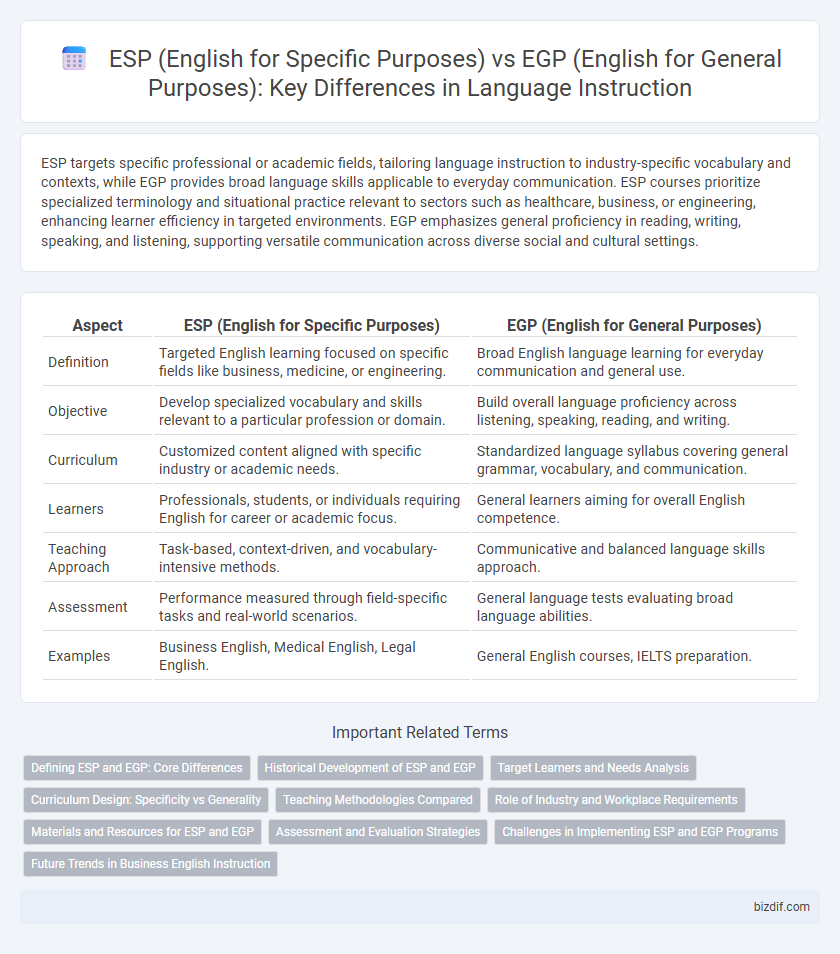
ESP targets specific professional or academic fields, tailoring language instruction to industry-specific vocabulary and contexts, while EGP provides broad language skills applicable to everyday communication. ESP courses prioritize specialized terminology and situational practice relevant to sectors such as healthcare, business, or engineering, enhancing learner efficiency in targeted environments. EGP emphasizes general proficiency in reading, writing, speaking, and listening, supporting versatile communication across diverse social and cultural settings.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | ESP (English for Specific Purposes) | EGP (English for General Purposes) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Targeted English learning focused on specific fields like business, medicine, or engineering. | Broad English language learning for everyday communication and general use. |
| Objective | Develop specialized vocabulary and skills relevant to a particular profession or domain. | Build overall language proficiency across listening, speaking, reading, and writing. |
| Curriculum | Customized content aligned with specific industry or academic needs. | Standardized language syllabus covering general grammar, vocabulary, and communication. |
| Learners | Professionals, students, or individuals requiring English for career or academic focus. | General learners aiming for overall English competence. |
| Teaching Approach | Task-based, context-driven, and vocabulary-intensive methods. | Communicative and balanced language skills approach. |
| Assessment | Performance measured through field-specific tasks and real-world scenarios. | General language tests evaluating broad language abilities. |
| Examples | Business English, Medical English, Legal English. | General English courses, IELTS preparation. |
Defining ESP and EGP: Core Differences
ESP (English for Specific Purposes) concentrates on tailored language skills targeting specialized fields such as medicine, engineering, or business, emphasizing industry-specific vocabulary and context-driven communication. EGP (English for General Purposes) focuses on broad language proficiency, including everyday conversation, general academic, and social communication skills without specialized jargon. The core difference lies in ESP's customization for professional or academic domains, while EGP aims at overall communicative competence across diverse, non-specialized settings.
