Flipped classrooms enhance language instruction by allowing students to engage with materials at their own pace before class, promoting active participation and personalized learning during sessions. Traditional classrooms rely heavily on teacher-led instruction, often limiting opportunities for real-time practice and interaction critical to language acquisition. Emphasizing flipped methods boosts speaking and comprehension skills through increased student engagement and collaborative activities.
Table of Comparison
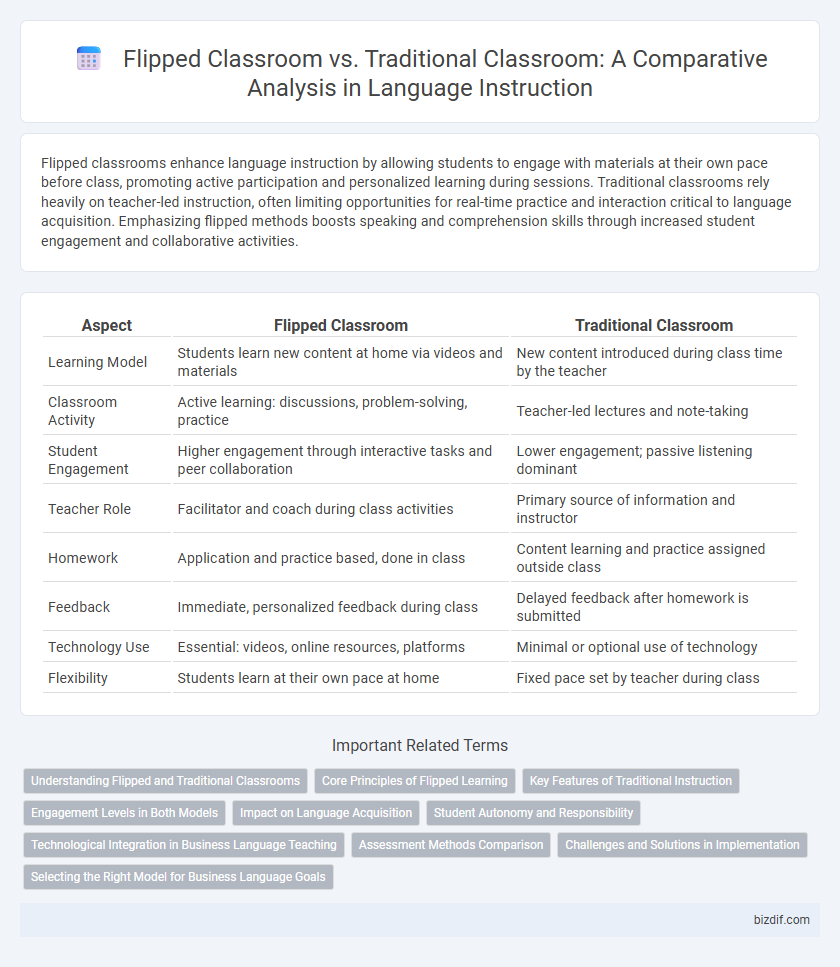
| Aspect | Flipped Classroom | Traditional Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Model | Students learn new content at home via videos and materials | New content introduced during class time by the teacher |
| Classroom Activity | Active learning: discussions, problem-solving, practice | Teacher-led lectures and note-taking |
| Student Engagement | Higher engagement through interactive tasks and peer collaboration | Lower engagement; passive listening dominant |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and coach during class activities | Primary source of information and instructor |
| Homework | Application and practice based, done in class | Content learning and practice assigned outside class |
| Feedback | Immediate, personalized feedback during class | Delayed feedback after homework is submitted |
| Technology Use | Essential: videos, online resources, platforms | Minimal or optional use of technology |
| Flexibility | Students learn at their own pace at home | Fixed pace set by teacher during class |
Understanding Flipped and Traditional Classrooms
Flipped classrooms reverse the traditional learning environment by delivering instructional content, often online, outside of class, enabling in-class time for interactive activities and personalized support. Traditional classrooms follow a lecture-based approach where teachers present new material during class and assign homework for practice. Understanding the differences in these models highlights how flipped classrooms promote active learning and collaboration, while traditional classrooms emphasize direct instruction and individual homework completion.
