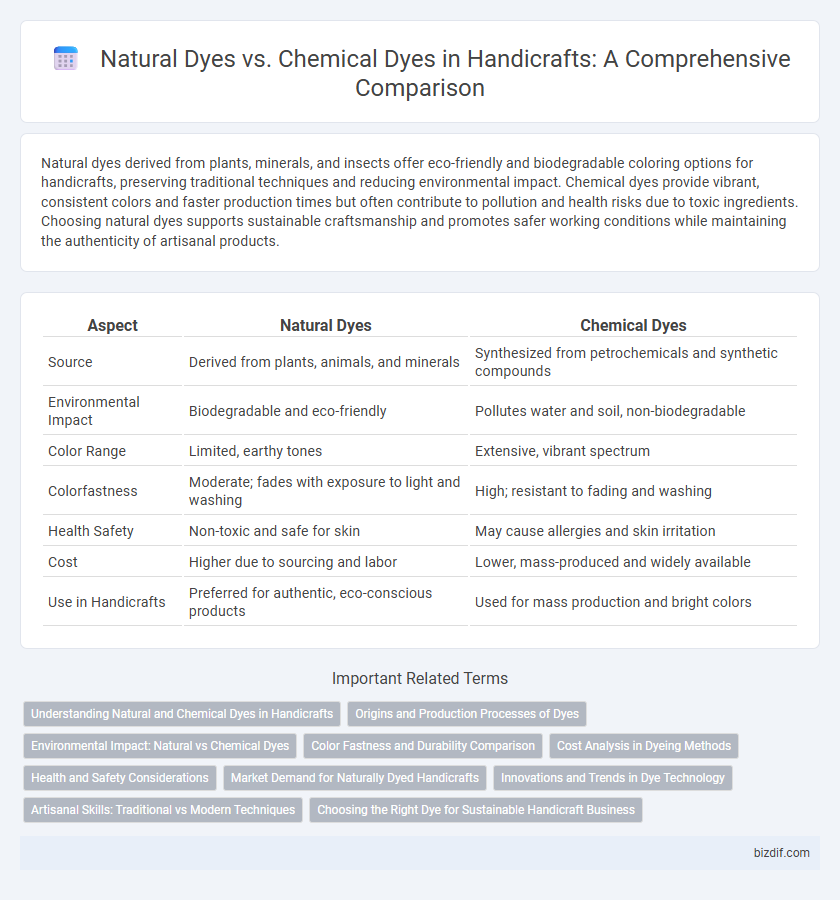
Natural dyes derived from plants, minerals, and insects offer eco-friendly and biodegradable coloring options for handicrafts, preserving traditional techniques and reducing environmental impact. Chemical dyes provide vibrant, consistent colors and faster production times but often contribute to pollution and health risks due to toxic ingredients. Choosing natural dyes supports sustainable craftsmanship and promotes safer working conditions while maintaining the authenticity of artisanal products.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Natural Dyes | Chemical Dyes |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from plants, animals, and minerals | Synthesized from petrochemicals and synthetic compounds |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Pollutes water and soil, non-biodegradable |
| Color Range | Limited, earthy tones | Extensive, vibrant spectrum |
| Colorfastness | Moderate; fades with exposure to light and washing | High; resistant to fading and washing |
| Health Safety | Non-toxic and safe for skin | May cause allergies and skin irritation |
| Cost | Higher due to sourcing and labor | Lower, mass-produced and widely available |
| Use in Handicrafts | Preferred for authentic, eco-conscious products | Used for mass production and bright colors |
Understanding Natural and Chemical Dyes in Handicrafts
Natural dyes in handicrafts are derived from plant, animal, and mineral sources, offering eco-friendly and biodegradable coloring options that enhance fabric texture and longevity. Chemical dyes, synthesized from petrochemicals or synthetic compounds, provide vibrant and consistent colors but often involve toxic substances harmful to the environment and artisan health. Understanding the balance between natural and chemical dyes is crucial for sustainable handicraft production, influencing colorfastness, environmental impact, and cultural authenticity.
