Clinical nutrition for pets emphasizes managing health conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and gastrointestinal disorders through tailored diets and therapeutic feeding plans. Sports nutrition focuses on optimizing athletic performance, energy levels, and recovery in active or working animals by providing appropriate nutrient balances and supplements. Both approaches require personalized assessment to ensure the pet's specific health and activity needs are met effectively.
Table of Comparison
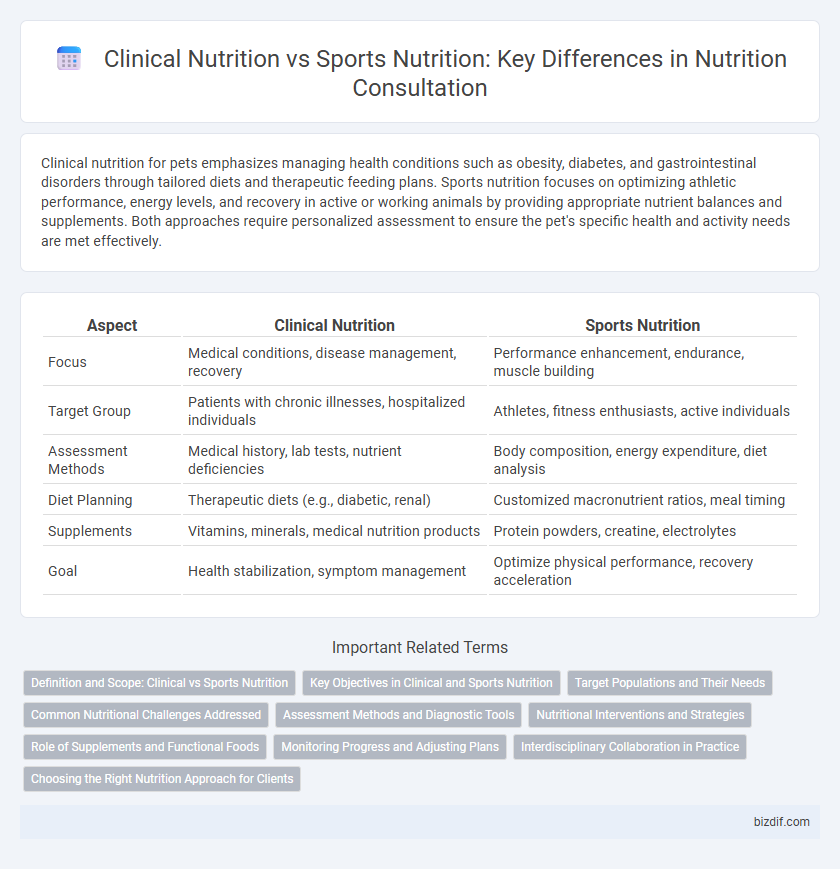
| Aspect | Clinical Nutrition | Sports Nutrition |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Medical conditions, disease management, recovery | Performance enhancement, endurance, muscle building |
| Target Group | Patients with chronic illnesses, hospitalized individuals | Athletes, fitness enthusiasts, active individuals |
| Assessment Methods | Medical history, lab tests, nutrient deficiencies | Body composition, energy expenditure, diet analysis |
| Diet Planning | Therapeutic diets (e.g., diabetic, renal) | Customized macronutrient ratios, meal timing |
| Supplements | Vitamins, minerals, medical nutrition products | Protein powders, creatine, electrolytes |
| Goal | Health stabilization, symptom management | Optimize physical performance, recovery acceleration |
Definition and Scope: Clinical vs Sports Nutrition
Clinical nutrition focuses on managing diseases and medical conditions through tailored dietary interventions to improve patient health outcomes, often involving hospital or clinical settings. Sports nutrition emphasizes optimizing athletic performance and recovery by designing specific nutrient plans that meet the energy demands and enhance physical capabilities of athletes. While clinical nutrition addresses therapeutic needs, sports nutrition concentrates on enhancing physical performance and endurance.
