Fact-checking ensures the accuracy and reliability of information about pets, verifying details such as breed characteristics, medical advice, and care instructions. Style-checking improves readability and engagement by enhancing grammar, tone, and flow while maintaining the author's voice. Balancing both approaches is essential for delivering trustworthy and appealing pet-related content.
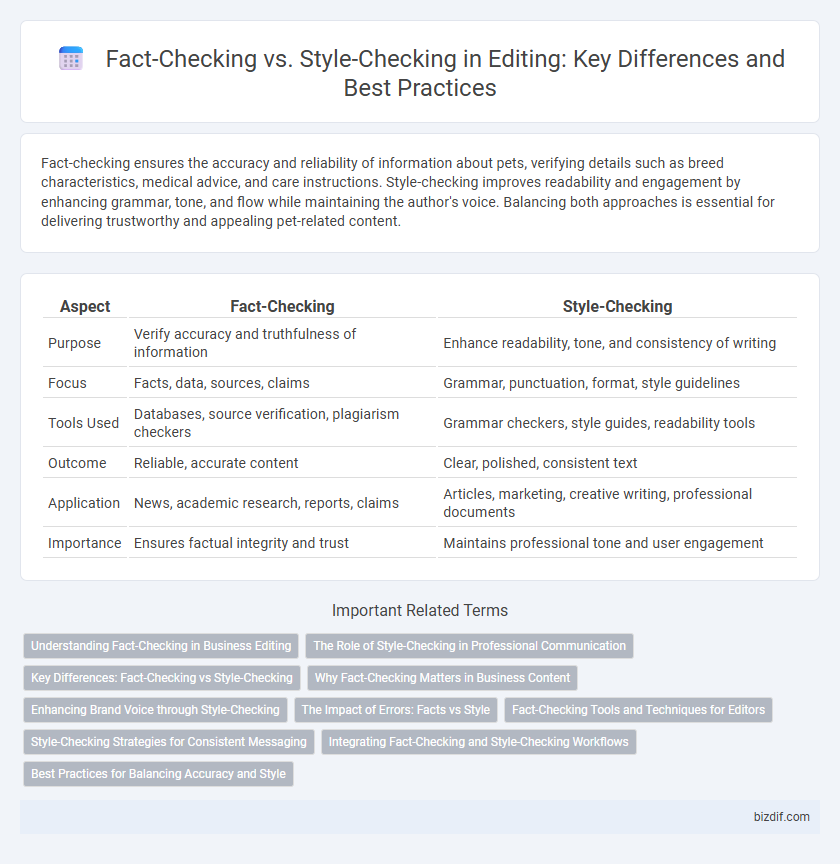
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fact-Checking | Style-Checking |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Verify accuracy and truthfulness of information | Enhance readability, tone, and consistency of writing |
| Focus | Facts, data, sources, claims | Grammar, punctuation, format, style guidelines |
| Tools Used | Databases, source verification, plagiarism checkers | Grammar checkers, style guides, readability tools |
| Outcome | Reliable, accurate content | Clear, polished, consistent text |
| Application | News, academic research, reports, claims | Articles, marketing, creative writing, professional documents |
| Importance | Ensures factual integrity and trust | Maintains professional tone and user engagement |
Understanding Fact-Checking in Business Editing
Fact-checking in business editing ensures the accuracy and reliability of information by verifying data, statistics, names, and claims against trusted sources. This process prevents the dissemination of misinformation, protects brand reputation, and enhances the credibility of business documents such as reports, proposals, and press releases. Fact-checking differs from style-checking, which focuses on grammar, punctuation, and formatting consistency rather than the truthfulness of content.
The Role of Style-Checking in Professional Communication
Style-checking enhances professional communication by ensuring consistency in tone, word choice, and formatting that aligns with organizational standards and target audience expectations. It refines clarity and readability, helping to maintain the credibility and professionalism of written content while adapting to specific industry jargon or brand voice. Effective style-checking complements fact-checking by shaping how accurate information is presented, thus optimizing the overall impact of communication.
Key Differences: Fact-Checking vs Style-Checking
Fact-checking verifies the accuracy and authenticity of information, ensuring all data points, dates, names, and claims are correct and supported by credible sources. Style-checking emphasizes consistency in grammar, punctuation, tone, and formatting according to specific style guides such as APA, MLA, or Chicago Manual of Style. The key difference lies in fact-checking's focus on content validity, while style-checking ensures clarity, coherence, and adherence to editorial standards.
Why Fact-Checking Matters in Business Content
Fact-checking in business content ensures accuracy, builds credibility, and protects brand reputation by verifying data, statistics, and claims before publication. Inaccurate information can lead to legal issues, loss of customer trust, and reduced sales, making rigorous fact-checking essential for maintaining authority and professionalism. Style-checking enhances readability and consistency, but it cannot substitute for the fundamental need to present verified, reliable information to stakeholders.
Enhancing Brand Voice through Style-Checking
Style-checking enhances brand voice by ensuring consistent tone, vocabulary, and syntax that align with the brand's identity, creating a unified and recognizable presence across all content. It refines the expression of values and personality, strengthening audience connection and trust. Fact-checking supports credibility but style-checking uniquely shapes how the brand is perceived emotionally and culturally.
The Impact of Errors: Facts vs Style
Fact-checking errors undermine the credibility and trustworthiness of the entire text, potentially spreading misinformation and damaging reputations. Style-checking errors affect readability and engagement, influencing the audience's perception of professionalism and clarity. Both types of errors compromise the effectiveness of communication, but factual inaccuracies carry more severe consequences for accuracy and authority.
Fact-Checking Tools and Techniques for Editors
Fact-checking tools such as ClaimBuster, Factmata, and Google Fact Check Explorer enable editors to verify the accuracy of information quickly, reducing errors before publication. Techniques like cross-referencing multiple credible sources, using primary documents, and accessing databases such as Snopes and PolitiFact enhance the reliability of content. Editors prioritize fact-checking to maintain journalistic integrity and prevent the spread of misinformation, distinguishing it from style-checking, which focuses on grammar, tone, and readability.
Style-Checking Strategies for Consistent Messaging
Style-checking strategies focus on ensuring consistent messaging by standardizing tone, voice, and formatting across content. Employing style guides like the AP Stylebook or Chicago Manual of Style helps maintain uniformity in punctuation, capitalization, and word choice. Automated tools such as Grammarly and Hemingway Editor streamline the process, enhancing clarity and readability while preserving the brand's unique style.
Integrating Fact-Checking and Style-Checking Workflows
Integrating fact-checking and style-checking workflows enhances editorial accuracy by combining verification of information with adherence to linguistic standards, reducing errors and inconsistencies. Utilizing tools that synchronize both processes streamlines editing, ensuring factual precision while maintaining tone, grammar, and formatting consistency. This unified approach improves efficiency and quality control in editorial projects by addressing content accuracy and stylistic coherence simultaneously.
Best Practices for Balancing Accuracy and Style
Fact-checking ensures the accuracy and credibility of content by verifying data, dates, names, and sources, while style-checking maintains consistency in tone, grammar, and formatting according to predefined guidelines like the AP Stylebook or Chicago Manual of Style. Best practices involve integrating fact-checking early in the editing process to prevent misinformation and applying style-checking in final revisions to polish readability and coherence. Employing advanced editing tools alongside human review enables editors to balance factual accuracy with stylistic clarity efficiently.
Fact-checking vs Style-checking Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com