Conflict-free diamonds are ethically sourced to ensure they are free from funding violence or exploitation, meeting strict international standards. Mined diamonds, while naturally formed, can sometimes be linked to environmental degradation and unethical labor practices if not responsibly sourced. Choosing conflict-free diamonds supports sustainable mining practices and promotes transparency in the jewelry industry.
Table of Comparison
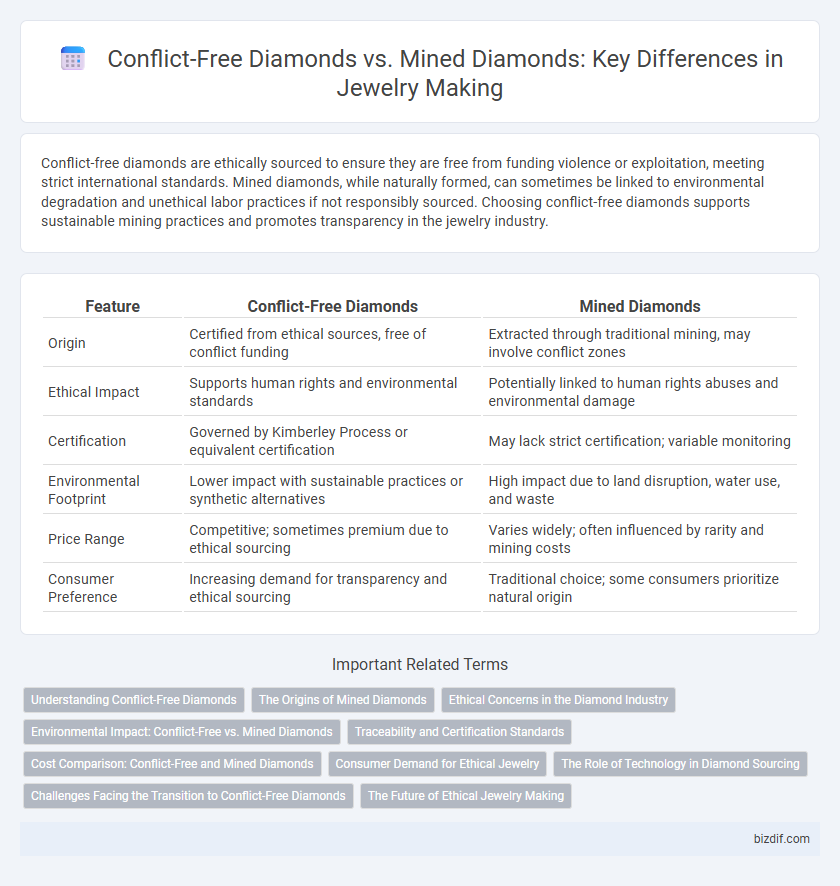
| Feature | Conflict-Free Diamonds | Mined Diamonds |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Certified from ethical sources, free of conflict funding | Extracted through traditional mining, may involve conflict zones |
| Ethical Impact | Supports human rights and environmental standards | Potentially linked to human rights abuses and environmental damage |
| Certification | Governed by Kimberley Process or equivalent certification | May lack strict certification; variable monitoring |
| Environmental Footprint | Lower impact with sustainable practices or synthetic alternatives | High impact due to land disruption, water use, and waste |
| Price Range | Competitive; sometimes premium due to ethical sourcing | Varies widely; often influenced by rarity and mining costs |
| Consumer Preference | Increasing demand for transparency and ethical sourcing | Traditional choice; some consumers prioritize natural origin |
Understanding Conflict-Free Diamonds
Conflict-free diamonds are those that have been ethically sourced, ensuring they do not finance armed conflict or human rights abuses, unlike some mined diamonds from conflict regions. These diamonds are certified through processes like the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme, which aims to trace their origin and guarantee ethical mining practices. Understanding conflict-free diamonds involves recognizing the importance of transparency in the supply chain and supporting responsible mining initiatives that promote social and environmental sustainability.
