Menu labeling compliance requires pet food manufacturers to provide standardized nutritional information on packaging to meet regulatory standards, ensuring transparency for consumers. Voluntary nutrition disclosure allows companies to share additional, detailed nutrient data beyond legal requirements, enhancing pet owners' ability to make informed dietary choices. Balancing mandatory compliance with voluntary transparency supports optimal pet health through better understanding of food content.
Table of Comparison
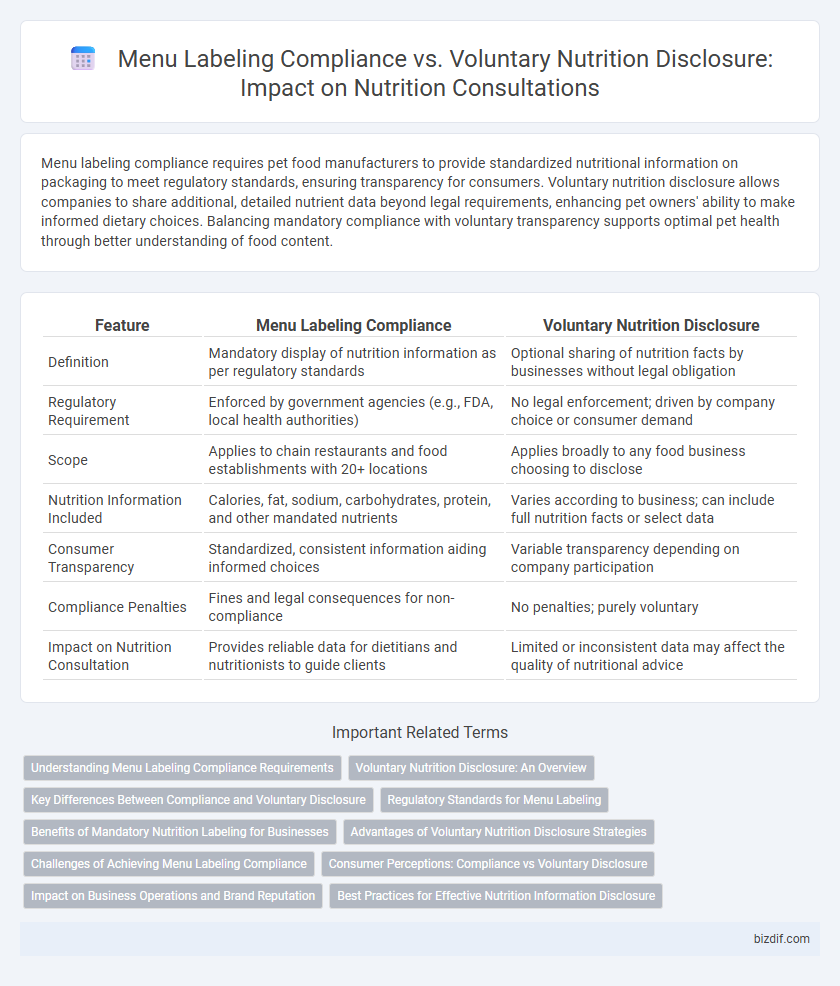
| Feature | Menu Labeling Compliance | Voluntary Nutrition Disclosure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mandatory display of nutrition information as per regulatory standards | Optional sharing of nutrition facts by businesses without legal obligation |
| Regulatory Requirement | Enforced by government agencies (e.g., FDA, local health authorities) | No legal enforcement; driven by company choice or consumer demand |
| Scope | Applies to chain restaurants and food establishments with 20+ locations | Applies broadly to any food business choosing to disclose |
| Nutrition Information Included | Calories, fat, sodium, carbohydrates, protein, and other mandated nutrients | Varies according to business; can include full nutrition facts or select data |
| Consumer Transparency | Standardized, consistent information aiding informed choices | Variable transparency depending on company participation |
| Compliance Penalties | Fines and legal consequences for non-compliance | No penalties; purely voluntary |
| Impact on Nutrition Consultation | Provides reliable data for dietitians and nutritionists to guide clients | Limited or inconsistent data may affect the quality of nutritional advice |
Understanding Menu Labeling Compliance Requirements
Menu labeling compliance requires food service establishments to display calorie information for standard menu items, adhering to federal regulations under the Affordable Care Act to ensure transparency and promote healthier consumer choices. Compliance involves providing accurate nutritional data, including calorie counts and serving sizes, on menus and menu boards, with penalties for non-adherence. Understanding these requirements is essential for restaurants to meet legal obligations and support informed decision-making among customers.
