Light editing enhances a pet photo by making subtle adjustments to brightness, contrast, and minor blemishes, preserving the animal's natural appearance. Heavy editing involves more extensive alterations, such as removing backgrounds, adding effects, or changing colors, which can significantly transform the image. Choosing between light and heavy editing depends on the intended use and desired visual impact of the pet photograph.
Table of Comparison
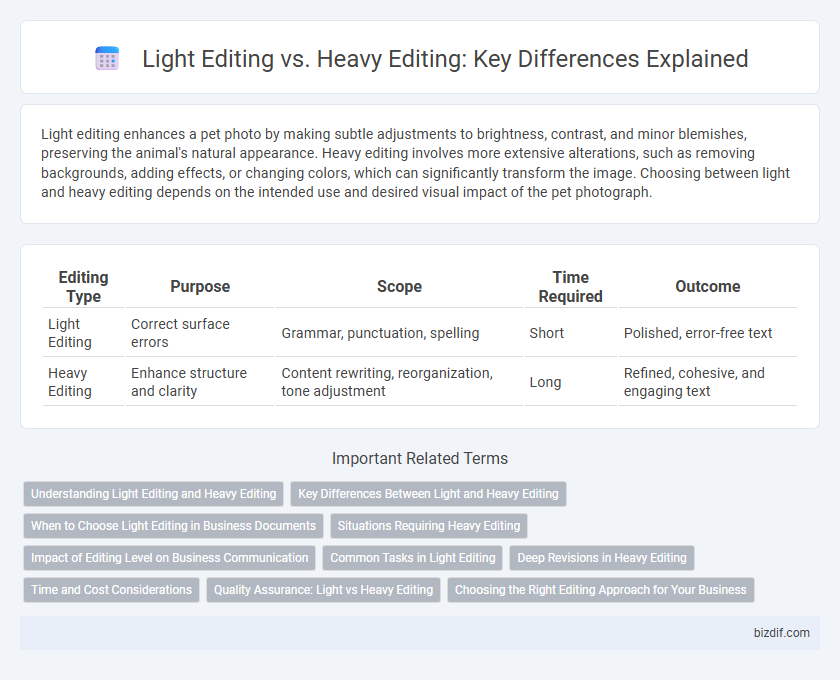
| Editing Type | Purpose | Scope | Time Required | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light Editing | Correct surface errors | Grammar, punctuation, spelling | Short | Polished, error-free text |
| Heavy Editing | Enhance structure and clarity | Content rewriting, reorganization, tone adjustment | Long | Refined, cohesive, and engaging text |
Understanding Light Editing and Heavy Editing
Light editing involves making minor corrections to grammar, punctuation, and spelling while preserving the original style and voice of the text, ideal for polishing drafts without altering content significantly. Heavy editing requires substantial revisions, including restructuring sentences, improving clarity, enhancing flow, and addressing content gaps to transform and refine the overall message. Understanding the difference ensures appropriate editing depth for manuscripts, balancing author intent with text quality.
Key Differences Between Light and Heavy Editing
Light editing primarily involves minor corrections such as grammar, punctuation, and style consistency to enhance readability without altering the original content significantly. Heavy editing requires comprehensive restructuring, fact-checking, and rewriting to improve clarity, flow, and overall coherence, often transforming the document substantially. Key differences include the depth of content modification, time investment, and the editor's role in shaping the final narrative.
When to Choose Light Editing in Business Documents
Light editing is ideal for business documents that require clarity and minor corrections without altering the original tone or intent. It focuses on refining grammar, punctuation, and style to enhance readability while preserving the author's voice. Choose light editing for routine reports, emails, or proposals that need professional polish but retain a personal or informal style.
Situations Requiring Heavy Editing
Situations requiring heavy editing include manuscripts with significant structural issues, inconsistent narrative flow, or extensive factual inaccuracies. Heavy editing is essential when a text demands substantial reworking of content, organization, and language to improve clarity, coherence, and overall quality. Such intensive editing is common in academic papers, novel drafts, and complex technical documents needing thorough revision.
Impact of Editing Level on Business Communication
Light editing enhances business communication by ensuring clarity and grammatical accuracy while preserving the original tone and intent of the message, facilitating quick and effective information exchange. Heavy editing transforms content more significantly, refining structure, style, and coherence to tailor messages for specific audiences or professional standards, often elevating brand credibility and persuasive impact. Choosing the appropriate editing level depends on the communication goals, target audience, and desired professionalism, directly influencing the effectiveness and reception of business messages.
Common Tasks in Light Editing
Light editing typically involves correcting basic grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors to enhance clarity without altering the original voice or structure. Common tasks include adjusting sentence flow, fixing typographical mistakes, and refining word choice for clearer communication. This level of editing ensures the text is polished while maintaining the author's intent and style.
Deep Revisions in Heavy Editing
Heavy editing involves deep revisions that go beyond surface-level corrections, focusing on restructuring content, enhancing clarity, and refining style to align with the intended audience and purpose. This process addresses structural inconsistencies, logical flow, and detailed content accuracy, ensuring the manuscript's overall coherence and impact. Deep revisions are essential for transforming raw drafts into polished works, requiring a comprehensive approach that shapes the narrative and argumentation effectively.
Time and Cost Considerations
Light editing typically requires less time and lower costs due to its focus on minor corrections and polishing, making it ideal for tight budgets and quick turnarounds. Heavy editing involves comprehensive revisions, including structural changes and content enhancement, which significantly increases both the time investment and financial expenses. Choosing between light and heavy editing depends on project complexity, deadline urgency, and available resources.
Quality Assurance: Light vs Heavy Editing
Light editing ensures basic quality assurance by correcting grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors while maintaining the original tone and structure, ideal for quick turnaround projects. Heavy editing involves comprehensive quality assurance, including restructuring content, enhancing clarity, and improving flow, which significantly elevates the overall quality and coherence of the text. Choosing between light and heavy editing depends on the project's requirements for precision, depth, and the intended audience's expectations.
Choosing the Right Editing Approach for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate editing approach depends on the project's scope and business goals, with light editing enhancing clarity and flow through minor adjustments, while heavy editing involves substantial restructuring and content overhaul. Light editing suits marketing materials and quick-turnaround content, ensuring consistency without altering the original voice. Heavy editing is ideal for comprehensive reports or complex documents requiring detailed revision to improve coherence, accuracy, and overall impact.
Light Editing vs Heavy Editing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com