Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online activities, fostering greater interaction and personalized feedback in language acquisition. Fully online learning offers flexibility and accessibility, enabling learners to study at their own pace but may lack immediate support and hands-on practice. Choosing between these methods depends on learners' needs for structure, engagement, and convenience in mastering a new language.
Table of Comparison
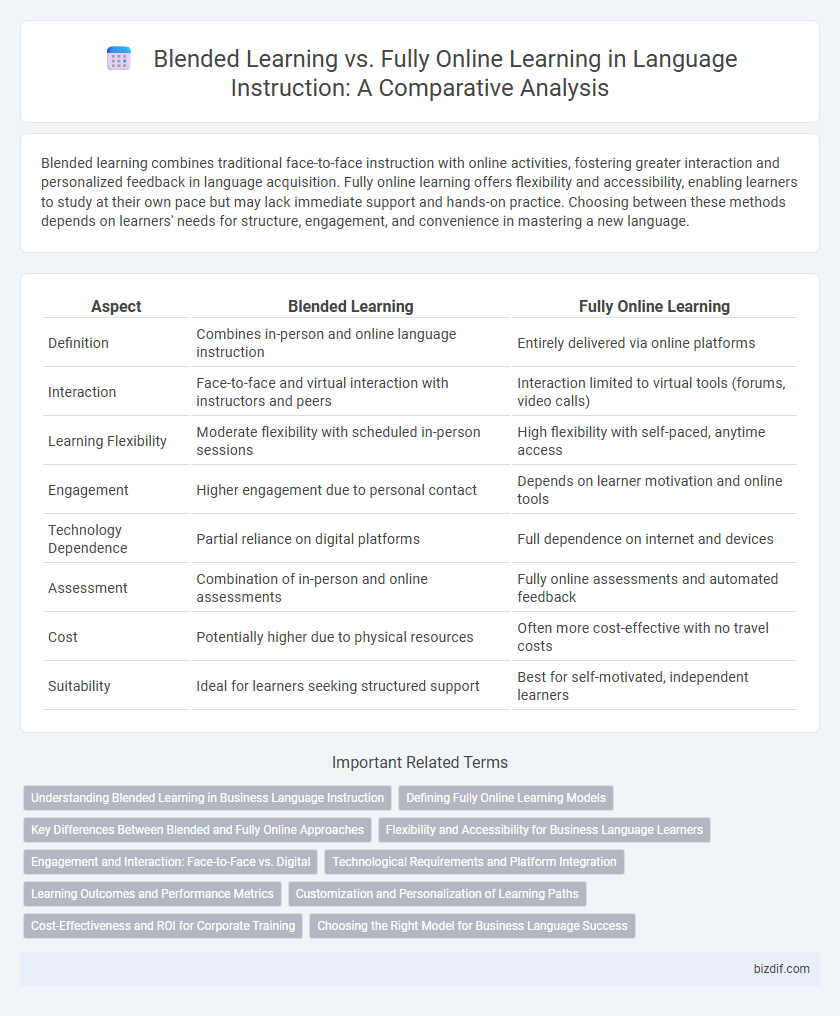
| Aspect | Blended Learning | Fully Online Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines in-person and online language instruction | Entirely delivered via online platforms |
| Interaction | Face-to-face and virtual interaction with instructors and peers | Interaction limited to virtual tools (forums, video calls) |
| Learning Flexibility | Moderate flexibility with scheduled in-person sessions | High flexibility with self-paced, anytime access |
| Engagement | Higher engagement due to personal contact | Depends on learner motivation and online tools |
| Technology Dependence | Partial reliance on digital platforms | Full dependence on internet and devices |
| Assessment | Combination of in-person and online assessments | Fully online assessments and automated feedback |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to physical resources | Often more cost-effective with no travel costs |
| Suitability | Ideal for learners seeking structured support | Best for self-motivated, independent learners |
Understanding Blended Learning in Business Language Instruction
Blended learning in business language instruction combines face-to-face interaction with online digital tools, enhancing learner engagement and contextual understanding. This hybrid approach allows for tailored feedback and real-time practice in speaking and negotiation skills alongside flexible, self-paced grammar and vocabulary modules. Studies show that blended learning improves language retention and practical application more effectively than fully online formats by integrating immersive experiences with technology-driven content.
