Bilingual education integrates instruction in two languages, enabling students to develop proficiency while maintaining their native language, often leading to balanced literacy and cognitive flexibility. Immersion programs prioritize teaching content exclusively in a second language, accelerating language acquisition through full exposure but potentially posing initial challenges for comprehension. Both approaches offer distinct benefits for language instruction, with choices depending on learners' needs and educational goals.
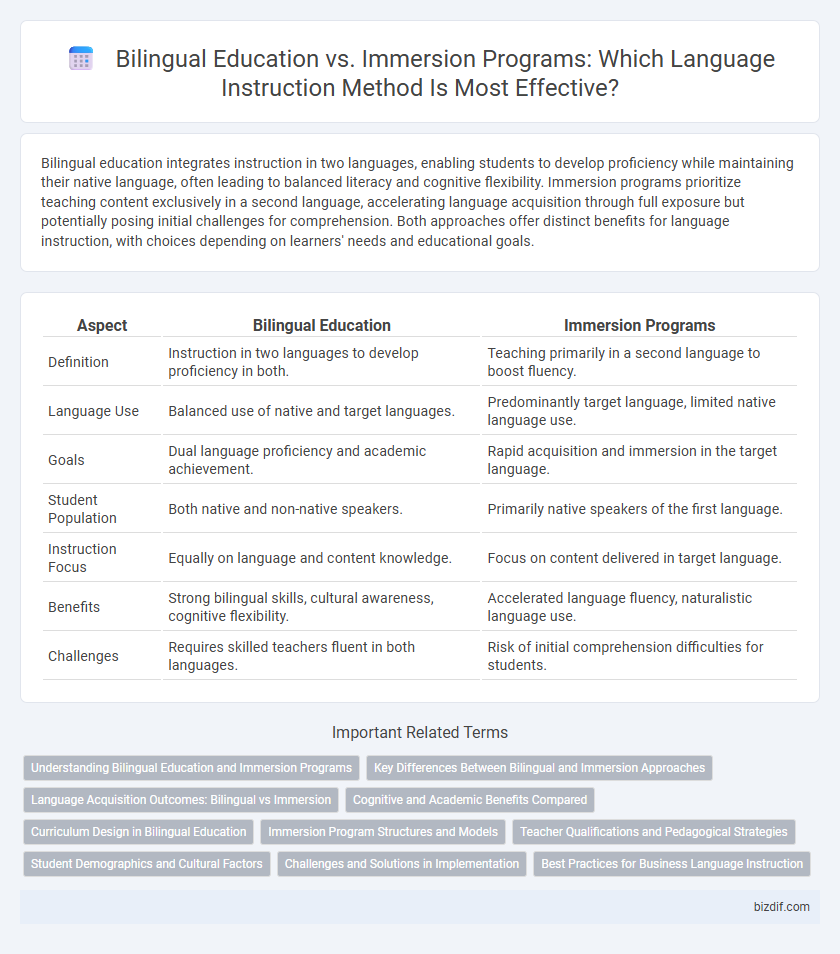
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Bilingual Education | Immersion Programs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instruction in two languages to develop proficiency in both. | Teaching primarily in a second language to boost fluency. |
| Language Use | Balanced use of native and target languages. | Predominantly target language, limited native language use. |
| Goals | Dual language proficiency and academic achievement. | Rapid acquisition and immersion in the target language. |
| Student Population | Both native and non-native speakers. | Primarily native speakers of the first language. |
| Instruction Focus | Equally on language and content knowledge. | Focus on content delivered in target language. |
| Benefits | Strong bilingual skills, cultural awareness, cognitive flexibility. | Accelerated language fluency, naturalistic language use. |
| Challenges | Requires skilled teachers fluent in both languages. | Risk of initial comprehension difficulties for students. |
Understanding Bilingual Education and Immersion Programs
Bilingual education integrates instruction in two languages, promoting proficiency and literacy in both while supporting cognitive development. Immersion programs immerse students primarily in the target language, accelerating language acquisition through contextual and interactive learning. Understanding these approaches reveals distinct benefits for language retention and cultural competence, guiding educators in selecting appropriate methodologies.