Origins and Production Processes of Dyes
Natural dyes are derived from organic sources such as plants, insects, and minerals, involving extraction methods like boiling and fermentation to release pigments. Chemical dyes are synthesized from petrochemicals through complex industrial processes including sulfonation, nitration, and reduction to create vibrant and diverse colorants. The production of natural dyes emphasizes eco-friendly techniques and renewable materials, while chemical dyes rely on extensive chemical reactions and non-renewable resources for mass manufacturing.
Environmental Impact: Natural vs Chemical Dyes
Natural dyes derived from plants, minerals, and insects significantly reduce water pollution and biodegrade without releasing harmful toxins, making them an eco-friendly choice for handicrafts. Chemical dyes, often synthetic and petroleum-based, contribute to hazardous wastewater with heavy metals and carcinogens, posing severe threats to aquatic ecosystems and human health. The environmental impact of natural dyes is substantially lower, promoting sustainable handicraft practices and preserving biodiversity.
Color Fastness and Durability Comparison
Natural dyes derived from plant, mineral, and animal sources offer eco-friendly coloration but often exhibit lower color fastness and durability compared to chemical dyes. Chemical dyes, synthesized from petroleum-based compounds, provide higher resistance to fading, washing, and light exposure, ensuring longer-lasting vibrancy crucial for commercial handicrafts. Advances in mordants and fixing agents for natural dyes are improving their durability, yet chemical dyes remain the preferred choice for products requiring consistent and robust color retention.
Cost Analysis in Dyeing Methods
Natural dyes generally incur higher initial costs due to the sourcing and extraction of plant-based materials, yet they offer cost savings over time through their biodegradability and minimal environmental impact. Chemical dyes, while often cheaper upfront and providing consistent color fastness, may lead to increased expenses related to wastewater treatment and environmental regulations. The overall cost analysis favors natural dyes for sustainable production, despite higher labor and raw material investments during the dyeing process.
Health and Safety Considerations
Natural dyes derived from plants and minerals are generally safer for artisans due to their non-toxic and biodegradable properties, reducing risks of skin irritation and respiratory issues. Chemical dyes often contain hazardous substances like heavy metals and synthetic compounds, posing significant health hazards including allergic reactions and long-term exposure risks. Proper ventilation, protective equipment, and adherence to safety guidelines are essential when handling chemical dyes to minimize health complications in handicraft production.
Market Demand for Naturally Dyed Handicrafts
Market demand for naturally dyed handicrafts continues to grow as consumers increasingly seek eco-friendly and sustainable products. Natural dyes derived from plants, minerals, and insects offer unique, vibrant colors that appeal to environmentally conscious buyers. This rising preference drives artisan markets and supports traditional dyeing techniques, boosting the global handicraft industry's value.
Innovations and Trends in Dye Technology
Natural dyes derived from plant, mineral, and insect sources have seen a resurgence due to eco-friendly innovations such as bio-mordants and solar dyeing techniques, enhancing colorfastness and sustainability. Chemical dyes continue to evolve with advancements in digital inkjet printing and low-water fixation processes, reducing environmental impact while expanding color vibrancy and precision. Emerging trends emphasize hybrid dye formulations combining natural and synthetic elements to balance ecological benefits with performance demands in contemporary handicraft textiles.
Artisanal Skills: Traditional vs Modern Techniques
Natural dyes demand intricate artisanal skills rooted in traditional techniques, such as extracting pigments from plants, minerals, and insects, which require deep knowledge of local flora and precise timing. Chemical dyes enable faster production with consistent color results but often rely on modern machinery and synthetic processes that reduce the hands-on craftsmanship found in natural dyeing. The artisanal mastery in natural dyeing preserves cultural heritage through techniques like mordant application and hand-dyeing, contrasting sharply with the efficiency-focused, mechanized methods of chemical dye manufacture.
Choosing the Right Dye for Sustainable Handicraft Business
Natural dyes, derived from plant, mineral, and insect sources, offer eco-friendly alternatives that reduce environmental pollution and appeal to eco-conscious consumers in the handicraft market. Chemical dyes, while providing vibrant and consistent colors, often involve toxic substances that can harm ecosystems and pose health risks during production and use. Selecting natural dyes supports sustainability goals, enhances product uniqueness, and aligns with growing demand for green handicraft products, making them ideal for long-term business viability.
Natural Dyes vs Chemical Dyes Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com