Ethical sourcing in jewelry making prioritizes the use of conflict-free gemstones and recycled metals, ensuring environmental sustainability and fair labor practices. Traditional sourcing often relies on established supply chains that may involve exploitative mining and ecological degradation. Choosing ethically sourced materials enhances transparency and supports responsible craftsmanship in the jewelry industry.
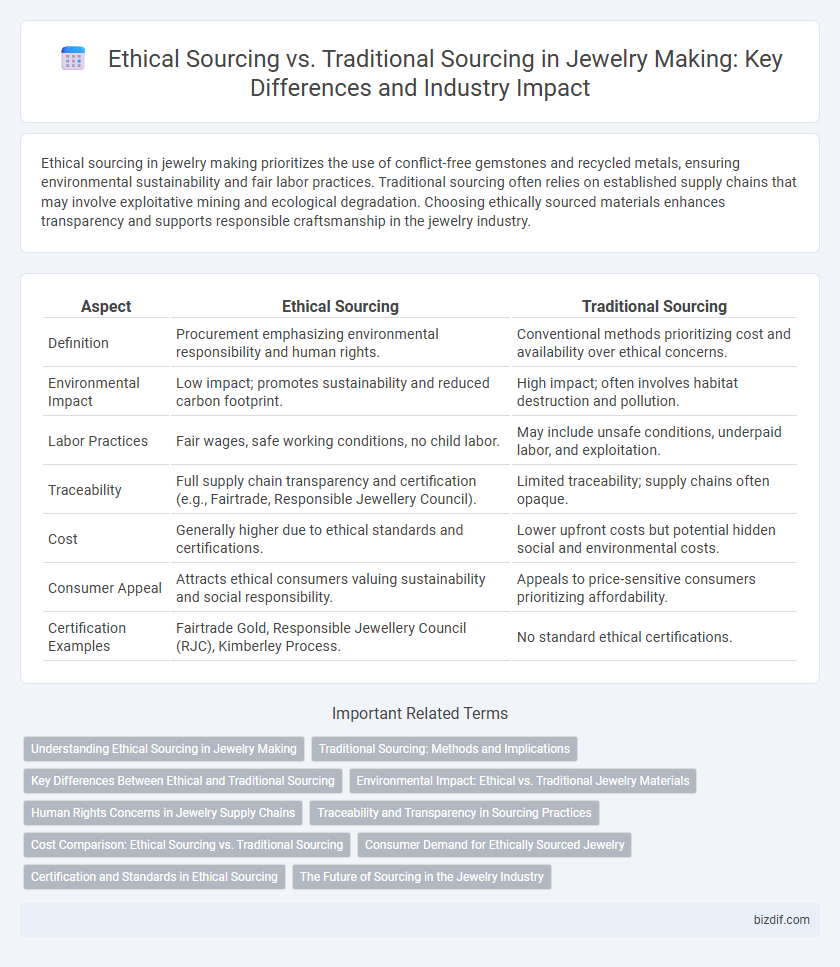
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Ethical Sourcing | Traditional Sourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Procurement emphasizing environmental responsibility and human rights. | Conventional methods prioritizing cost and availability over ethical concerns. |
| Environmental Impact | Low impact; promotes sustainability and reduced carbon footprint. | High impact; often involves habitat destruction and pollution. |
| Labor Practices | Fair wages, safe working conditions, no child labor. | May include unsafe conditions, underpaid labor, and exploitation. |
| Traceability | Full supply chain transparency and certification (e.g., Fairtrade, Responsible Jewellery Council). | Limited traceability; supply chains often opaque. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to ethical standards and certifications. | Lower upfront costs but potential hidden social and environmental costs. |
| Consumer Appeal | Attracts ethical consumers valuing sustainability and social responsibility. | Appeals to price-sensitive consumers prioritizing affordability. |
| Certification Examples | Fairtrade Gold, Responsible Jewellery Council (RJC), Kimberley Process. | No standard ethical certifications. |
Understanding Ethical Sourcing in Jewelry Making
Ethical sourcing in jewelry making emphasizes obtaining materials through practices that ensure fair labor, environmental sustainability, and transparency in the supply chain. Unlike traditional sourcing, which often prioritizes cost and availability, ethical sourcing involves certifications such as Fairmined and responsively addresses issues like conflict minerals and human rights abuses. This approach helps artisans and brands build trust with conscious consumers seeking responsibly crafted jewelry.
