Vegan meal prepping for pets prioritizes plant-based ingredients rich in essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants, promoting overall health and reducing the risk of certain diseases. Omnivore meal prep incorporates a balanced mix of animal proteins and plant foods, providing complete amino acids and essential fatty acids necessary for optimal pet growth and energy. Choosing between vegan and omnivore prep depends on a pet's dietary needs, health status, and owner preferences, ensuring nutritional adequacy is always maintained.
Table of Comparison
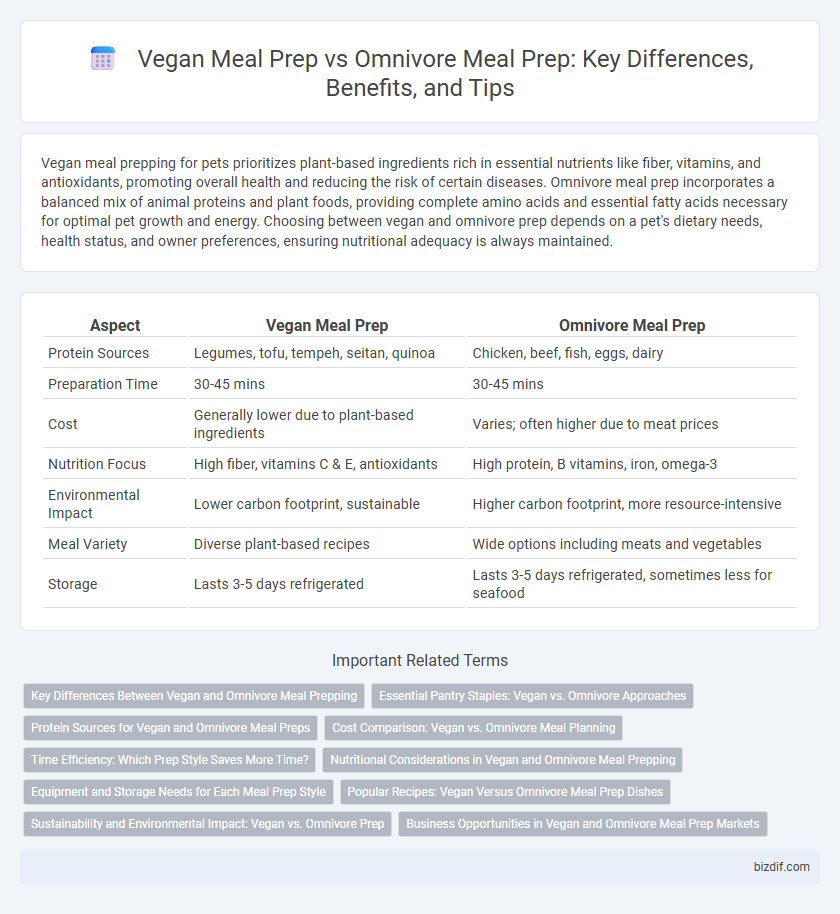
| Aspect | Vegan Meal Prep | Omnivore Meal Prep |
|---|---|---|
| Protein Sources | Legumes, tofu, tempeh, seitan, quinoa | Chicken, beef, fish, eggs, dairy |
| Preparation Time | 30-45 mins | 30-45 mins |
| Cost | Generally lower due to plant-based ingredients | Varies; often higher due to meat prices |
| Nutrition Focus | High fiber, vitamins C & E, antioxidants | High protein, B vitamins, iron, omega-3 |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, sustainable | Higher carbon footprint, more resource-intensive |
| Meal Variety | Diverse plant-based recipes | Wide options including meats and vegetables |
| Storage | Lasts 3-5 days refrigerated | Lasts 3-5 days refrigerated, sometimes less for seafood |
Key Differences Between Vegan and Omnivore Meal Prepping
Vegan meal prepping emphasizes plant-based ingredients such as legumes, grains, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, prioritizing nutrient-dense, fiber-rich foods while avoiding all animal products. Omnivore meal prepping incorporates a wider variety of protein sources, including meat, fish, dairy, and eggs, alongside vegetables and grains, requiring careful portioning of animal proteins for balanced nutrition. Vegan prep often demands attention to combining incomplete plant proteins to ensure sufficient amino acid intake, whereas omnivore prep typically provides complete proteins through animal-based foods.
Essential Pantry Staples: Vegan vs. Omnivore Approaches
Essential pantry staples for vegan meal prep emphasize legumes, grains, nuts, seeds, and plant-based protein sources like tofu and tempeh, ensuring nutrient diversity and protein adequacy. Omnivore prepping centers on a mix of animal proteins such as chicken, beef, and fish, combined with grains, dairy, and fresh produce to balance macronutrients. Both approaches rely on herbs, spices, and shelf-stable vegetables like canned tomatoes and frozen greens to maintain flavor and nutritional value throughout the week.