Historical Development of ESP and EGP
The historical development of ESP (English for Specific Purposes) began in the 1960s as a response to the increasing demand for English language skills tailored to specific academic, professional, or occupational fields, emphasizing targeted vocabulary and practical communication. EGP (English for General Purposes) has its roots in traditional language teaching, focusing on broad language acquisition and overall communicative competence without domain-specific constraints. The evolution of ESP reflects the shift towards learner-centered approaches, driven by industry needs, while EGP remains foundational in holistic language education.
Target Learners and Needs Analysis
ESP (English for Specific Purposes) targets learners who require English proficiency tailored to particular fields such as business, medicine, or engineering, emphasizing immediate applicability and specialized vocabulary. Needs analysis in ESP involves detailed assessment of learners' professional contexts, tasks, and genre-specific communication to design relevant course content. In contrast, EGP (English for General Purposes) serves a broader audience aiming to improve overall English skills without specific vocational or academic focus, relying on generalized needs assessment focused on communicative competence.
Curriculum Design: Specificity vs Generality
ESP curriculum design prioritizes domain-specific content tailored to learners' professional or academic needs, enhancing practical communication skills in targeted fields like business, medicine, or engineering. EGP curriculum focuses on broad language competencies, covering grammar, vocabulary, and everyday communication applicable across diverse contexts without specialized jargon. This specificity versus generality contrast shapes course objectives, materials, and assessment methods, ensuring ESP delivers relevance for specialized audiences while EGP provides foundational language proficiency.
Teaching Methodologies Compared
ESP teaching methodologies prioritize learner-centered, task-based approaches tailored to specific professional or academic needs, emphasizing authentic materials and industry-specific vocabulary. In contrast, EGP employs more generalized, grammar-translation and communicative methods aimed at broader language acquisition without specialized content focus. The effectiveness of ESP lies in its contextual relevance and immediate applicability, whereas EGP supports foundational language skills suitable for diverse contexts.
Role of Industry and Workplace Requirements
ESP prioritizes tailored language instruction aligned with specific industry contexts, addressing vocabulary, communication styles, and tasks relevant to professional fields like healthcare, engineering, or business. EGP focuses on broad language skills applicable to general communication and everyday situations, lacking direct emphasis on specialized workplace demands. Industry and workplace requirements drive the need for ESP by defining precise linguistic competencies necessary for effective job performance and sector-specific interactions.
Materials and Resources for ESP and EGP
ESP materials are designed with specialized vocabulary and scenarios tailored to specific fields such as medicine, engineering, or business, incorporating authentic texts, technical manuals, and industry-related case studies. EGP resources emphasize general language skills through diverse content like everyday conversations, news articles, and literary texts aimed at improving overall communication competence. The selection of materials in ESP is driven by learners' professional needs, while EGP materials focus on broad language acquisition, making resource relevance crucial in curriculum design.
Assessment and Evaluation Strategies
ESP assessment emphasizes tailored evaluation methods that measure proficiency in domain-specific vocabulary and context-driven communication skills relevant to professional fields. EGP evaluation utilizes standardized tests to gauge general language abilities across grammar, vocabulary, and conversational competence without specialized content focus. Both strategies prioritize formative and summative assessments but differ significantly in aligning evaluation criteria with specific learner goals and contextual applications.
Challenges in Implementing ESP and EGP Programs
Implementing ESP programs presents challenges such as developing specialized curricula tailored to diverse professional fields and securing instructors with both language proficiency and industry-specific knowledge. EGP programs face difficulties in addressing the broad, varying language needs of learners while maintaining engagement and practical relevance across different contexts. Both approaches require careful alignment of learning objectives with student goals and effective resource allocation to ensure successful language acquisition outcomes.
Future Trends in Business English Instruction
Future trends in Business English instruction emphasize the growing integration of ESP (English for Specific Purposes) to meet industry-specific communication demands, enabling learners to acquire targeted vocabulary and skills for sectors like finance, marketing, and technology. Advances in technology and digital communication tools further support personalized ESP curricula, enhancing practical application and real-world fluency. EGP (English for General Purposes) remains foundational but increasingly serves as a stepping stone toward specialized ESP programs tailored to evolving business contexts and global professional environments.
ESP (English for Specific Purposes) vs EGP (English for General Purposes) Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com