Traditional Sourcing: Methods and Implications
Traditional sourcing in jewelry making often involves mining practices that rely on established supply chains, frequently linked to significant environmental degradation and exploitative labor conditions. These methods prioritize cost efficiency and availability over sustainability, leading to conflicts and social issues within mining communities. Despite its economic benefits, traditional sourcing faces increasing criticism for its lack of transparency and ethical accountability in the global jewelry industry.
Key Differences Between Ethical and Traditional Sourcing
Ethical sourcing in jewelry making prioritizes conflict-free materials, environmental sustainability, and fair labor practices, while traditional sourcing often relies on established supply chains with less transparency and potential exploitation. Key differences include the traceability of raw materials, adherence to strict environmental regulations, and commitment to social responsibility in ethical sourcing. Traditional sourcing typically focuses on cost efficiency and availability, sometimes at the expense of ethical considerations.
Environmental Impact: Ethical vs. Traditional Jewelry Materials
Ethical sourcing in jewelry prioritizes sustainable mining practices that minimize environmental degradation, reduce carbon footprints, and ensure responsible waste management. Traditional sourcing often involves extensive land disruption, pollution from toxic chemicals like cyanide and mercury, and significant biodiversity loss. Shifting to ethically sourced materials helps protect ecosystems and promotes long-term environmental stewardship within the jewelry industry.
Human Rights Concerns in Jewelry Supply Chains
Ethical sourcing in jewelry prioritizes human rights by ensuring fair labor practices, eliminating child labor, and promoting safe working conditions throughout supply chains. Traditional sourcing often lacks transparency, increasing risks of exploitation, poor wages, and unsafe environments for miners and artisans. Brands adopting ethical sourcing frameworks like Fairtrade and Responsible Jewelry Council certification actively address these concerns to enhance social responsibility.
Traceability and Transparency in Sourcing Practices
Ethical sourcing in jewelry making emphasizes full traceability and transparency, ensuring every material is responsibly mined and verified from origin to final product. Traditional sourcing often lacks comprehensive documentation, making it challenging to confirm the ethical standards of materials used. Advanced technologies like blockchain are increasingly employed in ethical sourcing to provide measurable supply chain transparency and verify the authenticity of gemstones and metals.
Cost Comparison: Ethical Sourcing vs. Traditional Sourcing
Ethical sourcing in jewelry making often involves higher upfront costs due to stringent labor practices, fair wages, and sustainable materials, whereas traditional sourcing typically benefits from lower expenses tied to mass production and less regulated supply chains. Despite the initially higher price, ethical sourcing can reduce long-term risks such as reputational damage and supply chain disruptions. Consumers increasingly value transparency and sustainability, making ethically sourced jewelry a competitive investment despite its premium cost compared to traditional alternatives.
Consumer Demand for Ethically Sourced Jewelry
Consumer demand for ethically sourced jewelry has surged, driven by increased awareness of labor practices and environmental impact in mining regions. Ethical sourcing prioritizes traceability, fair wages, and sustainable materials, contrasting with traditional sourcing that often lacks transparency. Brands adopting ethical sourcing strategies experience higher customer loyalty and market differentiation in the competitive jewelry industry.
Certification and Standards in Ethical Sourcing
Certification and standards in ethical sourcing ensure that jewelry materials are obtained through responsible practices meeting rigorous environmental and social criteria. Recognized labels like Fairtrade Gold and the Responsible Jewellery Council certification validate transparency and fair labor conditions. These certifications contrast traditional sourcing, which often lacks traceability and oversight, influencing consumer trust and industry accountability.
The Future of Sourcing in the Jewelry Industry
Ethical sourcing in the jewelry industry prioritizes sustainability, fair labor practices, and environmental stewardship, contrasted with traditional sourcing's focus on cost and availability. Innovations such as blockchain for supply chain transparency and lab-grown gemstones are reshaping the future of sourcing by ensuring provenance and minimizing ecological impact. Consumer demand for ethically sourced materials drives brands to adopt responsible practices, positioning ethical sourcing as the cornerstone of future jewelry production.
Ethical sourcing vs Traditional sourcing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com