The Origins of Mined Diamonds
Mined diamonds originate from deep within the Earth's mantle, formed under intense heat and pressure over billions of years and extracted through extensive mining operations in countries like Russia, Botswana, and Canada. These diamonds often carry complex geopolitical implications due to mining practices, with concerns about environmental impact and labor conditions in some regions. Conflict-free diamonds, by contrast, are certified through the Kimberley Process to ensure they are not sourced from areas of armed conflict or human rights abuses.
Ethical Concerns in the Diamond Industry
Conflict-free diamonds are sourced through strict verification processes ensuring they are not involved in funding violence or human rights abuses, contrasting with some mined diamonds that have historically been linked to unethical labor practices and environmental damage. The diamond industry faces ongoing scrutiny over child labor, unsafe working conditions, and ecological degradation in mining regions. Ethical concerns drive consumer demand for transparency and certification programs like the Kimberley Process, which aims to prevent conflict diamonds from entering the mainstream market.
Environmental Impact: Conflict-Free vs. Mined Diamonds
Conflict-free diamonds are sourced through ethical channels that minimize environmental degradation, often involving strict regulations and sustainable mining practices. In contrast, traditional mined diamonds significantly impact ecosystems through land disruption, deforestation, and water pollution, contributing to biodiversity loss. Sustainable alternatives prioritize reducing carbon emissions and habitat destruction while supporting local communities.
Traceability and Certification Standards
Conflict-free diamonds adhere to rigorous traceability protocols and certification standards such as the Kimberley Process and Responsible Jewellery Council accreditation, ensuring ethical sourcing free from human rights abuses and conflict financing. Mined diamonds often lack transparent supply chain documentation, posing risks of association with unethical labor practices and environmental harm. Enhanced certification and blockchain technologies increasingly improve the verifiability and trustworthiness of conflict-free diamonds in the jewelry industry.
Cost Comparison: Conflict-Free and Mined Diamonds
Conflict-free diamonds typically command higher prices due to their ethical sourcing and certification processes, which ensure they are free from human rights abuses. Mined diamonds, while often less expensive, can involve environmental and social costs not reflected in the market price. Consumers increasingly weigh these ethical considerations alongside cost, making conflict-free diamonds a preferred choice despite the premium.
Consumer Demand for Ethical Jewelry
Consumer demand for ethical jewelry drives the preference for conflict-free diamonds, which guarantee sourcing without funding violence or exploitation in mining regions. Mined diamonds often face scrutiny due to concerns over environmental impact and labor conditions, prompting buyers to seek transparency and certification in their purchases. Brands offering conflict-free diamonds capitalize on growing awareness and ethical considerations in the jewelry market, increasing consumer trust and market share.
The Role of Technology in Diamond Sourcing
Technology plays a critical role in ensuring the ethical sourcing of conflict-free diamonds by enabling advanced tracking systems like blockchain to verify the origin of each stone. Sophisticated imaging and spectroscopy tools enhance the detection of synthetic or illicit diamonds, improving transparency within the supply chain. These technological innovations help jewelers and consumers distinguish between mined diamonds and responsibly sourced alternatives, promoting accountability and sustainability in the jewelry industry.
Challenges Facing the Transition to Conflict-Free Diamonds
Transitioning to conflict-free diamonds involves significant challenges such as complex supply chain verification, higher sourcing costs, and limited availability of certified stones. Mining operations often occur in regions with weak regulatory frameworks, making comprehensive transparency difficult to achieve. Furthermore, the demand for conflict-free diamonds requires robust blockchain and traceability technologies to ensure ethical sourcing without compromising consumer trust.
The Future of Ethical Jewelry Making
Conflict-free diamonds, sourced through transparent supply chains, are reshaping the future of ethical jewelry making by prioritizing human rights and environmental sustainability over traditional mined diamonds, which often involve exploitative labor and ecological damage. Innovations such as lab-grown diamonds and blockchain certification ensure traceability and conflict-free assurance, meeting growing consumer demand for responsible luxury. Adopting these ethical alternatives signals a transformative shift towards sustainable practices in the jewelry industry.
Conflict-free diamonds vs Mined diamonds Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com