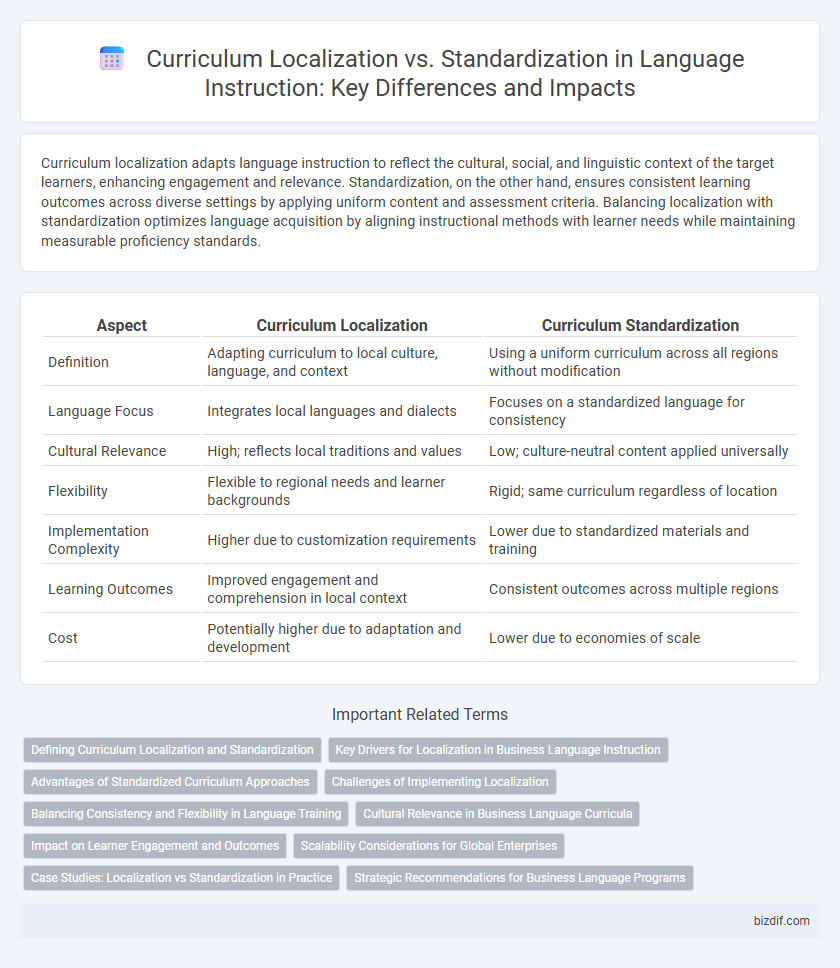
Curriculum localization adapts language instruction to reflect the cultural, social, and linguistic context of the target learners, enhancing engagement and relevance. Standardization, on the other hand, ensures consistent learning outcomes across diverse settings by applying uniform content and assessment criteria. Balancing localization with standardization optimizes language acquisition by aligning instructional methods with learner needs while maintaining measurable proficiency standards.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Curriculum Localization | Curriculum Standardization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adapting curriculum to local culture, language, and context | Using a uniform curriculum across all regions without modification |
| Language Focus | Integrates local languages and dialects | Focuses on a standardized language for consistency |
| Cultural Relevance | High; reflects local traditions and values | Low; culture-neutral content applied universally |
| Flexibility | Flexible to regional needs and learner backgrounds | Rigid; same curriculum regardless of location |
| Implementation Complexity | Higher due to customization requirements | Lower due to standardized materials and training |
| Learning Outcomes | Improved engagement and comprehension in local context | Consistent outcomes across multiple regions |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to adaptation and development | Lower due to economies of scale |
Defining Curriculum Localization and Standardization
Curriculum localization involves adapting educational content to reflect local culture, language, and societal values, ensuring relevance and engagement for diverse learner groups. Curriculum standardization refers to the development of uniform educational frameworks and materials that maintain consistent learning outcomes across different regions. Defining these concepts highlights the balance between culturally responsive teaching and the need for consistent educational quality worldwide.
