Materiality defines the physical properties and durability of surfaces, influencing the overall functionality and aesthetic of an interior space. Texture enhances tactile and visual interest, creating depth and contrast that enrich user experience. Balancing materiality with texture ensures a harmonious design that is both practical and visually engaging.
Table of Comparison
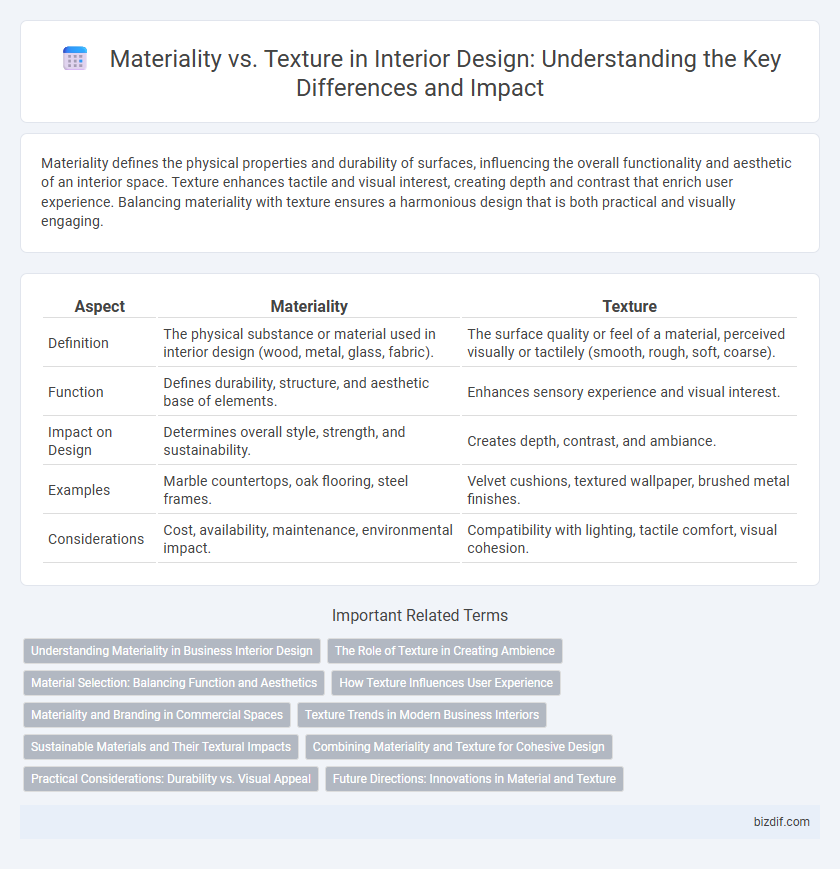
| Aspect | Materiality | Texture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The physical substance or material used in interior design (wood, metal, glass, fabric). | The surface quality or feel of a material, perceived visually or tactilely (smooth, rough, soft, coarse). |
| Function | Defines durability, structure, and aesthetic base of elements. | Enhances sensory experience and visual interest. |
| Impact on Design | Determines overall style, strength, and sustainability. | Creates depth, contrast, and ambiance. |
| Examples | Marble countertops, oak flooring, steel frames. | Velvet cushions, textured wallpaper, brushed metal finishes. |
| Considerations | Cost, availability, maintenance, environmental impact. | Compatibility with lighting, tactile comfort, visual cohesion. |
Understanding Materiality in Business Interior Design
Understanding materiality in business interior design involves selecting materials that not only enhance aesthetic appeal but also ensure durability and functionality under high-traffic conditions. Material choices such as natural woods, metals, and stone contribute to the overall sensory experience by adding depth and character, while also supporting brand identity through tactile engagement. Prioritizing materiality enables designers to create cohesive, sustainable environments that meet both operational demands and user comfort.
The Role of Texture in Creating Ambience
Texture plays a crucial role in creating ambience by adding depth and tactile interest to interior spaces, influencing how a room feels and is perceived. Materials with varied textures, such as rough stone, smooth leather, or soft fabrics, evoke specific emotional responses and contribute to the overall mood. Integrating textured surfaces strategically enhances sensory experience, balancing visual appeal with comfort and character in interior design.
Material Selection: Balancing Function and Aesthetics
Material selection in interior design requires a strategic balance between function and aesthetics, ensuring durability while enhancing visual appeal. Choosing high-quality materials with appropriate textures can elevate the spatial experience by creating tactile contrasts and depth. Prioritizing both practical performance and sensory engagement leads to cohesive, inviting environments that meet lifestyle demands.
How Texture Influences User Experience
Texture enhances user experience by providing tactile and visual stimulation, creating depth and comfort in interior spaces. The interplay between smooth, rough, soft, or rigid materials shapes emotional responses, affecting mood and perceived warmth or coolness. Thoughtful texture selection guides spatial perception and usability, making environments more engaging and functional.
Materiality and Branding in Commercial Spaces
Materiality in commercial interior design plays a crucial role in reinforcing brand identity by selecting materials that embody the brand's values and aesthetics, such as sustainable wood for eco-friendly companies or sleek metals for tech firms. High-quality, tactile materials not only enhance the sensory experience but also communicate professionalism and trustworthiness to clients and customers. Strategic material choices influence spatial perception and emotional response, making them essential tools for creating cohesive and memorable branded environments.
Texture Trends in Modern Business Interiors
Texture trends in modern business interiors emphasize tactile contrasts that enhance spatial experience and brand identity. Incorporating materials such as matte metals, natural woods, and soft textiles promotes visual depth and warmth while supporting acoustic comfort and ergonomic functionality. Embracing textured wall panels, layered textiles, and mixed materials fosters dynamic environments that boost employee wellbeing and productivity.
Sustainable Materials and Their Textural Impacts
Sustainable materials such as reclaimed wood, bamboo, and recycled metals offer unique textural qualities that enhance the sensory experience of interior spaces while reducing environmental impact. The natural grain of reclaimed wood adds warmth and authenticity, whereas bamboo provides a smooth, tactile surface with a renewable growth cycle. Incorporating these eco-friendly materials balances materiality and texture, promoting sustainable design without compromising aesthetic appeal.
Combining Materiality and Texture for Cohesive Design
Combining materiality and texture enhances interior design by creating depth and tactile interest that captivates the senses. Utilizing natural materials like wood or stone alongside varied textures, such as smooth leather or coarse linen, fosters a balanced and cohesive ambiance. Strategic layering of these elements elevates spatial harmony and reinforces the overall aesthetic narrative.
Practical Considerations: Durability vs. Visual Appeal
Materiality in interior design emphasizes durability, selecting materials like hardwood or stone for their long-lasting qualities and resistance to wear in high-traffic areas. Texture prioritizes visual appeal, using tactile surfaces such as velvet or woven fabrics to create sensory interest and depth in a space. Balancing materiality and texture ensures interiors are both functional and aesthetically engaging, meeting practical needs while enhancing the overall atmosphere.
Future Directions: Innovations in Material and Texture
Future directions in interior design emphasize the integration of smart materials with adaptive textures, enabling surfaces to change in response to environmental stimuli or user preferences. Innovations such as 3D-printed composites and nanomaterial coatings enhance durability while providing customizable tactile experiences. These advancements redefine materiality by merging functionality and aesthetics, pushing the boundaries of sensory engagement in interior environments.
Materiality vs Texture Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com