A nutrition consultation for pets targeting gut health emphasizes balanced fiber intake and probiotics to support digestion and nutrient absorption, reducing inflammation and promoting a healthy microbiome. In contrast, a metabolic health-focused plan prioritizes regulating blood sugar levels, optimizing fat metabolism, and preventing obesity through tailored macronutrient distribution and portion control. Both approaches aim to improve overall well-being but address distinct physiological processes critical to a pet's long-term health.
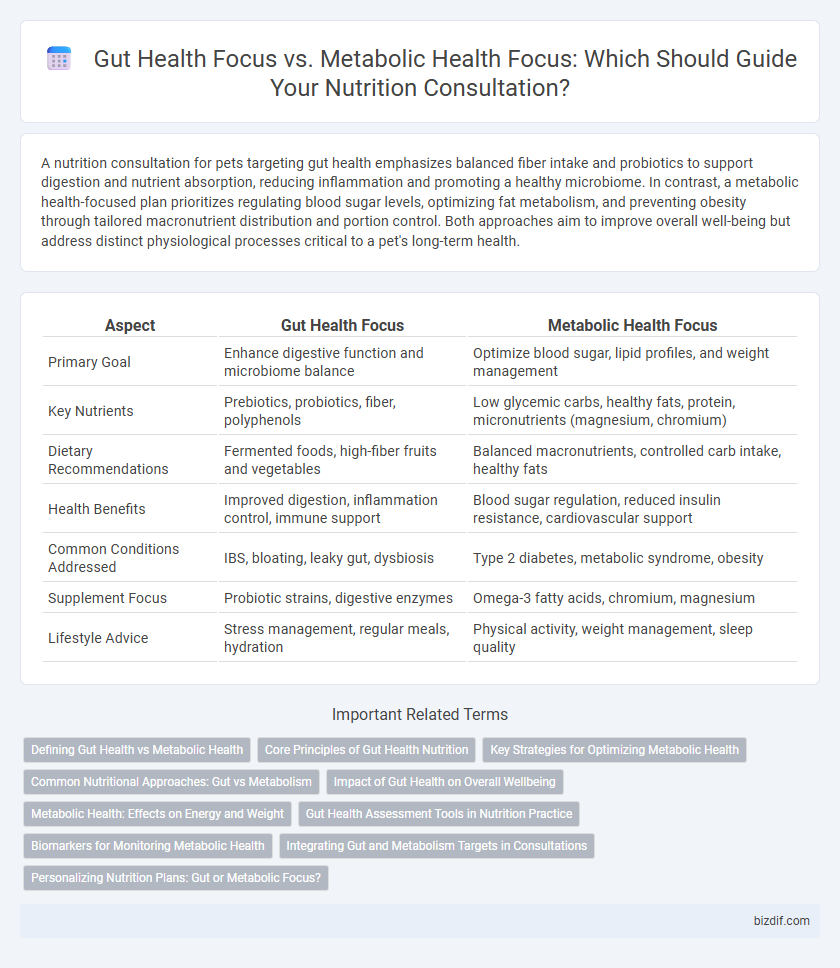
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Gut Health Focus | Metabolic Health Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Enhance digestive function and microbiome balance | Optimize blood sugar, lipid profiles, and weight management |
| Key Nutrients | Prebiotics, probiotics, fiber, polyphenols | Low glycemic carbs, healthy fats, protein, micronutrients (magnesium, chromium) |
| Dietary Recommendations | Fermented foods, high-fiber fruits and vegetables | Balanced macronutrients, controlled carb intake, healthy fats |
| Health Benefits | Improved digestion, inflammation control, immune support | Blood sugar regulation, reduced insulin resistance, cardiovascular support |
| Common Conditions Addressed | IBS, bloating, leaky gut, dysbiosis | Type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, obesity |
| Supplement Focus | Probiotic strains, digestive enzymes | Omega-3 fatty acids, chromium, magnesium |
| Lifestyle Advice | Stress management, regular meals, hydration | Physical activity, weight management, sleep quality |
Defining Gut Health vs Metabolic Health
Gut health centers on the balance and function of the gastrointestinal tract, including the microbiome's diversity and integrity of the gut lining, which influences digestion, immune response, and inflammation. Metabolic health refers to the body's ability to maintain optimal levels of blood sugar, lipids, blood pressure, and insulin sensitivity, critical for preventing conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Both gut health and metabolic health are interconnected, with gut microbiota playing a significant role in metabolic regulation and overall systemic health.
