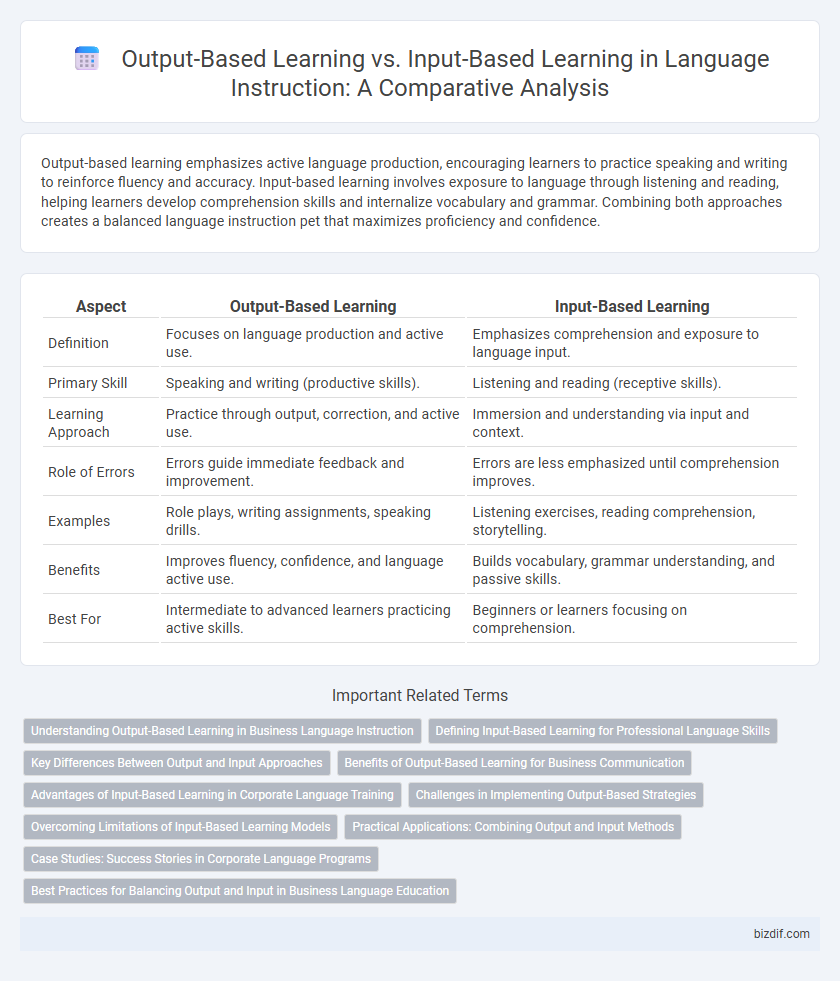
Output-based learning emphasizes active language production, encouraging learners to practice speaking and writing to reinforce fluency and accuracy. Input-based learning involves exposure to language through listening and reading, helping learners develop comprehension skills and internalize vocabulary and grammar. Combining both approaches creates a balanced language instruction pet that maximizes proficiency and confidence.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Output-Based Learning | Input-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on language production and active use. | Emphasizes comprehension and exposure to language input. |
| Primary Skill | Speaking and writing (productive skills). | Listening and reading (receptive skills). |
| Learning Approach | Practice through output, correction, and active use. | Immersion and understanding via input and context. |
| Role of Errors | Errors guide immediate feedback and improvement. | Errors are less emphasized until comprehension improves. |
| Examples | Role plays, writing assignments, speaking drills. | Listening exercises, reading comprehension, storytelling. |
| Benefits | Improves fluency, confidence, and language active use. | Builds vocabulary, grammar understanding, and passive skills. |
| Best For | Intermediate to advanced learners practicing active skills. | Beginners or learners focusing on comprehension. |
Understanding Output-Based Learning in Business Language Instruction
Output-based learning in business language instruction emphasizes active production of language through speaking and writing, enhancing practical communication skills vital for professional contexts. This approach fosters deeper cognitive processing by requiring learners to formulate responses, negotiate meaning, and adapt language to specific business scenarios. Empirical studies suggest output-based tasks significantly improve fluency, accuracy, and confidence in workplace communication compared to input-based methods alone.