Core Principles of Flipped Learning
Flipped learning centers on reversing traditional teaching by delivering instructional content outside the classroom, allowing for active, interactive activities during class time. Core principles include pre-class preparation, in-class active learning, and ongoing formative assessment to enhance student engagement and comprehension. This model fosters personalized learning and deeper understanding compared to traditional lecture-based education.
Key Features of Traditional Instruction
Traditional instruction in language education emphasizes teacher-centered delivery, with instructors directing lessons through lectures and structured activities. Student engagement primarily involves listening, note-taking, and memorization, while immediate feedback occurs during class through quizzes or oral questioning. Classroom time is dedicated to introducing new material, with homework reinforcing practice outside the formal setting.
Engagement Levels in Both Models
Flipped classrooms significantly increase student engagement by allowing learners to interact with multimedia content before class, fostering active participation during in-person sessions. Traditional classrooms typically rely on passive listening and note-taking, which can limit students' involvement and motivation. Higher engagement in flipped models correlates with improved language retention and practical application.
Impact on Language Acquisition
Flipped classrooms enhance language acquisition by promoting active engagement and allowing students to review material at their own pace, leading to improved comprehension and retention of linguistic structures. Traditional classrooms often rely on passive learning through lectures, which may limit opportunities for interactive language practice and immediate feedback. Research indicates that flipped models foster greater communicative competence and learner autonomy, accelerating fluency development compared to conventional methods.
Student Autonomy and Responsibility
The flipped classroom model increases student autonomy by requiring learners to engage with instructional materials independently before class, fostering self-directed learning and time management skills. In contrast, traditional classrooms often rely on teacher-led instruction, limiting opportunities for students to take ownership of their learning process. Enhanced student responsibility in flipped classrooms promotes deeper comprehension and active participation during in-class activities.
Technological Integration in Business Language Teaching
Flipped classrooms leverage advanced digital tools such as interactive video lessons and real-time analytics platforms to enhance business language instruction, allowing students to engage with vocabulary and industry-specific jargon outside the traditional time constraints. In contrast, traditional classrooms primarily rely on face-to-face instruction and printed materials, limiting immediate feedback and adaptive learning opportunities. The integration of technology in flipped models supports personalized learning pathways and practical application, which are crucial for mastering complex communication skills in business contexts.
Assessment Methods Comparison
Flipped classrooms employ formative assessments such as quizzes and peer reviews during class to provide immediate feedback, enhancing language retention compared to traditional classrooms that often rely on summative assessments like tests and exams. Technology integration in flipped models allows for adaptive assessment tools and real-time analytics, supporting personalized language learning paths. Traditional classrooms typically emphasize end-of-unit evaluations, which may delay feedback and limit opportunities for students to apply corrections in ongoing language practice.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementation
Challenges in implementing flipped classrooms include student resistance to increased pre-class preparation and limited access to technology, while traditional classrooms often face difficulties engaging diverse learning styles. Solutions involve integrating user-friendly digital platforms and providing training sessions to enhance digital literacy, alongside incorporating varied instructional materials to accommodate all learners. Addressing these challenges improves participation and effectiveness in both flipped and traditional language instruction settings.
Selecting the Right Model for Business Language Goals
Selecting the right model for business language goals hinges on understanding the advantages of both flipped and traditional classrooms. Flipped classrooms enhance learner engagement by allowing employees to study foundational concepts independently, freeing up in-class time for interactive, real-world language practice critical for business communication. Traditional classrooms provide structured guidance and immediate feedback, which is beneficial for mastering complex grammar and vocabulary essential in professional settings.
Flipped classroom vs Traditional classroom Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com