Editing for print requires careful consideration of resolution, color accuracy, and layout to ensure the final product looks crisp and professional on physical media. Editing for digital emphasizes optimizing file size, screen compatibility, and interactive elements to enhance user experience across various devices. Both approaches demand tailored adjustments to meet the specific technical and aesthetic standards of their respective formats.
Table of Comparison
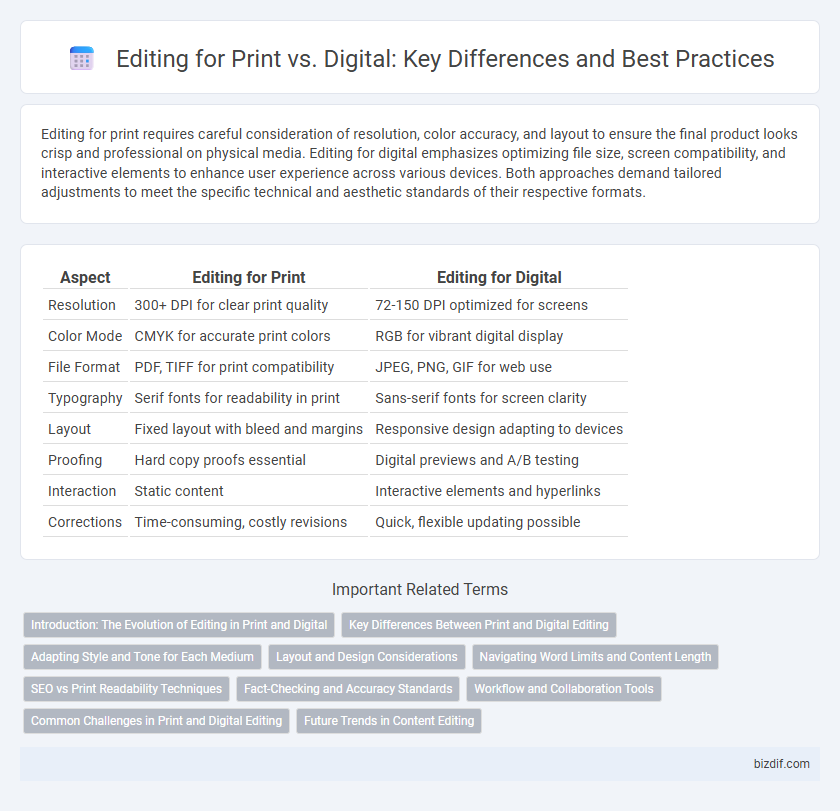
| Aspect | Editing for Print | Editing for Digital |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution | 300+ DPI for clear print quality | 72-150 DPI optimized for screens |
| Color Mode | CMYK for accurate print colors | RGB for vibrant digital display |
| File Format | PDF, TIFF for print compatibility | JPEG, PNG, GIF for web use |
| Typography | Serif fonts for readability in print | Sans-serif fonts for screen clarity |
| Layout | Fixed layout with bleed and margins | Responsive design adapting to devices |
| Proofing | Hard copy proofs essential | Digital previews and A/B testing |
| Interaction | Static content | Interactive elements and hyperlinks |
| Corrections | Time-consuming, costly revisions | Quick, flexible updating possible |
Introduction: The Evolution of Editing in Print and Digital
Editing has transformed significantly from traditional print methods to digital platforms, emphasizing precision in print and flexibility in digital formats. Print editing prioritizes layout consistency, typographical accuracy, and resolution for physical media, while digital editing focuses on SEO optimization, multimedia integration, and real-time updates. The evolution reflects technological advances shaping editorial standards and workflows across both mediums.
Key Differences Between Print and Digital Editing
Editing for print demands meticulous attention to typography, resolution, and color accuracy to ensure the final product meets physical quality standards, while digital editing prioritizes screen readability, SEO optimization, and interactive elements. Print editing often involves lengthy revision cycles due to production timelines and fixed layouts, whereas digital editing allows for rapid updates and flexible formatting across multiple devices. Understanding the distinction in file formats and distribution methods is crucial, with print relying on high-resolution PDFs and digital requiring adaptive HTML or content management systems.
Adapting Style and Tone for Each Medium
Editing for print demands a polished, formal style with consistent tone and precise punctuation to meet traditional publishing standards. In contrast, editing for digital platforms prioritizes conversational tone, readability, and SEO optimization to engage online audiences effectively. Adapting style and tone ensures content resonates appropriately with the intended medium, enhancing user experience and maximizing impact.
Layout and Design Considerations
Editing for print requires precise attention to layout elements such as margins, bleed, and typography to ensure clarity and readability on physical pages. Digital editing emphasizes responsive design, scalable graphics, and interactive elements that adapt seamlessly across various screen sizes and devices. Optimizing for each medium involves balancing visual hierarchy and user experience to achieve effective communication.
Navigating Word Limits and Content Length
Editing for print requires strict adherence to word limits and content length due to physical space constraints, ensuring that text fits precisely within page layouts. Digital editing allows more flexibility with length, but clarity and reader engagement remain critical to maintain user attention and optimize SEO performance. Balancing concise, impactful language with platform-specific requirements enhances overall content effectiveness across both mediums.
SEO vs Print Readability Techniques
Editing for print prioritizes clarity, consistency, and error-free content to ensure readability on physical media, emphasizing typographical standards and layout design. SEO-focused editing for digital platforms requires integrating relevant keywords, optimizing meta tags, and enhancing content structure to improve search engine rankings and user engagement. Both approaches demand tailored techniques: print editing enhances tactile comprehension and visual appeal, while digital editing drives discoverability and accessibility online.
Fact-Checking and Accuracy Standards
Editing for print demands rigorous fact-checking and adherence to strict accuracy standards due to the permanence and wide distribution of physical copies. Digital editing allows for rapid updates and corrections, but still requires meticulous verification to maintain credibility and avoid misinformation. Both formats prioritize factual integrity, yet print editors often implement more exhaustive validation processes before publication.
Workflow and Collaboration Tools
Editing for print demands rigid adherence to layout specifications and final proofing stages, emphasizing precision in typography and color accuracy. Digital editing workflows prioritize flexibility, enabling real-time collaboration through cloud-based tools like Google Docs and Adobe Creative Cloud, which streamline version control and feedback integration. These platforms facilitate asynchronous teamwork, enhancing efficiency and reducing turnaround time in digital publishing environments.
Common Challenges in Print and Digital Editing
Editing for print requires meticulous attention to formatting consistency, color accuracy, and resolution to ensure high-quality physical reproduction, while digital editing demands adaptability to various screen sizes, faster turnaround, and SEO-friendly content optimization. Common challenges in print include managing precise pagination, bleed areas, and color profiles, whereas digital editors often grapple with metadata integration, hyperlink functionality, and responsive design verification. Both formats necessitate rigorous proofreading and style adherence but differ significantly in technical specifications and end-user interaction.
Future Trends in Content Editing
Future trends in content editing emphasize the integration of AI-powered tools that adapt editing techniques for both print and digital media, enhancing precision and contextual relevance. Automation and machine learning enable dynamic content customization tailored to diverse platforms, improving user engagement and accessibility. Advances in real-time collaboration software also streamline editorial workflows, ensuring faster revisions and consistent quality across multiple publication formats.
Editing for Print vs Editing for Digital Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com