Modernism in interior design emphasizes clean lines, functional spaces, and minimal ornamentation, promoting simplicity and order. Postmodernism contrasts by incorporating eclectic styles, bold colors, and playful forms that challenge traditional aesthetics. The shift reflects a move from strict functionality to expressive, personalized environments.
Table of Comparison
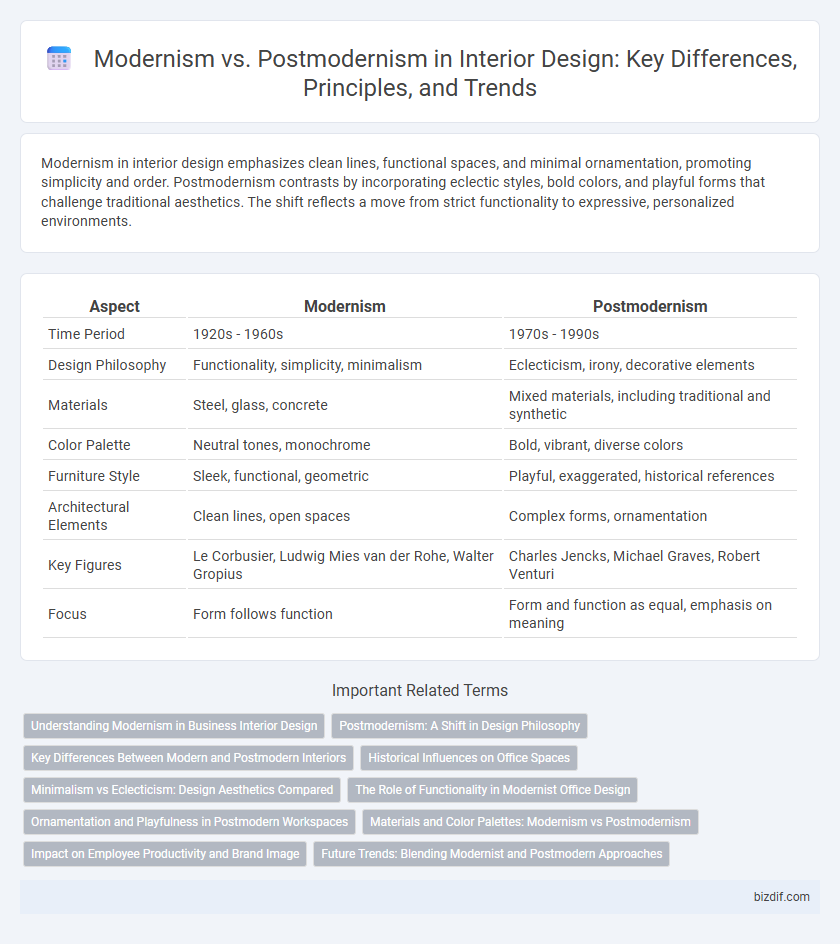
| Aspect | Modernism | Postmodernism |
|---|---|---|
| Time Period | 1920s - 1960s | 1970s - 1990s |
| Design Philosophy | Functionality, simplicity, minimalism | Eclecticism, irony, decorative elements |
| Materials | Steel, glass, concrete | Mixed materials, including traditional and synthetic |
| Color Palette | Neutral tones, monochrome | Bold, vibrant, diverse colors |
| Furniture Style | Sleek, functional, geometric | Playful, exaggerated, historical references |
| Architectural Elements | Clean lines, open spaces | Complex forms, ornamentation |
| Key Figures | Le Corbusier, Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, Walter Gropius | Charles Jencks, Michael Graves, Robert Venturi |
| Focus | Form follows function | Form and function as equal, emphasis on meaning |
Understanding Modernism in Business Interior Design
Modernism in business interior design emphasizes clean lines, functional layouts, and the use of industrial materials such as steel, glass, and concrete to create efficient and uncluttered workspaces. This design philosophy prioritizes simplicity and practicality, promoting productivity through open floor plans and minimal ornamentation that supports a professional and focused environment. Key characteristics include neutral color palettes, integrated technology, and modular furniture that align with corporate branding and contemporary business needs.
