security | Provides SSL encryption and PCI compliance | Handles fraud detection and transaction verification |
| Use Case | Online stores requiring secure payment acceptance | Businesses needing transaction processing and fund settlement |
Understanding Payment Gateways and Payment Processors
Payment gateways serve as the secure bridge between an online store and the payment processor, capturing and encrypting customer payment data during checkout. Payment processors handle the actual transaction by communicating with banks and credit card networks to authorize and settle payments. Understanding the distinct roles of payment gateways and processors is essential for optimizing e-commerce payment security and transaction efficiency.
Key Differences Between Payment Gateways and Payment Processors
Payment gateways act as the secure bridge between the customer and the merchant by encrypting sensitive payment data to authorize transactions, while payment processors handle the actual transaction by communicating with banks and card networks to transfer funds. Key differences include the gateway's role in data encryption and fraud prevention, contrasting with the processor's function of managing transaction approvals and fund settlements. Understanding these distinctions is essential for optimizing transaction security, speed, and reliability in e-commerce environments.
How Payment Gateways Work in E-commerce
Payment gateways in e-commerce securely capture and transmit customers' payment information from the website to the payment processor, ensuring encrypted data transfer through SSL technology. They validate card details, check for fraud using real-time risk assessment tools, and facilitate authorization requests with acquiring banks. By providing a seamless interface for payment authentication, payment gateways enhance transaction speed and security, boosting customer trust and conversion rates.
The Role of Payment Processors in Online Transactions
Payment processors act as the critical intermediaries that facilitate the authorization, processing, and settlement of online payment transactions between merchants and customers. They securely transmit transaction data from the payment gateway to the acquiring bank, ensuring real-time communication and fraud detection. Efficient payment processing enhances customer experience by minimizing transaction failures and accelerating fund transfers in e-commerce environments.
Security Features: Gateway vs Processor
Payment gateways employ advanced encryption protocols such as SSL/TLS to secure customer data during online transactions, ensuring real-time fraud detection and compliance with PCI DSS standards. Payment processors handle the authentication and settlement of payments, utilizing tokenization and multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access and reduce chargebacks. Both systems integrate secure data transmission methods, but gateways focus on front-end security while processors maintain back-end transaction integrity.
Integration Options for E-commerce Platforms
Payment gateway integration options for e-commerce platforms often include API-based connectors, hosted payment pages, and SDKs to streamline transaction processing. Payment processors typically operate behind the scenes, interfacing through the payment gateway using secure protocols without direct integration requirements on the merchant's end. Choosing a payment gateway with flexible integration options ensures seamless checkout experiences and supports various coding environments and e-commerce frameworks.
Cost Comparison: Fees and Charges
Payment gateways typically charge a setup fee ranging from $0 to $200, a monthly fee between $10 and $30, and transaction fees around 1.4% to 3.5% per transaction, while payment processors primarily charge per-transaction fees averaging 2.9% plus $0.30 without monthly fees. Selecting a payment gateway may incur additional costs for advanced features like fraud detection or multi-currency support, increasing the total expense. In contrast, payment processors offer simpler pricing models but can become costly with higher transaction volumes due to cumulative per-transaction charges.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Online Store
Selecting the right payment solution for your online store requires understanding the distinct roles of payment gateways and payment processors. A payment gateway securely captures and transmits customer payment information, while the payment processor handles the actual transaction authorization and settlement. Prioritize seamless integration, transaction fees, and supported payment methods to ensure efficient checkout and enhanced customer experience.
Payment Gateway and Processor Compliance Standards
Payment gateways and payment processors must adhere to strict compliance standards such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) to secure cardholder data during transactions. Payment gateways serve as the secure interface between the customer and the payment processor, ensuring data encryption and fraud detection meet industry regulations. Payment processors handle the authorization and settlement of transactions, requiring compliance with regulations like PCI DSS and regional frameworks such as PSD2 in Europe for Strong Customer Authentication.
Future Trends in Online Payment Technology
Payment gateways and payment processors are evolving rapidly, integrating AI-driven fraud detection to enhance transaction security and reduce chargebacks. The rise of blockchain technology and cryptocurrency payments is reshaping online payment ecosystems, offering decentralization and increased transparency. Advanced biometric authentication and seamless multi-currency support are set to improve user experience and expand global e-commerce markets.
Payment Gateway vs Payment Processor Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com