Voluntary Nutrition Disclosure: An Overview
Voluntary nutrition disclosure allows food service operators to provide detailed nutritional information beyond mandatory menu labeling requirements, enhancing transparency and consumer trust. This practice supports informed decision-making by offering data on calories, macronutrients, allergens, and other dietary considerations tailored to the specific menu items. Embracing voluntary disclosure can improve brand reputation and align with growing consumer demand for health-conscious dining options.
Key Differences Between Compliance and Voluntary Disclosure
Menu labeling compliance mandates the display of calorie counts and nutrition information on menus and menu boards for regulated food establishments under the FDA rules, ensuring standardized consumer access to essential nutritional data. Voluntary nutrition disclosure allows food businesses to provide detailed nutrient content beyond regulatory requirements, such as sodium, sugars, and fat, catering to health-conscious consumers who seek more comprehensive dietary information. The key difference lies in the legal obligation for compliance versus the flexibility and marketing advantage of voluntary disclosure, influencing transparency and consumer trust in nutrition consultation services.
Regulatory Standards for Menu Labeling
Regulatory standards for menu labeling mandate that chain restaurants with 20 or more locations provide calorie information on menus and menu boards, ensuring transparency and promoting informed consumer choices. These regulations, enforced by the FDA under the Nutrition Labeling and Education Act (NLEA), require accurate nutrient data for standard menu items, including calorie counts and nutrient content disclosures. Voluntary nutrition disclosure allows smaller establishments to offer nutritional information without legal obligation, but compliance with mandatory labeling ensures consistent public health benefits and supports nationwide efforts to address obesity and diet-related diseases.
Benefits of Mandatory Nutrition Labeling for Businesses
Mandatory nutrition labeling drives transparency and builds consumer trust by providing clear, consistent information on calorie counts and nutrient content. It supports businesses in meeting regulatory requirements, reducing legal risks, and avoiding penalties associated with non-compliance. Enhanced menu labeling can boost competitive advantage by catering to health-conscious customers and fostering informed purchasing decisions.
Advantages of Voluntary Nutrition Disclosure Strategies
Voluntary nutrition disclosure strategies offer flexibility for businesses to highlight key nutritional benefits tailored to their target audience, enhancing consumer trust and brand transparency. These strategies enable customized menu labeling that can emphasize unique health attributes, supporting informed dietary choices without the constraints of regulatory mandates. By proactively sharing nutrition information, businesses can differentiate themselves in the competitive food service market and encourage healthier consumer behaviors.
Challenges of Achieving Menu Labeling Compliance
Achieving menu labeling compliance poses significant challenges including ensuring accurate calorie counts and meeting complex regulatory requirements set forth by the FDA. Businesses often face difficulties integrating consistent nutrition information across diverse menus while managing frequent recipe updates and ingredient variations. Balancing transparency with operational feasibility requires substantial training and investment in reliable nutritional analysis tools.
Consumer Perceptions: Compliance vs Voluntary Disclosure
Consumer perceptions of menu labeling compliance typically emphasize trust and reliability, as mandatory disclosures ensure consistent nutritional information across establishments. In contrast, voluntary nutrition disclosure often fosters a perception of transparency and brand responsibility, appealing to health-conscious consumers seeking detailed insights. Studies indicate that consumers are more likely to favor establishments with compliance-based labels for accuracy, while voluntary disclosures can enhance customer engagement and satisfaction when implemented effectively.
Impact on Business Operations and Brand Reputation
Menu labeling compliance mandates transparent display of nutritional information, enhancing consumer trust while ensuring adherence to legal standards. Voluntary nutrition disclosure allows businesses to proactively showcase health-conscious options, positioning the brand as responsible and customer-focused. Both practices influence operational workflows, requiring accurate data management and staff training, ultimately impacting brand reputation and competitive advantage.
Best Practices for Effective Nutrition Information Disclosure
Menu labeling compliance ensures mandatory nutrition information aligns with regulatory standards like FDA requirements, promoting transparency and consumer trust. Voluntary nutrition disclosure allows businesses to provide detailed nutritional insights beyond compliance, enhancing customer engagement and catering to health-conscious audiences. Best practices include standardizing nutrient data presentation, using clear and concise language, and regularly updating information to reflect menu changes.
Menu Labeling Compliance vs Voluntary Nutrition Disclosure Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com