Defining Fully Online Learning Models
Fully online learning models deliver language instruction exclusively through digital platforms without any in-person sessions, enabling flexible access to course materials and real-time virtual interaction. These models utilize multimedia resources, adaptive assessments, and synchronous or asynchronous communication tools to support individualized language acquisition. Emphasizing autonomous learning, fully online programs rely on Learning Management Systems (LMS) to structure content delivery and track learner progress remotely.
Key Differences Between Blended and Fully Online Approaches
Blended learning combines face-to-face classroom instruction with online activities, offering flexibility and direct interaction, while fully online learning relies exclusively on virtual platforms for content delivery and communication. In blended environments, learners benefit from immediate feedback and social engagement, contrasting with the self-paced, technology-dependent nature of fully online courses. The key differences include interaction modes, learning pace, and technological requirements, influencing student engagement and instructional design strategies.
Flexibility and Accessibility for Business Language Learners
Blended learning offers business language learners increased flexibility by combining in-person sessions with online components, allowing for adaptable scheduling and varied learning modalities. Fully online learning enhances accessibility by enabling learners to participate from any location and on their own time, removing geographical and temporal barriers. Both methods cater to busy professionals, but blended learning supports hands-on practice while fully online learning maximizes convenience and global reach.
Engagement and Interaction: Face-to-Face vs. Digital
Blended learning enhances engagement by combining face-to-face interaction with digital tools, allowing learners to benefit from real-time feedback and collaborative activities while leveraging online resources for flexible practice. Fully online learning relies predominantly on digital platforms, which can limit spontaneous interactions but offers diverse multimedia content and asynchronous forums to support student participation. Effective language instruction integrates synchronous video sessions and interactive tasks in both models to maintain motivation and deepen conversational skills.
Technological Requirements and Platform Integration
Blended learning demands seamless integration of physical classroom tools with digital platforms, often requiring interoperable learning management systems (LMS) that support both in-person and virtual interactions. Fully online learning relies heavily on robust, cloud-based platforms capable of handling asynchronous and synchronous communication, multimedia content delivery, and real-time assessments without the need for physical infrastructure. Both formats necessitate high-speed internet connectivity and multimedia-compatible devices, but blended learning additionally requires technology that bridges the gap between face-to-face and remote components for a cohesive educational experience.
Learning Outcomes and Performance Metrics
Blended learning combines face-to-face instruction with online components, often resulting in higher learning outcomes and improved engagement compared to fully online learning, as evidenced by increased retention rates and better performance metrics in language acquisition assessments. Fully online learning offers flexibility and accessibility but may exhibit lower interaction quality, potentially affecting speaking proficiency and immediate feedback effectiveness. Studies indicate that blended approaches enhance vocabulary retention and grammar accuracy, while fully online platforms excel in adaptive learning technologies and personalized pacing.
Customization and Personalization of Learning Paths
Blended learning offers enhanced customization by combining face-to-face instruction with digital resources, allowing educators to tailor learning paths based on individual student needs and real-time feedback. Fully online learning platforms leverage adaptive technologies and data analytics to personalize content delivery, pacing, and assessments, providing flexible, learner-centered experiences. Both models prioritize differentiated instruction, but blended learning integrates direct human interaction, which can enrich personalized guidance and support.
Cost-Effectiveness and ROI for Corporate Training
Blended learning combines in-person and online instruction, reducing travel and facility costs while enhancing engagement, resulting in higher ROI for corporate training programs. Fully online learning minimizes overhead by eliminating physical space needs and allows scalable access across global teams, offering a cost-effective solution for large enterprises. Companies investing in blended models often see improved learner retention and productivity, whereas fully online training excels in flexibility and rapid deployment, impacting overall cost-effectiveness differently based on organizational goals.
Choosing the Right Model for Business Language Success
Blended learning combines face-to-face instruction with online components, offering interactive language practice and real-time feedback essential for business communication skills. Fully online learning provides flexibility and access to a broad range of digital resources, catering to busy professionals requiring self-paced language study. Selecting the right model depends on company goals, employee schedules, and the need for personalized interaction in mastering business language proficiency.
Blended learning vs Fully online learning Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com