Local craftsmanship preserves unique cultural heritage and offers personalized, high-quality products that reflect regional traditions. Global manufacturing enables mass production, reducing costs and increasing accessibility but often sacrifices artisanal detail and authenticity. Balancing these approaches supports sustainable economies while meeting diverse consumer demands.
Table of Comparison
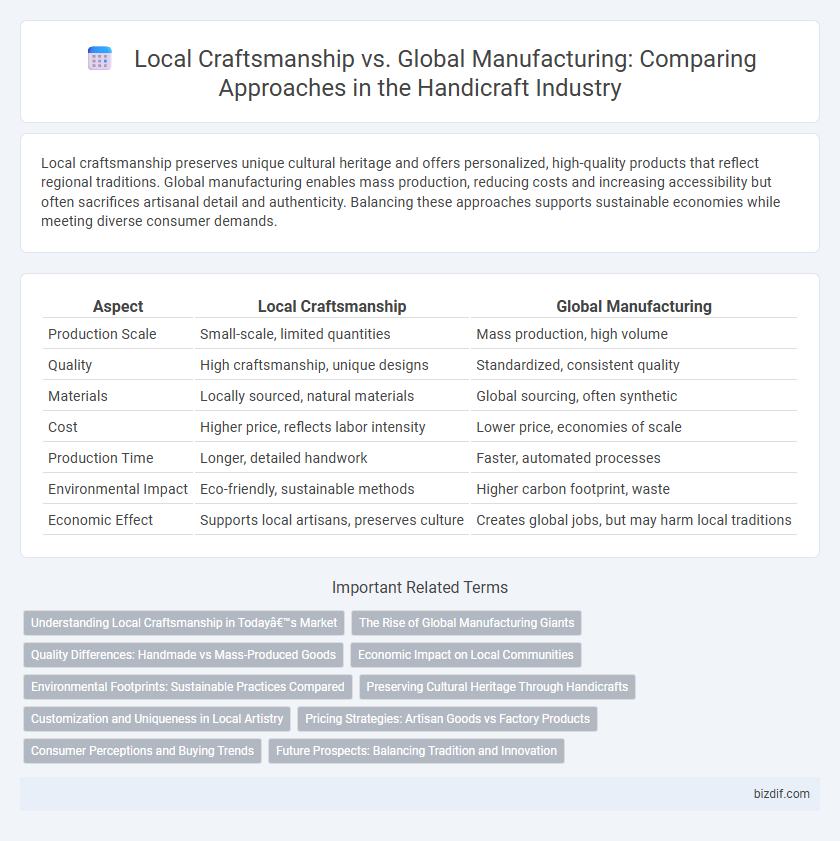
| Aspect | Local Craftsmanship | Global Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Production Scale | Small-scale, limited quantities | Mass production, high volume |
| Quality | High craftsmanship, unique designs | Standardized, consistent quality |
| Materials | Locally sourced, natural materials | Global sourcing, often synthetic |
| Cost | Higher price, reflects labor intensity | Lower price, economies of scale |
| Production Time | Longer, detailed handwork | Faster, automated processes |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, sustainable methods | Higher carbon footprint, waste |
| Economic Effect | Supports local artisans, preserves culture | Creates global jobs, but may harm local traditions |
Understanding Local Craftsmanship in Today’s Market
Local craftsmanship preserves unique cultural heritage and traditional techniques that global manufacturing often overlooks, offering consumers authentic, high-quality products. In today's market, understanding local craftsmanship enhances appreciation for sustainable practices and supports economic development within communities. Emphasizing artisanal skills helps meet growing demand for personalized and ethically produced goods, distinguishing them from mass-produced alternatives.
The Rise of Global Manufacturing Giants
The rise of global manufacturing giants has significantly impacted local craftsmanship by introducing mass-produced, cost-efficient goods that dominate international markets. These manufacturing hubs leverage advanced technology and economies of scale, often overshadowing artisanal products in price and availability. Despite this, local craftsmanship thrives in niches emphasizing uniqueness, cultural heritage, and quality, which global factories rarely replicate.
Quality Differences: Handmade vs Mass-Produced Goods
Local craftsmanship offers superior quality due to meticulous attention to detail and skilled artisanship, resulting in unique, durable, and high-value products. In contrast, global manufacturing prioritizes mass production efficiency, often compromising on material quality and finishing. Handmade goods reflect cultural heritage and individual creativity, while mass-produced items tend to lack personalization and intricate design elements.
Economic Impact on Local Communities
Local craftsmanship fosters economic resilience by supporting small businesses and preserving traditional skills, generating employment in rural areas. In contrast, global manufacturing often prioritizes cost efficiency, leading to job displacement and reduced economic benefits for local artisans. Investment in local handicrafts promotes sustainable economic growth and cultural heritage preservation within communities.
Environmental Footprints: Sustainable Practices Compared
Local craftsmanship significantly reduces environmental footprints through the use of locally sourced materials and traditional techniques that minimize waste and energy consumption. In contrast, global manufacturing often relies on large-scale production processes that increase carbon emissions, resource depletion, and pollution due to transportation and mass production. Sustainable practices in local craftsmanship promote circular economies and preserve cultural heritage while enabling reduced ecological impact compared to industrialized global supply chains.
Preserving Cultural Heritage Through Handicrafts
Local craftsmanship preserves cultural heritage by maintaining traditional techniques and authentic materials, which global manufacturing often overlooks in favor of mass production. Handicrafts embody unique regional identities and artisanal skills that foster cultural continuity and community pride. Supporting local artisans not only safeguards intangible cultural assets but also promotes sustainable economies resistant to industrial homogenization.
Customization and Uniqueness in Local Artistry
Local craftsmanship offers unparalleled customization and uniqueness by incorporating traditional techniques and cultural heritage into each piece, creating items that reflect regional identity and personal stories. Global manufacturing prioritizes mass production and uniformity, often sacrificing individuality and intricate detailing found in artisanal work. The emphasis on bespoke design in local artistry promotes sustainable practices and supports community livelihoods, contrasting with the standardized outputs of global factories.
Pricing Strategies: Artisan Goods vs Factory Products
Artisan goods often command premium prices due to their unique craftsmanship, limited production, and high-quality materials, appealing to niche markets valuing authenticity and tradition. In contrast, global manufacturing leverages economies of scale, enabling mass production at lower costs, which results in more competitively priced factory products aimed at broad consumer bases. Pricing strategies for local craftsmanship emphasize exclusivity and cultural value, whereas global manufacturing focuses on affordability and volume-driven sales.
Consumer Perceptions and Buying Trends
Local craftsmanship is increasingly valued for its authenticity, cultural heritage, and unique quality, driving consumer preference towards handmade, artisanal products. Global manufacturing offers mass-produced, cost-effective goods, appealing to price-sensitive buyers but often lacking the personalized touch associated with handicrafts. Consumer trends reveal a growing demand for sustainable and ethically-made items, with buyers willing to invest more in locally crafted products that support community artisans and preserve traditional skills.
Future Prospects: Balancing Tradition and Innovation
Local craftsmanship preserves cultural heritage by maintaining traditional techniques passed down through generations, fostering unique, high-quality artisanal products. Global manufacturing leverages advanced technologies and economies of scale to produce goods efficiently, often prioritizing quantity over individuality. Future prospects involve integrating digital tools and sustainable practices within local craftsmanship to enhance innovation while respecting tradition, enabling artisans to compete globally without losing cultural identity.
Local craftsmanship vs Global manufacturing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com