Core Principles of Gut Health Nutrition
Gut health nutrition centers on optimizing the gut microbiome through high-fiber, prebiotic, and probiotic-rich foods to enhance digestion and immune function. Emphasizing hydration, balanced nutrient absorption, and minimizing processed sugars supports intestinal barrier integrity and reduces inflammation. Core principles include personalized dietary adjustments, promoting microbial diversity, and consistent meal timing to maintain gut homeostasis.
Key Strategies for Optimizing Metabolic Health
Optimizing metabolic health centers on strategies such as improving insulin sensitivity through balanced macronutrient intake, increasing physical activity to enhance mitochondrial function, and incorporating nutrient-dense foods rich in antioxidants and fiber. Emphasizing glycemic control with low-glycemic index carbohydrates supports stable blood sugar levels, while adequate hydration and sleep promote hormonal balance essential for metabolism. Targeted supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, and vitamin D further supports metabolic pathways and reduces inflammation.
Common Nutritional Approaches: Gut vs Metabolism
Common nutritional approaches for gut health prioritize prebiotic fibers, probiotics, and anti-inflammatory foods to enhance microbiome diversity and support digestion. Metabolic health strategies emphasize balanced macronutrient distribution, low glycemic index foods, and controlled caloric intake to regulate blood sugar and improve insulin sensitivity. Both approaches integrate nutrient-dense options but target specific biomarkers related to gut microbiota composition or metabolic function.
Impact of Gut Health on Overall Wellbeing
Gut health plays a crucial role in overall wellbeing by influencing digestion, immune function, and mental health through the gut-brain axis. A balanced gut microbiome improves nutrient absorption and reduces inflammation, which supports metabolic processes and energy regulation. Prioritizing gut health in nutrition consultation enhances metabolic health outcomes by promoting better blood sugar control and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Metabolic Health: Effects on Energy and Weight
Metabolic health directly influences energy levels and weight management by optimizing how the body processes glucose and fats, reducing insulin resistance, and enhancing mitochondrial function. Improved metabolic health supports stable blood sugar levels, increases basal metabolic rate, and promotes efficient fat oxidation, which collectively contribute to sustained energy and effective weight control. Targeting metabolic health through personalized nutrition consultation can lead to meaningful improvements in energy balance and body composition.
Gut Health Assessment Tools in Nutrition Practice
Gut health assessment tools in nutrition practice include stool analysis, breath tests, and gut microbiome profiling to evaluate digestive function and microbial balance. These methods provide insights into inflammation, dysbiosis, and gastrointestinal disorders, enabling targeted dietary interventions. Emphasizing gut health supports overall digestion, immune function, and nutrient absorption, distinguishing it from broader metabolic health assessments focused on blood sugar and lipid regulation.
Biomarkers for Monitoring Metabolic Health
Biomarkers such as fasting glucose, HbA1c, and lipid profiles are essential for monitoring metabolic health during nutrition consultations, providing objective data on insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular risk. Gut health focus prioritizes markers like gut microbiota diversity and inflammatory cytokines, whereas metabolic health emphasizes biochemical indicators related to energy metabolism and nutrient utilization. Accurate assessment of these biomarkers enables personalized dietary interventions that target either microbiome balance or metabolic optimization for better overall health outcomes.
Integrating Gut and Metabolism Targets in Consultations
Integrating gut health and metabolic health targets in nutrition consultations enhances personalized treatment by addressing the complex interplay between the gut microbiome and metabolic functions. Strategies that optimize gut flora through prebiotics, probiotics, and fiber intake can improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and support metabolic balance. Tailoring interventions to simultaneously improve gut integrity and metabolic markers leads to more effective outcomes in managing conditions like diabetes, obesity, and digestive disorders.
Personalizing Nutrition Plans: Gut or Metabolic Focus?
Personalizing nutrition plans requires assessing key biomarkers like gut microbiota diversity for gut health focus and insulin sensitivity for metabolic health focus. Tailoring dietary interventions to support gut barrier function or optimize glucose metabolism helps achieve targeted health outcomes. Integrating individual lifestyle factors and genetic predispositions enhances the precision of gut versus metabolic-focused nutrition strategies.
Gut health focus vs Metabolic health focus Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com