Protein Sources for Vegan and Omnivore Meal Preps
Vegan meal prepping relies heavily on plant-based protein sources such as lentils, chickpeas, tofu, tempeh, and quinoa, which provide essential amino acids and are rich in fiber and antioxidants. Omnivore meal prepping emphasizes animal-based proteins like chicken, beef, eggs, and fish, offering complete proteins with high bioavailability of essential nutrients like vitamin B12 and iron. Balancing macronutrients in both vegan and omnivore meal preps ensures optimal muscle maintenance and overall health benefits.
Cost Comparison: Vegan vs. Omnivore Meal Planning
Vegan meal prepping generally proves more cost-effective due to the lower prices of staple ingredients like legumes, grains, and seasonal vegetables compared to meat and dairy products. Omnivore meal planning often incurs higher expenses driven by the need for diverse protein sources such as beef, poultry, and seafood, which tend to be pricier and less shelf-stable. Bulk purchasing of plant-based items combined with reduced refrigeration costs further enhances the affordability of vegan diets in meal prepping scenarios.
Time Efficiency: Which Prep Style Saves More Time?
Vegan meal prep typically saves more time due to fewer cooking steps and easy-to-prepare ingredients such as legumes, grains, and vegetables that require minimal cooking. Omnivore prep often demands separate cooking for various proteins like meat, poultry, or fish, increasing overall kitchen time. Time efficiency in meal prepping favors vegan approaches by streamlining chopping, cooking, and cleaning processes.
Nutritional Considerations in Vegan and Omnivore Meal Prepping
Vegan meal prepping requires careful planning to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, omega-3 fatty acids, and complete proteins, often sourced from legumes, nuts, seeds, and fortified foods. Omnivore meal prepping naturally incorporates complete proteins and readily bioavailable nutrients such as heme iron and vitamin D from animal products, simplifying nutritional balance. Both approaches benefit from incorporating a variety of whole foods, but vegans must pay particular attention to supplementation or fortified foods to prevent deficiencies.
Equipment and Storage Needs for Each Meal Prep Style
Vegan meal prepping often requires equipment such as blenders, food processors, and steaming baskets to handle plant-based ingredients like legumes, vegetables, and grains, while omnivore prep relies more on grills, roasting pans, and meat thermometers for handling proteins like chicken, beef, and fish. Storage needs for vegan prep typically involve airtight containers for cooked beans, tofu, and chopped vegetables to maintain freshness and prevent spoilage, whereas omnivore meal prep emphasizes refrigeration and vacuum sealing to safely store cooked meats and prevent bacterial growth. Both styles benefit from stackable, BPA-free containers to optimize fridge space and maintain meal organization throughout the week.
Popular Recipes: Vegan Versus Omnivore Meal Prep Dishes
Vegan meal prep recipes often highlight nutrient-dense ingredients such as chickpeas, quinoa, and tofu, emphasizing plant-based proteins and fiber-rich vegetables. Omnivore meal prep dishes typically incorporate a variety of animal proteins like chicken, beef, and fish paired with complex carbohydrates such as brown rice or sweet potatoes. Popular vegan meals include Buddha bowls and lentil salads, while omnivore preps commonly feature grilled chicken with roasted veggies or steak with mashed potatoes.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Vegan vs. Omnivore Prep
Vegan meal prepping significantly reduces carbon emissions and water usage compared to omnivore prep, as plant-based ingredients require fewer natural resources and generate less greenhouse gas. Incorporating legumes, grains, and fresh vegetables supports biodiversity and decreases deforestation linked to livestock farming. Emphasizing sustainable sourcing and seasonal produce further enhances the environmental benefits of vegan meal prep over omnivore options.
Business Opportunities in Vegan and Omnivore Meal Prep Markets
The vegan meal prep market is experiencing rapid growth driven by increasing consumer demand for plant-based, health-conscious options, creating lucrative opportunities for entrepreneurs to offer specialized, nutrient-dense vegan meal kits. In contrast, the omnivore meal prep market maintains a larger customer base with diverse protein preferences, encouraging businesses to innovate around convenience, flavor variety, and dietary customization. Both markets present significant revenue potential through subscription models, e-commerce platforms, and partnerships with fitness and wellness brands aiming to capitalize on evolving dietary trends.
Vegan Prep vs Omnivore Prep Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com