The Whole30 Diet emphasizes a 30-day elimination of sugar, grains, dairy, and legumes to reset eating habits and identify food sensitivities, while the Paleo Diet promotes lifelong consumption of whole, unprocessed foods resembling those of early humans. Both diets prioritize natural ingredients and lean proteins but differ in duration and reintroduction phases, making the Whole30 more of a short-term reset and Paleo a sustainable lifestyle approach. Understanding these distinctions helps pet owners tailor nutrition strategies for their pets, ensuring optimal health outcomes through diet.
Table of Comparison
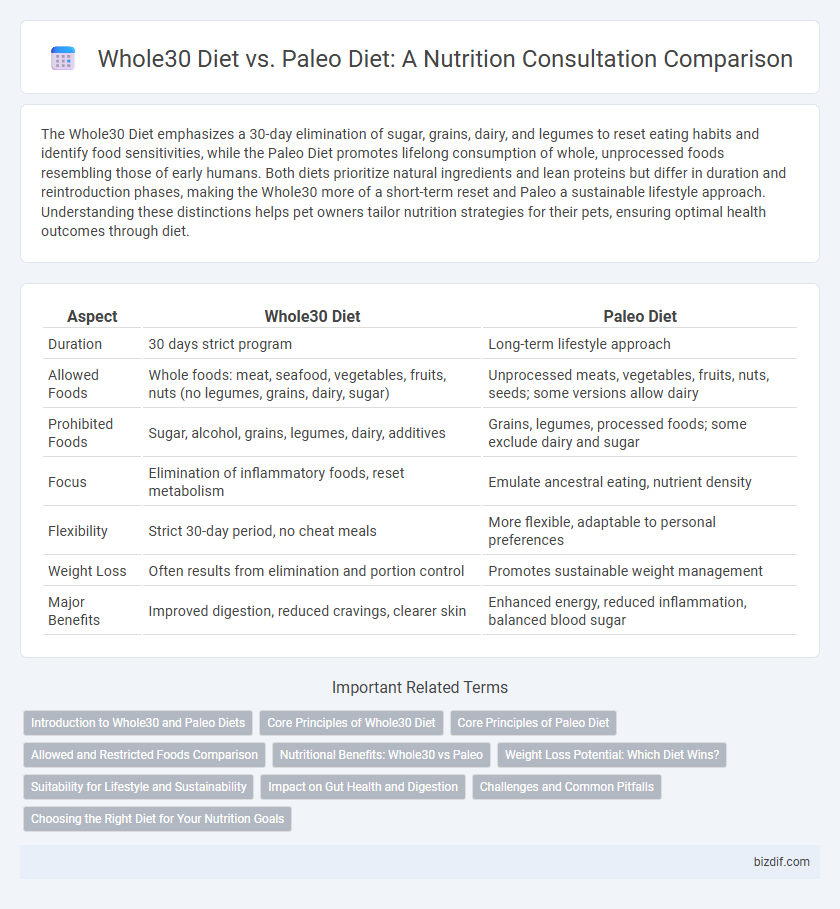
| Aspect | Whole30 Diet | Paleo Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | 30 days strict program | Long-term lifestyle approach |
| Allowed Foods | Whole foods: meat, seafood, vegetables, fruits, nuts (no legumes, grains, dairy, sugar) | Unprocessed meats, vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds; some versions allow dairy |
| Prohibited Foods | Sugar, alcohol, grains, legumes, dairy, additives | Grains, legumes, processed foods; some exclude dairy and sugar |
| Focus | Elimination of inflammatory foods, reset metabolism | Emulate ancestral eating, nutrient density |
| Flexibility | Strict 30-day period, no cheat meals | More flexible, adaptable to personal preferences |
| Weight Loss | Often results from elimination and portion control | Promotes sustainable weight management |
| Major Benefits | Improved digestion, reduced cravings, clearer skin | Enhanced energy, reduced inflammation, balanced blood sugar |
Introduction to Whole30 and Paleo Diets
The Whole30 diet emphasizes a 30-day elimination of sugar, grains, dairy, legumes, and processed foods to reset metabolism and identify food sensitivities. The Paleo diet mimics the eating patterns of Paleolithic ancestors, focusing on whole, unprocessed foods such as lean meats, vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds while excluding grains, legumes, and dairy. Both diets promote nutrient-dense foods but differ in duration and strictness regarding reintroduction of eliminated food groups.
