A dietitian is a professionally certified expert with accredited education and clinical training, qualified to provide medical nutrition therapy and create personalized diet plans for pets with specific health conditions. A nutritionist may have varying levels of education and certification, focusing mainly on general dietary advice and wellness rather than clinical treatment. Choosing a board-certified veterinary dietitian ensures precise nutritional management tailored to your pet's health needs.
Table of Comparison
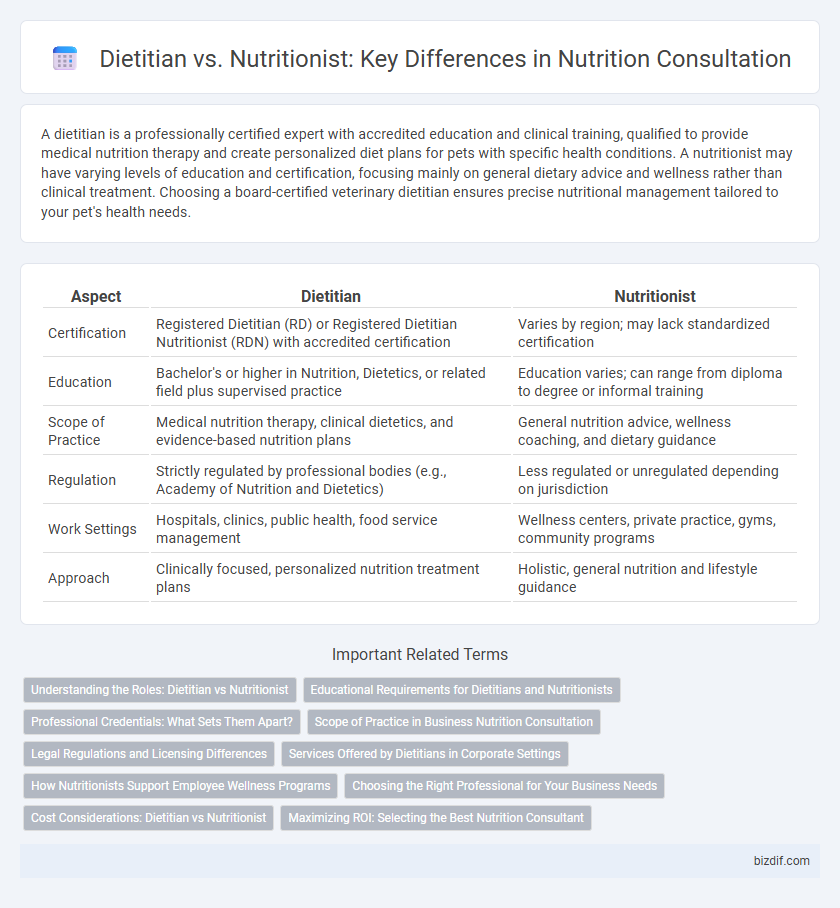
| Aspect | Dietitian | Nutritionist |
|---|---|---|
| Certification | Registered Dietitian (RD) or Registered Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN) with accredited certification | Varies by region; may lack standardized certification |
| Education | Bachelor's or higher in Nutrition, Dietetics, or related field plus supervised practice | Education varies; can range from diploma to degree or informal training |
| Scope of Practice | Medical nutrition therapy, clinical dietetics, and evidence-based nutrition plans | General nutrition advice, wellness coaching, and dietary guidance |
| Regulation | Strictly regulated by professional bodies (e.g., Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics) | Less regulated or unregulated depending on jurisdiction |
| Work Settings | Hospitals, clinics, public health, food service management | Wellness centers, private practice, gyms, community programs |
| Approach | Clinically focused, personalized nutrition treatment plans | Holistic, general nutrition and lifestyle guidance |
Understanding the Roles: Dietitian vs Nutritionist
Dietitians are licensed healthcare professionals with accredited degrees and clinical training who provide evidence-based medical nutrition therapy for managing chronic diseases and health conditions. Nutritionists often have diverse educational backgrounds and may offer general dietary advice, wellness coaching, or community nutrition programs without mandatory licensure requirements. Understanding these distinctions ensures individuals seeking nutrition consultation receive appropriate and qualified support tailored to their health needs.