Defining Input-Based Learning for Professional Language Skills
Input-based learning for professional language skills emphasizes comprehensive exposure to authentic materials such as industry-specific texts, audio recordings, and real-world conversations, allowing learners to internalize vocabulary, grammar, and contextual usage naturally. This approach prioritizes receptive skills development by engaging with diverse input sources that mirror professional communication settings. Continuous interaction with meaningful input enhances comprehension and forms a foundation for effective output in specialized language contexts.
Key Differences Between Output and Input Approaches
Output-based learning emphasizes active language production, enhancing speaking and writing skills through practice and feedback, while input-based learning focuses on comprehension by exposing learners to listening and reading materials. The output approach encourages cognitive engagement and internalization of language structures by requiring learners to formulate responses, whereas the input approach relies on passive absorption to build vocabulary and grammar recognition. Key differences lie in learner engagement levels, with output promoting expressive abilities and input enhancing receptive skills essential for foundational language acquisition.
Benefits of Output-Based Learning for Business Communication
Output-based learning enhances business communication by actively engaging learners in producing language, which improves fluency, accuracy, and confidence during real-world interactions. This method fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills essential for crafting clear emails, presentations, and negotiations. Research indicates that practicing output accelerates language retention and aids in mastering professional vocabulary and tone, critical for effective workplace communication.
Advantages of Input-Based Learning in Corporate Language Training
Input-based learning in corporate language training enhances comprehension and vocabulary acquisition by exposing learners to meaningful, context-rich materials relevant to their industry. This approach reduces learner anxiety and increases retention through passive absorption of grammar and sentence structures in authentic communication settings. Employees develop practical language skills faster, improving workplace communication efficiency and overall productivity.
Challenges in Implementing Output-Based Strategies
Output-based learning faces challenges such as learner anxiety when producing language without sufficient input exposure, limited vocabulary for accurate expression, and increased cognitive load during active communication. Teachers often struggle to balance corrective feedback with encouragement to maintain student motivation and confidence. Additionally, integrating authentic output activities requires substantial classroom time and resources, which may not be feasible in all educational settings.
Overcoming Limitations of Input-Based Learning Models
Output-based learning enhances language acquisition by actively engaging learners in producing language, which overcomes the passive reception limitations of input-based models. This approach fosters improved fluency, retention, and practical language use by prioritizing speaking and writing exercises that reinforce comprehension. Empirical studies indicate that integrating output activities accelerates proficiency development compared to reliance solely on input exposure.
Practical Applications: Combining Output and Input Methods
Output-based learning enhances language retention by encouraging active use through speaking and writing exercises, while input-based learning strengthens comprehension via listening and reading activities. Practical applications integrate these methods by designing tasks that require learners to process input and produce output, such as role-playing scenarios after listening to dialogues. Combining output and input strategies fosters balanced language skills development, improving fluency and comprehension simultaneously.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Corporate Language Programs
Case studies in corporate language programs demonstrate that output-based learning, emphasizing speaking and writing practice, significantly improves employee communication skills and confidence. Key examples include multinational companies where tailored output activities led to measurable increases in workforce language proficiency and enhanced cross-cultural collaboration. These success stories highlight the effectiveness of active language production over passive input methods in achieving practical business communication goals.
Best Practices for Balancing Output and Input in Business Language Education
Effective business language education integrates output-based learning, emphasizing active speaking and writing, with input-based learning, focusing on listening and reading comprehension. Best practices include creating immersive scenarios that require practical language use while providing ample exposure to authentic materials, such as industry-specific reports and presentations. Balancing interactive communication exercises with structured input enhances language acquisition and boosts learners' confidence in professional contexts.
Output-based learning vs Input-based learning Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com