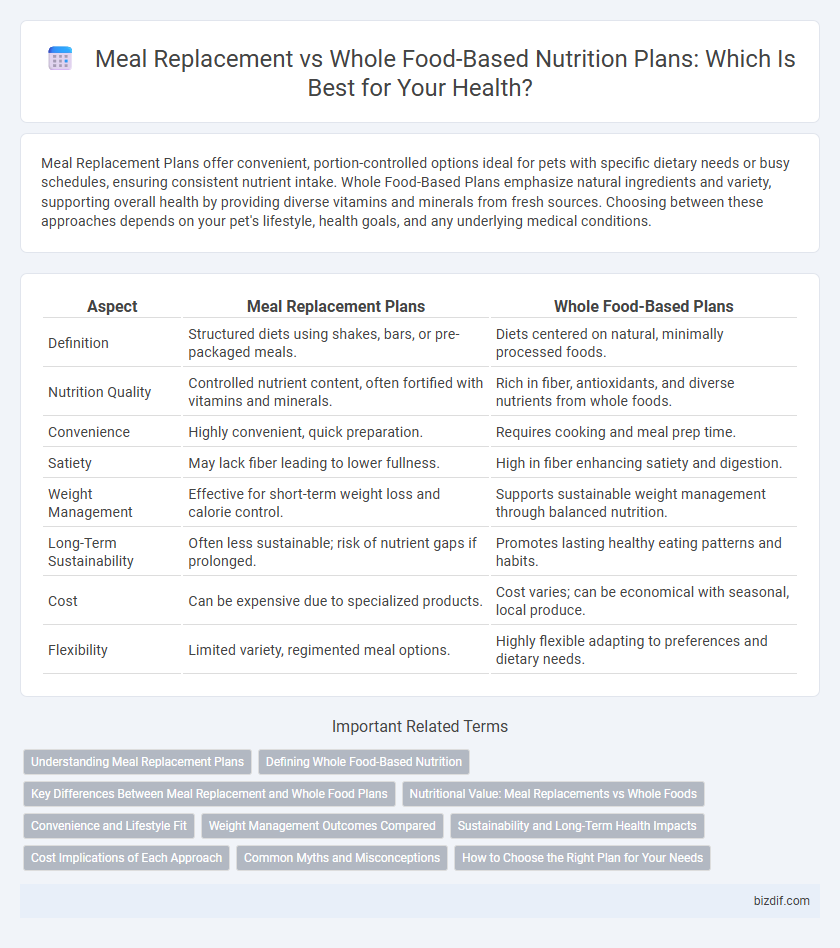
Meal Replacement Plans offer convenient, portion-controlled options ideal for pets with specific dietary needs or busy schedules, ensuring consistent nutrient intake. Whole Food-Based Plans emphasize natural ingredients and variety, supporting overall health by providing diverse vitamins and minerals from fresh sources. Choosing between these approaches depends on your pet's lifestyle, health goals, and any underlying medical conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Meal Replacement Plans | Whole Food-Based Plans |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured diets using shakes, bars, or pre-packaged meals. | Diets centered on natural, minimally processed foods. |
| Nutrition Quality | Controlled nutrient content, often fortified with vitamins and minerals. | Rich in fiber, antioxidants, and diverse nutrients from whole foods. |
| Convenience | Highly convenient, quick preparation. | Requires cooking and meal prep time. |
| Satiety | May lack fiber leading to lower fullness. | High in fiber enhancing satiety and digestion. |
| Weight Management | Effective for short-term weight loss and calorie control. | Supports sustainable weight management through balanced nutrition. |
| Long-Term Sustainability | Often less sustainable; risk of nutrient gaps if prolonged. | Promotes lasting healthy eating patterns and habits. |
| Cost | Can be expensive due to specialized products. | Cost varies; can be economical with seasonal, local produce. |
| Flexibility | Limited variety, regimented meal options. | Highly flexible adapting to preferences and dietary needs. |
Understanding Meal Replacement Plans
Meal replacement plans utilize scientifically formulated shakes, bars, or powders designed to provide controlled calories and essential nutrients in convenient portions. These plans target precise macronutrient ratios and vitamin-mineral balance to support weight management and metabolic health. Understanding the composition and role of meal replacements helps optimize dietary adherence while ensuring nutritional adequacy during caloric restriction or busy lifestyles.