Educational Requirements for Dietitians and Nutritionists
Dietitians typically must earn a bachelor's degree in dietetics, nutrition, or a related field, complete supervised practice through an accredited program, and pass a national examination to obtain licensure or certification. Nutritionists generally have more varied educational backgrounds, often holding degrees in nutrition or health sciences, with fewer standardized requirements, though some states regulate their practice strictly. Understanding these distinctions in educational pathways helps clarify the professional qualifications and expertise each brings to nutrition consultation.
Professional Credentials: What Sets Them Apart?
Dietitians possess nationally accredited certifications such as the Registered Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN) credential, which requires rigorous education, supervised practice, and passing a national exam. Nutritionists may lack standardized credentials and vary widely in qualifications, with some holding certifications from recognized bodies like the Certified Nutrition Specialist (CNS). The distinction lies in dietitians' regulated licensure and evidence-based training, ensuring consistent professional standards in nutrition consultation.
Scope of Practice in Business Nutrition Consultation
Dietitians possess regulated qualifications and clinical expertise to conduct detailed nutritional assessments and develop personalized diet plans, making them essential in medical and therapeutic nutrition consultation. Nutritionists often have broader, less regulated scopes, focusing on general wellness, food education, and lifestyle-based advice within business nutrition consultation. The scope of practice for dietitians generally includes evidence-based interventions and collaboration with healthcare teams, whereas nutritionists emphasize preventive care and holistic dietary guidance.
Legal Regulations and Licensing Differences
Dietitians are licensed healthcare professionals regulated by state or national boards, requiring formal education, supervised practice, and passing a credentialing exam, ensuring standardized legal protections and accountability. Nutritionists often lack standardized licensing or legal recognition, leading to significant variability in qualifications and scope of practice across jurisdictions. Understanding these legal and regulatory distinctions is crucial for clients seeking qualified nutrition guidance and for compliance within healthcare frameworks.
Services Offered by Dietitians in Corporate Settings
Dietitians in corporate settings provide tailored nutrition services including wellness program development, individualized dietary assessments, and evidence-based meal planning to enhance employee health and productivity. Their expertise encompasses managing chronic conditions, conducting nutritional seminars, and designing workplace nutrition policies aligned with organizational goals. This targeted approach supports improved workforce well-being and reduces healthcare costs through scientifically grounded interventions.
How Nutritionists Support Employee Wellness Programs
Nutritionists play a crucial role in employee wellness programs by designing personalized meal plans that enhance productivity and reduce health risks. Their expertise in dietary assessments helps identify nutritional deficiencies, promoting healthier lifestyle choices among employees. Collaborating with HR teams, nutritionists implement educational workshops that drive sustained wellness improvements in the workplace.
Choosing the Right Professional for Your Business Needs
Choosing the right professional between a dietitian and a nutritionist hinges on the level of expertise and certification required for your business needs. Registered dietitians (RDs) have met specific educational and licensure standards, ensuring evidence-based nutrition advice crucial for clinical or regulated environments. Nutritionists may offer valuable guidance in less formal settings, but hiring an RD ensures compliance and accuracy in nutrition counseling for businesses aiming to maintain high professional standards.
Cost Considerations: Dietitian vs Nutritionist
Dietitian services generally cost more than nutritionist consultations due to their extensive medical training and ability to provide clinical nutrition therapy. Nutritionists often offer more affordable pricing but may lack the credentialing and evidence-based practice that dietitians possess. Consumers should weigh the cost difference against the level of expertise and personalized care required for their nutrition goals.
Maximizing ROI: Selecting the Best Nutrition Consultant
Choosing between a dietitian and a nutritionist significantly impacts maximizing ROI in nutrition consultation. Registered dietitians possess accredited certifications and clinical training that ensure evidence-based, personalized dietary plans delivering measurable health improvements. Nutritionists may offer general guidance but often lack standardized credentials essential for optimizing long-term health outcomes and cost-effectiveness.
Dietitian vs Nutritionist Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com