Postmodernism: A Shift in Design Philosophy
Postmodernism in interior design marks a shift from the minimalist principles of Modernism to a more eclectic and expressive approach, characterized by bold colors, playful forms, and historical references. This design philosophy embraces irony, pastiche, and ornamentation, challenging the functional rigidity and uniformity of Modernist aesthetics. Iconic postmodern designers like Ettore Sottsass and the Memphis Group emphasize individuality and narrative, creating spaces that communicate personality and cultural context.
Key Differences Between Modern and Postmodern Interiors
Modern interiors prioritize simplicity, clean lines, and functional forms often using neutral colors and natural materials like wood and metal. Postmodern interiors embrace eclectic styles, bold colors, and decorative elements, combining historical references with playful, ironic details. While modernism focuses on minimalism and order, postmodernism challenges conventions by mixing textures, patterns, and unconventional shapes for a more expressive and dynamic space.
Historical Influences on Office Spaces
Modernism in office design emerged from early 20th-century ideals emphasizing simplicity, functionality, and the absence of ornamentation, heavily influenced by the Bauhaus movement and industrial advancements. Postmodernism reacted against modernist rigidity by incorporating eclectic styles, decorative elements, and historical references, reflecting a cultural shift during the late 20th century towards diversity and individual expression. These historical influences transformed office environments, with modernism promoting open layouts and efficiency, while postmodernism introduced playful forms and symbolic designs to enhance creativity and identity.
Minimalism vs Eclecticism: Design Aesthetics Compared
Minimalism in modernist interior design emphasizes clean lines, functionality, and a restrained color palette to create serene, clutter-free spaces. In contrast, postmodern eclecticism embraces bold patterns, diverse textures, and a mix of historical references to evoke personality and visual interest. This juxtaposition highlights modernism's pursuit of simplicity against postmodernism's celebration of complexity and individuality.
The Role of Functionality in Modernist Office Design
Modernist office design emphasizes functionality through clean lines, minimal ornamentation, and efficient space utilization, promoting productivity and clarity. The integration of ergonomic furniture and open-plan layouts reflects the modernist principle that form should follow function. This focus contrasts with postmodern design's eclectic and decorative approach, prioritizing aesthetic expression over strict functionalism.
Ornamentation and Playfulness in Postmodern Workspaces
Postmodern workspaces distinguish themselves from modernism through vibrant ornamentation, embracing bold colors, eclectic patterns, and whimsical details that challenge minimalist norms. While modernism prioritizes functionality and simplicity, postmodern design infuses playfulness, mixing historical references with unexpected textures to create engaging environments. This approach fosters creativity and individuality, transforming workspaces into dynamic areas that encourage collaboration and innovation.
Materials and Color Palettes: Modernism vs Postmodernism
Modernism in interior design emphasizes minimalism, using materials such as steel, glass, and concrete with a neutral color palette dominated by whites, blacks, and grays to create clean, functional spaces. Postmodernism breaks from this rigidity by incorporating eclectic materials like plastic, neon, and mixed media, paired with bold, vibrant colors including pinks, yellows, and blues to challenge traditional design norms. The contrast between smooth, industrial surfaces in Modernism and the playful, often textured finishes of Postmodern interiors highlights their differing approaches to materiality and color expression.
Impact on Employee Productivity and Brand Image
Modernism in interior design promotes minimalism and functional spaces that enhance employee productivity through reduced distractions and streamlined workflows. Postmodernism introduces eclectic, bold aesthetics that stimulate creativity and reflect a brand's unique identity, improving employee engagement and customer perception. Both styles impact workspace dynamics differently, with modernism prioritizing efficiency and postmodernism emphasizing expressive brand image.
Future Trends: Blending Modernist and Postmodern Approaches
Future trends in interior design emphasize a seamless fusion of Modernist simplicity and Postmodern eclecticism, creating spaces that balance functionality with bold aesthetic statements. Designers integrate Modernism's clean lines and minimalism with Postmodernism's playful colors, patterns, and historical references to craft versatile, innovative environments. This hybrid approach leverages sustainable materials and advanced technology to align with evolving lifestyle needs and environmental consciousness.
Modernism vs Postmodernism Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com