Content localization tailors language instruction materials to specific cultural and regional contexts, enhancing learner engagement and comprehension by addressing local idioms, customs, and preferences. Content standardization ensures consistency and uniformity across language courses, facilitating streamlined delivery and easier scalability for diverse audiences. Balancing localization and standardization optimizes effectiveness by combining cultural relevance with cohesive pedagogical objectives.
Table of Comparison
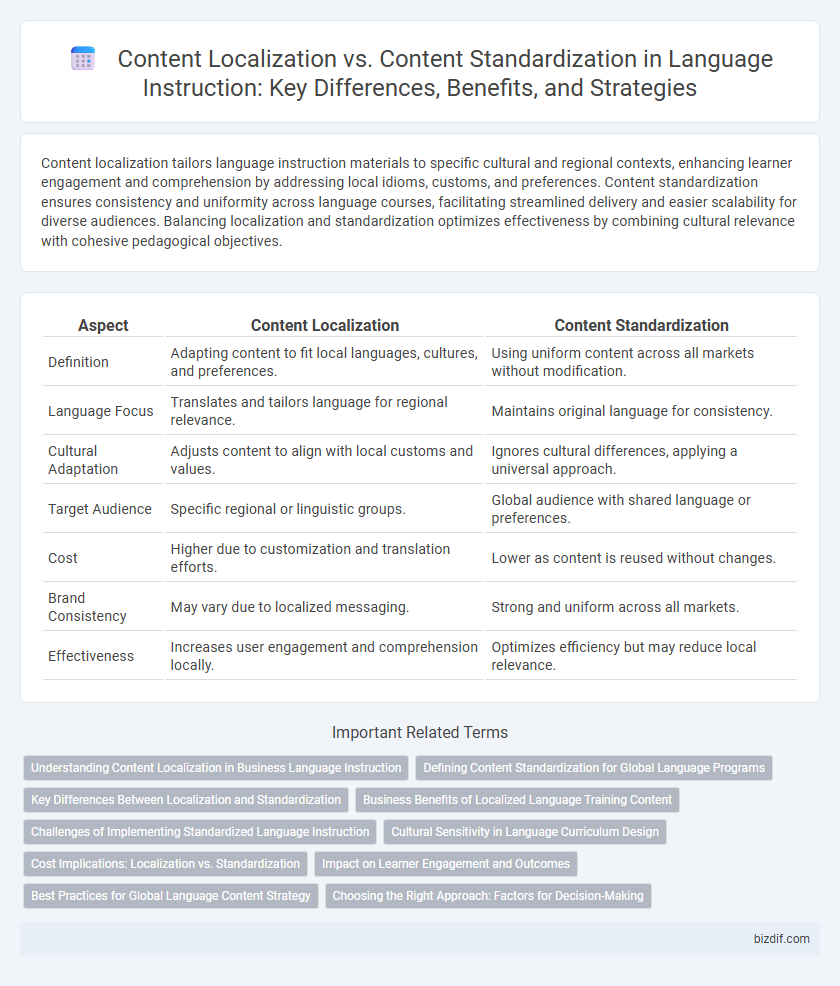
| Aspect | Content Localization | Content Standardization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adapting content to fit local languages, cultures, and preferences. | Using uniform content across all markets without modification. |
| Language Focus | Translates and tailors language for regional relevance. | Maintains original language for consistency. |
| Cultural Adaptation | Adjusts content to align with local customs and values. | Ignores cultural differences, applying a universal approach. |
| Target Audience | Specific regional or linguistic groups. | Global audience with shared language or preferences. |
| Cost | Higher due to customization and translation efforts. | Lower as content is reused without changes. |
| Brand Consistency | May vary due to localized messaging. | Strong and uniform across all markets. |
| Effectiveness | Increases user engagement and comprehension locally. | Optimizes efficiency but may reduce local relevance. |
Understanding Content Localization in Business Language Instruction
Content localization in business language instruction involves adapting training materials to reflect the cultural, linguistic, and contextual nuances of the target market, enhancing learner engagement and comprehension. It goes beyond simple translation by incorporating local idioms, business practices, and communication styles, ensuring the instruction resonates authentically with the audience. This approach improves the effectiveness of language programs by addressing specific regional and cultural business environments, which leads to better performance and communication in global markets.