Defining Whole Food-Based Nutrition
Whole food-based nutrition emphasizes consuming minimally processed, nutrient-dense foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and legumes to support optimal health and sustained energy. This approach prioritizes natural vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants found in unrefined foods, promoting better digestion and long-term well-being. Compared to meal replacement plans, whole food-based plans offer a diverse range of macronutrients and phytochemicals essential for metabolic balance and disease prevention.
Key Differences Between Meal Replacement and Whole Food Plans
Meal replacement plans prioritize convenience and precise calorie control by using pre-packaged shakes or bars with standardized nutrient content, making adherence simpler for weight management. Whole food-based plans emphasize nutrient density, variety, and minimally processed ingredients, promoting long-term health through balanced macronutrients and micronutrients. Key differences include the level of food processing, customization potential, digestive benefits, and impact on eating habits and satiety.
Nutritional Value: Meal Replacements vs Whole Foods
Meal replacement plans provide controlled portions with precise macronutrient ratios, often fortified with vitamins and minerals to ensure nutritional adequacy. Whole food-based plans offer diverse phytonutrients, fiber, and antioxidants naturally found in fruits, vegetables, grains, and proteins, supporting long-term health and digestion. Nutritional value in whole foods is more bioavailable and synergistic, promoting better absorption and metabolic synergy compared to isolated nutrients in meal replacements.
Convenience and Lifestyle Fit
Meal replacement plans offer unmatched convenience for busy lifestyles by providing pre-portioned, nutrient-dense options that save time on meal preparation. Whole food-based plans prioritize natural ingredients and flexibility, accommodating diverse taste preferences and dietary needs while promoting sustainable eating habits. Choosing between these approaches depends on individual lifestyle demands and long-term nutrition goals.
Weight Management Outcomes Compared
Meal replacement plans offer controlled calorie intake and portion sizes, which can lead to rapid initial weight loss but may lack essential nutrients found in whole food-based plans. Whole food-based plans promote sustainable weight management by emphasizing nutrient-dense foods, fiber, and healthy fats that support metabolism and satiety. Studies indicate that while meal replacements can be effective short-term tools, whole food plans yield better long-term adherence and improved metabolic health outcomes.
Sustainability and Long-Term Health Impacts
Meal replacement plans provide convenience and controlled calorie intake but may lack essential nutrients and fiber needed for long-term health sustainability. Whole food-based plans emphasize diverse nutrient density, promoting gut health and metabolic balance, which support sustained weight management and reduced chronic disease risk. Prioritizing whole foods enhances nutrient bioavailability and encourages sustainable eating habits vital for lifelong wellness.
Cost Implications of Each Approach
Meal replacement plans often incur higher ongoing costs due to the need for purchasing specialized products and supplements, which can add up significantly over time. Whole food-based plans typically involve buying fresh ingredients, which may seem cost-efficient but can vary depending on season and location, impacting overall affordability. Evaluating budget constraints alongside nutritional needs is essential when choosing between the higher upfront costs of meal replacements and the variable but potentially lower expenses of whole food-based approaches.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Meal replacement plans are often misunderstood as nutritionally inadequate, yet many are scientifically formulated to provide essential vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients comparable to whole food diets. Whole food-based plans are mistakenly assumed to guarantee better health outcomes, despite potential issues with portion control and nutrient variability. Both approaches require personalized evaluation to ensure optimal nutrition tailored to individual health goals and lifestyle needs.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Needs
Choosing the right plan between meal replacement and whole food-based options depends on individual goals, lifestyle, and nutritional requirements. Meal replacement plans offer convenience and controlled calorie intake, ideal for weight management or busy schedules, while whole food-based plans emphasize nutrient-dense, varied foods for long-term health and sustained energy. Consulting a nutrition expert can help tailor a plan that balances macronutrients, micronutrients, and personal preferences for optimal results.
Meal Replacement Plans vs Whole Food-Based Plans Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com