Key Objectives in Clinical and Sports Nutrition
Clinical nutrition primarily aims to manage chronic diseases, support recovery, and optimize overall health through tailored dietary interventions and medical nutrition therapy. Sports nutrition focuses on enhancing athletic performance, promoting muscle recovery, and optimizing energy metabolism through nutrient timing, macronutrient balance, and hydration strategies. Both fields prioritize individualized plans but differ in objectives: clinical nutrition targets healing and disease prevention, while sports nutrition centers on performance optimization and physical endurance.
Target Populations and Their Needs
Clinical nutrition primarily addresses the dietary needs of patients managing medical conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and gastrointestinal disorders, emphasizing nutrient therapy to support recovery and prevent complications. Sports nutrition targets athletes and physically active individuals, focusing on optimizing performance, endurance, and muscle recovery through tailored macronutrient ratios, hydration strategies, and timing of nutrient intake. Understanding the distinct metabolic demands and health goals of these populations ensures personalized nutrition plans that enhance both clinical outcomes and athletic achievements.
Common Nutritional Challenges Addressed
Clinical nutrition primarily addresses challenges such as malnutrition, nutrient deficiencies, chronic disease management, and specialized dietary needs for conditions like diabetes or gastrointestinal disorders. Sports nutrition focuses on optimizing performance through managing energy balance, hydration, muscle recovery, and nutrient timing to enhance athletic output. Both fields emphasize personalized nutrient strategies to improve health outcomes and functional capacity.
Assessment Methods and Diagnostic Tools
Clinical nutrition relies on comprehensive assessment methods such as biochemical tests, anthropometric measurements, and medical history reviews to diagnose nutritional deficiencies and disease-related malnutrition. Sports nutrition uses performance-related diagnostic tools including metabolic testing, body composition analysis, and exercise stress tests to optimize energy intake and enhance athletic performance. Both fields integrate laboratory data and individualized assessments to tailor nutrition interventions effectively.
Nutritional Interventions and Strategies
Clinical nutrition emphasizes tailored nutritional interventions to manage chronic diseases, improve patient outcomes, and support recovery through evidence-based dietary modifications. Sports nutrition focuses on optimizing athletic performance and recovery by implementing strategies such as nutrient timing, macronutrient balancing, and hydration tailored to the specific demands of training and competition. Both fields utilize personalized assessment and monitoring to adjust interventions based on individual metabolic needs and health status.
Role of Supplements and Functional Foods
Clinical nutrition emphasizes the use of supplements and functional foods to manage medical conditions, supporting recovery, immune function, and metabolic balance. Sports nutrition focuses on optimizing performance and recovery through targeted supplementation, including protein powders, electrolytes, and energy boosters tailored to athletic demands. Both disciplines utilize functional foods rich in bioactive compounds, but clinical nutrition prioritizes therapeutic effects, whereas sports nutrition aims for enhanced physical output and endurance.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Plans
Clinical nutrition emphasizes ongoing monitoring of patients' biochemical markers and medical conditions to tailor dietary interventions effectively, ensuring optimal management of chronic diseases. Sports nutrition prioritizes tracking athletic performance metrics, recovery rates, and body composition to adjust macronutrient ratios and hydration strategies, enhancing physical output and endurance. Both fields employ personalized assessments and dynamic plan modifications based on progress data to maximize health outcomes and performance.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration in Practice
Clinical nutrition emphasizes managing chronic diseases and medical conditions through tailored dietary interventions, while sports nutrition focuses on optimizing athletic performance and recovery. Interdisciplinary collaboration combines expertise from dietitians, physicians, physical therapists, and coaches to create comprehensive nutrition plans that address both health and performance goals. This integrative approach enhances patient outcomes by aligning clinical treatment with sports-specific nutritional strategies.
Choosing the Right Nutrition Approach for Clients
Clinical nutrition targets medical conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and gastrointestinal disorders, emphasizing therapeutic dietary interventions tailored to individual health needs. Sports nutrition focuses on optimizing athletic performance through customized meal plans, hydration strategies, and supplementation based on training intensity and sport-specific demands. Selecting the right nutrition approach requires assessing client goals, medical history, and activity level to ensure effective, personalized dietary guidance.
Clinical nutrition vs Sports nutrition Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com