Defining Content Standardization for Global Language Programs
Content standardization in global language programs involves creating consistent, uniform instructional materials that maintain the same language and terminology across all regions, ensuring coherent messaging and brand identity. This approach simplifies content management and reduces translation costs by using identical content worldwide, while supporting scalable language training initiatives. Emphasizing standardization helps organizations deliver efficient and measurable global language instruction aligned with corporate standards.
Key Differences Between Localization and Standardization
Content localization adapts language, cultural references, and formatting to resonate with specific regional audiences, ensuring relevance and engagement. In contrast, content standardization maintains uniformity across markets by using consistent language and messaging worldwide, promoting brand consistency. Key differences involve tailored linguistic nuances and cultural sensitivity in localization versus homogeneous content delivery in standardization.
Business Benefits of Localized Language Training Content
Localized language training content enhances learner engagement by reflecting cultural nuances and industry-specific terminology, resulting in higher retention and application rates. This tailored approach supports global business expansion by facilitating effective communication and collaboration across diverse markets. Companies achieving localized training typically see improved employee performance, faster onboarding, and increased customer satisfaction in international operations.
Challenges of Implementing Standardized Language Instruction
Implementing standardized language instruction faces challenges such as cultural nuances and regional dialects that affect learners' comprehension and engagement. Uniform content may overlook local expressions, idiomatic phrases, and context-specific meanings, reducing effectiveness. Balancing consistency with adaptability requires careful linguistic and pedagogical considerations to ensure relevancy across diverse learner populations.
Cultural Sensitivity in Language Curriculum Design
Content localization in language curriculum design emphasizes adapting materials to reflect the cultural norms, values, and idiomatic expressions of the target audience, enhancing student engagement and comprehension. Content standardization maintains uniformity across regions by using consistent linguistic frameworks and educational goals, which may overlook cultural nuances important for effective communication. Prioritizing cultural sensitivity within localization ensures respectful representation and meaningful learning experiences, fostering deeper intercultural competence.
Cost Implications: Localization vs. Standardization
Content localization demands higher upfront costs due to translation, cultural adaptation, and market-specific customization, which can significantly increase production expenses. Content standardization reduces costs by using uniform content across markets, minimizing the need for multiple language versions and localized adjustments. Organizations must weigh these cost implications against potential ROI, as localized content often drives better engagement and conversion in diverse regions despite higher initial expenses.
Impact on Learner Engagement and Outcomes
Content localization enhances learner engagement by tailoring language, cultural references, and examples to the target audience, resulting in higher retention rates and improved comprehension. Content standardization ensures consistency across regions, supporting unified learning outcomes but may reduce relatability and motivation among diverse learners. Balancing localization with standardization optimizes both engagement and educational effectiveness by addressing specific learner needs while maintaining core instructional quality.
Best Practices for Global Language Content Strategy
Effective global language content strategy requires balancing content localization and content standardization to resonate with diverse audiences while maintaining brand consistency. Localization involves adapting language, cultural nuances, and regional preferences to enhance user engagement and relevance, whereas standardization ensures uniform messaging and cost efficiency across markets. Best practices include leveraging data-driven insights for targeted localization, implementing scalable workflows, and harmonizing terminology to optimize both global reach and local impact.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors for Decision-Making
Choosing the right approach between content localization and content standardization depends on factors such as target audience diversity, cultural nuances, and business goals. Content localization involves adapting language, idioms, and cultural references to resonate authentically with specific regions, enhancing user engagement and relevance. Conversely, content standardization ensures consistency and brand uniformity across multiple markets, streamlining operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Content Localization vs Content Standardization Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com