Key Differences Between Bilingual and Immersion Approaches
Bilingual education involves teaching students in two languages to develop proficiency and literacy in both, while immersion programs primarily use the target language for instruction to foster natural language acquisition. Bilingual education often balances language use by integrating curriculum content and language goals, whereas immersion emphasizes intensive exposure to one language with gradual incorporation of the native language. Key differences include instructional language distribution, cognitive objectives, and long-term language proficiency outcomes.
Language Acquisition Outcomes: Bilingual vs Immersion
Immersion programs accelerate second language fluency by surrounding students with consistent target-language input, fostering natural language acquisition and higher conversational proficiency. Bilingual education emphasizes balanced development in both languages, supporting academic content mastery and cognitive flexibility, but may progress more gradually in second language fluency. Studies indicate that immersion often yields superior oral language outcomes, while bilingual education strengthens literacy and academic achievement across both languages.
Cognitive and Academic Benefits Compared
Bilingual education programs promote cognitive flexibility and metalinguistic awareness by maintaining and developing proficiency in two languages simultaneously, leading to enhanced executive function skills and improved problem-solving abilities. Immersion programs, where students learn content entirely in a target language, accelerate language proficiency and content mastery, resulting in higher academic achievement and stronger language transfer skills. Studies show that both approaches contribute to improved cognitive development, with bilingual education typically supporting sustained bilingual literacy and immersion programs fostering rapid language acquisition and academic success in the second language.
Curriculum Design in Bilingual Education
Bilingual education curriculum design integrates simultaneous instruction in two languages, ensuring balanced linguistic development and cultural competence. It employs content-based instruction where subjects like math and science are taught in both languages to reinforce academic and language skills. This approach promotes cognitive flexibility and long-term bilingual proficiency by scaffolding language acquisition with meaningful context.
Immersion Program Structures and Models
Immersion programs utilize structured models such as full immersion, partial immersion, and dual-language immersion to promote language acquisition through content instruction in the target language. Full immersion programs instruct nearly all subjects in the second language, while partial immersion splits time between the target language and the native language, facilitating gradual bilingual proficiency. Dual-language immersion integrates native speakers of both languages, fostering balanced bilingualism and cross-cultural understanding within the classroom environment.
Teacher Qualifications and Pedagogical Strategies
Bilingual education programs require teachers to hold specialized certifications in both languages of instruction, ensuring fluency and cultural competence, whereas immersion programs prioritize native-level language proficiency and expertise in immersive pedagogical techniques. Effective bilingual educators employ differentiated instruction and scaffolded language development strategies, while immersion teachers focus on contextual learning, total physical response, and interactive language use to enhance acquisition. Both modalities demand ongoing professional development in second language acquisition theories and culturally responsive teaching methods to optimize student outcomes.
Student Demographics and Cultural Factors
Bilingual education programs primarily serve students from diverse linguistic backgrounds, aiming to maintain their native language while developing proficiency in a second language, often benefiting immigrant communities and language minorities. Immersion programs typically attract students from more homogeneous language groups seeking full fluency through exclusive use of the target language, fostering cultural appreciation and cognitive flexibility. Understanding student demographics and cultural factors is crucial for tailoring instructional methods that support identity development and academic achievement in both educational models.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementation
Bilingual education faces challenges such as balancing language proficiency across subjects and addressing diverse learner backgrounds, requiring tailored curriculum design and ongoing teacher training. Immersion programs struggle with maintaining student engagement and preventing language attrition, solved by integrating culturally relevant materials and fostering home-language support. Both approaches benefit from collaborative community involvement and adaptive assessment methods to enhance language acquisition and academic achievement.
Best Practices for Business Language Instruction
Bilingual education and immersion programs offer distinct advantages for business language instruction by fostering fluency and cultural competence through contextual learning. Effective strategies include integrating real-world business scenarios, leveraging technology for interactive practice, and emphasizing collaborative communication skills to enhance workplace language proficiency. Tailoring instruction to industry-specific vocabulary and cross-cultural negotiation techniques maximizes relevance and learner engagement in professional environments.
Bilingual Education vs Immersion Programs Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com