Core Principles of Whole30 Diet
The Whole30 Diet emphasizes a strict 30-day elimination of sugar, alcohol, grains, legumes, dairy, and processed foods to reset metabolism and identify food sensitivities. It promotes whole, unprocessed foods and discourages cheat meals or calorie counting to improve digestion, energy levels, and overall health. Unlike Paleo, Whole30 requires a precise commitment without reintroducing eliminated foods until the program ends.
Core Principles of Paleo Diet
The Paleo Diet emphasizes consuming whole, unprocessed foods similar to those eaten by early humans, prioritizing lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds while excluding grains, legumes, dairy, and refined sugars. Its core principles center on optimizing health by mimicking ancestral dietary patterns to reduce chronic disease risks and improve metabolic function. This diet encourages nutrient-dense foods and natural eating habits that align with human evolutionary adaptations.
Allowed and Restricted Foods Comparison
The Whole30 diet permits lean proteins, vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds while strictly excluding added sugars, grains, legumes, dairy, and alcohol for 30 days to reset eating habits. The Paleo diet emphasizes unprocessed foods like meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds but allows natural sweeteners and occasionally dairy and legumes, making it less restrictive. Both diets avoid processed foods and grains, but Whole30 imposes a temporary, stricter elimination phase compared to Paleo's more flexible, long-term approach.
Nutritional Benefits: Whole30 vs Paleo
The Whole30 diet emphasizes eliminating processed foods, sugar, grains, dairy, and legumes for 30 days, promoting gut health and reducing inflammation through a strict reset approach. The Paleo diet, inspired by ancestral eating patterns, encourages the consumption of lean meats, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds while excluding grains, legumes, and dairy, supporting nutrient density and blood sugar regulation. Both diets are rich in whole, nutrient-dense foods, yet Whole30's strict elimination phase can highlight food sensitivities, whereas Paleo allows more long-term dietary flexibility for sustainable micronutrient intake.
Weight Loss Potential: Which Diet Wins?
The Whole30 diet emphasizes a strict 30-day elimination of processed foods, sugar, grains, and legumes to reset metabolism and reduce inflammation, potentially leading to rapid weight loss. The Paleo diet allows a broader range of foods, including natural fats and starchy vegetables, which supports sustainable, long-term weight management by promoting nutrient density and satiety. For weight loss potential, Whole30 may offer quicker initial results, but the Paleo diet's flexibility enhances adherence and maintenance of healthy body weight over time.
Suitability for Lifestyle and Sustainability
The Whole30 diet emphasizes a strict 30-day elimination of processed foods, sugar, grains, legumes, and dairy, making it a short-term reset ideal for individuals seeking immediate dietary clarity but challenging for long-term sustainability. The Paleo diet, focusing on unprocessed foods like lean meats, vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds, aligns better with a long-term, flexible lifestyle by allowing occasional reintroductions of certain food groups and accommodating gradual habit changes. Both diets demand significant commitment, but Paleo's adaptability generally offers greater suitability for sustainable, long-term nutritional health.
Impact on Gut Health and Digestion
The Whole30 diet emphasizes a 30-day elimination of processed foods, sugars, grains, and legumes, which can reduce gut inflammation and support digestive reset. The Paleo diet promotes long-term consumption of unprocessed meats, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, fostering a diverse microbiome and enhanced nutrient absorption. Both diets improve gut health by eliminating common irritants but differ in duration and emphasis on reintroduction phases critical for assessing individual digestive tolerance.
Challenges and Common Pitfalls
Whole30 and Paleo diets both emphasize whole foods but present unique challenges; Whole30's strict 30-day elimination can lead to social isolation and difficulty maintaining long-term results, while Paleo's less rigid guidelines may cause confusion around processed food limits. Common pitfalls include inadequate nutrient intake due to overly restrictive food choices and challenges in meal planning, which can result in reliance on convenience foods that undermine dietary goals. Understanding the nuances of each diet's restrictions and focusing on balanced nutrition is essential for sustainable success.
Choosing the Right Diet for Your Nutrition Goals
The Whole30 diet emphasizes a strict 30-day elimination of processed foods, dairy, grains, and legumes to reset eating habits and identify food sensitivities, while the Paleo diet allows for a more flexible, long-term approach focusing on lean meats, vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds based on prehistoric eating patterns. Choosing the right diet depends on your nutrition goals: Whole30 is ideal for short-term detoxification and behavioral changes, whereas Paleo supports sustained weight management and metabolic health. Assessing personal food tolerances, lifestyle, and long-term commitment helps tailor the diet to optimize nutrient intake and achieve specific health outcomes.
Whole30 Diet vs Paleo Diet Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com