Developmental editing focuses on shaping the overall structure, content, and flow of a pet-themed manuscript to enhance clarity and engagement, while mechanical editing addresses grammar, punctuation, and spelling accuracy. Developmental editors provide strategic feedback on plot coherence and character development, ensuring the story resonates with pet lovers. Mechanical editing ensures the final text is polished and free of errors, making the reading experience smooth and professional.
Table of Comparison
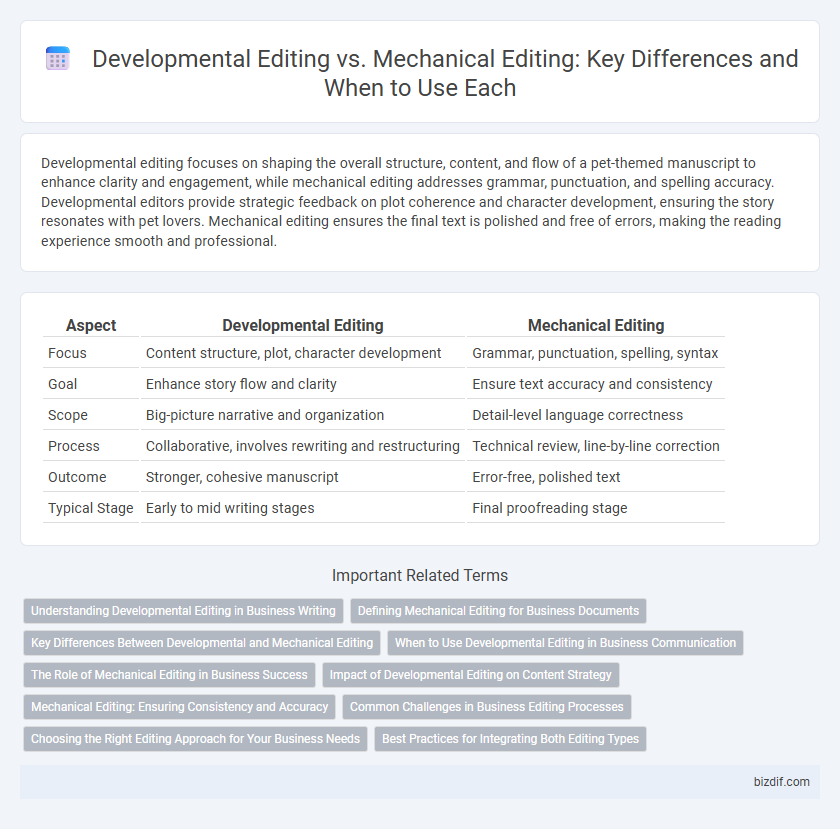
| Aspect | Developmental Editing | Mechanical Editing |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Content structure, plot, character development | Grammar, punctuation, spelling, syntax |
| Goal | Enhance story flow and clarity | Ensure text accuracy and consistency |
| Scope | Big-picture narrative and organization | Detail-level language correctness |
| Process | Collaborative, involves rewriting and restructuring | Technical review, line-by-line correction |
| Outcome | Stronger, cohesive manuscript | Error-free, polished text |
| Typical Stage | Early to mid writing stages | Final proofreading stage |
Understanding Developmental Editing in Business Writing
Developmental editing in business writing focuses on the overall structure, content flow, and clarity to ensure the message aligns with strategic objectives and engages the target audience effectively. This type of editing addresses organization, tone, and key arguments, facilitating coherent and persuasive communication that supports business goals. Mechanical editing, in contrast, concentrates on grammar, punctuation, spelling, and formatting to polish the text without altering its core content.
Defining Mechanical Editing for Business Documents
Mechanical editing for business documents involves meticulously correcting grammar, punctuation, syntax, and formatting errors to ensure clarity and professionalism. This type of editing focuses on the surface-level mechanics rather than structure or content flow, making the text easily understandable and polished. By refining these technical aspects, mechanical editing enhances the document's credibility and readability in professional settings.
Key Differences Between Developmental and Mechanical Editing
Developmental editing focuses on the overall structure, content, and narrative flow of a manuscript, addressing plot, character development, and pacing to enhance the story's coherence and impact. Mechanical editing targets grammar, punctuation, spelling, and syntax errors to ensure clarity and adherence to language conventions. While developmental editing shapes the foundation and direction of a book, mechanical editing polishes the text at the sentence level for readability and correctness.
When to Use Developmental Editing in Business Communication
Developmental editing proves essential in business communication when organizational goals require clarity, structure, and audience alignment, especially during the creation of reports, proposals, or marketing materials. It focuses on content development, ensuring ideas are logically organized, persuasive, and tailored to target demographics, unlike mechanical editing which concentrates solely on grammar and punctuation. Employ developmental editing early in document creation to enhance message effectiveness and drive better decision-making outcomes.
The Role of Mechanical Editing in Business Success
Mechanical editing ensures error-free business documents by focusing on grammar, punctuation, spelling, and formatting, which enhances clarity and professionalism. Accurate mechanical editing upholds brand credibility and fosters trust with clients, crucial for successful business communications. This precision minimizes misunderstandings, streamlines decision-making, and supports overall business growth.
Impact of Developmental Editing on Content Strategy
Developmental editing significantly shapes content strategy by refining the structure, coherence, and overall narrative flow, ensuring that the message aligns with target audience goals and market demands. This type of editing identifies gaps, redundancies, and inconsistencies at the conceptual level, allowing for a more strategic and impactful content plan. Unlike mechanical editing, which focuses on grammar and syntax, developmental editing lays the foundation for a compelling and effective communication strategy.
Mechanical Editing: Ensuring Consistency and Accuracy
Mechanical editing focuses on ensuring consistency and accuracy in grammar, punctuation, spelling, and formatting throughout the manuscript. This process involves correcting typographical errors and standardizing language usage to maintain clarity and professionalism. By addressing surface-level issues, mechanical editing enhances readability and prepares the text for final publication.
Common Challenges in Business Editing Processes
Developmental editing in business editing focuses on structure, clarity, and content coherence, often facing challenges such as aligning messaging with brand strategy and adapting complex information for target audiences. Mechanical editing addresses grammar, punctuation, and formatting consistency, where common issues include maintaining style uniformity across large documents and catching typographical errors in tight deadlines. Both editing types require balancing precision with efficiency to ensure polished, effective business communications.
Choosing the Right Editing Approach for Your Business Needs
Developmental editing focuses on shaping the structure, content, and overall direction of your manuscript to align with business goals and audience engagement, while mechanical editing refines grammar, syntax, and punctuation for polish and clarity. Choosing the right editing approach depends on whether your project requires strategic content development or detailed language accuracy to enhance professional credibility and readability. Businesses prioritizing market impact and narrative coherence benefit from developmental editing, whereas those aiming to maintain consistent style and error-free text rely on mechanical editing.
Best Practices for Integrating Both Editing Types
Effective integration of developmental editing and mechanical editing requires establishing clear stages in the editorial workflow, where developmental editing addresses plot, structure, and character development before mechanical editing focuses on grammar, punctuation, and syntax. Utilizing collaborative tools and detailed feedback loops enables seamless communication between editors and authors, ensuring consistency and coherence throughout the manuscript. Prioritizing thorough developmental edits first reduces time and effort spent on mechanical corrections, enhancing overall editing efficiency and manuscript quality.
Developmental Editing vs Mechanical Editing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com