Key Drivers for Localization in Business Language Instruction
Business language instruction often requires curriculum localization to address cultural nuances, regional market demands, and specific industry terminology that vary by location. Key drivers for localization include improving learner engagement by reflecting local business practices, enhancing communication effectiveness in target markets, and complying with regional professional standards. These factors ensure that language training is relevant, practical, and aligned with the learners' working environment.
Advantages of Standardized Curriculum Approaches
Standardized curriculum approaches ensure consistent learning outcomes across diverse regions, facilitating easier assessment and benchmarking of language proficiency. They support scalability in language instruction programs by providing uniform content that can be efficiently delivered and updated. This uniformity enhances resource sharing, teacher training, and student mobility within educational systems.
Challenges of Implementing Localization
Implementing curriculum localization faces challenges such as resource constraints, including the need for culturally relevant materials and adequately trained educators familiar with local contexts. Language barriers and diverse dialects complicate the adaptation process, requiring continuous updates to maintain relevance and effectiveness. Resistance from stakeholders accustomed to standardized curricula can hinder acceptance and integration of localized content within education systems.
Balancing Consistency and Flexibility in Language Training
Curriculum localization tailors language instruction to cultural and regional nuances, enhancing learner engagement and relevance while maintaining core linguistic competencies. Standardization ensures consistent quality and measurable outcomes across diverse learner groups, facilitating certification and benchmark comparisons. Balancing consistency and flexibility requires integrating localized content within a standardized framework, allowing adaptation to specific learner needs without compromising fundamental language skills.
Cultural Relevance in Business Language Curricula
Curriculum localization in business language instruction enhances cultural relevance by integrating regional business practices, communication styles, and industry-specific terminology that resonate with learners' local contexts. Standardization, while facilitating uniformity and scalability, often overlooks nuanced cultural differences critical for effective cross-cultural communication. Emphasizing cultural relevance in localized curricula improves learner engagement, intercultural competence, and practical language application in diverse business environments.
Impact on Learner Engagement and Outcomes
Curriculum localization tailors content to reflect the cultural background, language, and experiences of learners, significantly enhancing engagement by making lessons more relatable and accessible. Standardized curricula provide consistent learning outcomes across diverse populations but may risk reduced motivation due to lack of cultural relevance. Studies indicate that localized curricula improve learner retention and comprehension, leading to better academic performance in language instruction contexts.
Scalability Considerations for Global Enterprises
Curriculum localization enables global enterprises to tailor language instruction to regional cultural nuances and linguistic variations, increasing learner engagement and instructional effectiveness. Standardization supports scalable deployment of consistent language training across multiple locations, ensuring uniform proficiency benchmarks and streamlined resource management. Balancing localization with standardized core content maximizes scalability while addressing diverse learner needs in international markets.
Case Studies: Localization vs Standardization in Practice
Case studies demonstrate that curriculum localization enhances student engagement by integrating culturally relevant content and adapting teaching methods to local contexts, leading to improved comprehension and retention. Conversely, standardization ensures consistency in learning outcomes across different regions, facilitating easier assessment and mobility for students and educators. Evidence from diverse educational settings highlights the benefits of a hybrid approach, combining localized content with standardized core competencies to balance relevance and uniformity in language instruction.
Strategic Recommendations for Business Language Programs
Business language programs achieve greater effectiveness by tailoring curriculum localization to local cultural nuances and market-specific vocabulary, enhancing learner engagement and practical application. Implementing a standardized core framework ensures consistent language proficiency benchmarks, facilitating global business communication and scalability across diverse regions. Strategic integration of both approaches optimizes resource allocation and maximizes return on investment by aligning language instruction with organizational goals and regional business demands.
Curriculum Localization vs Standardization Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com