The first pass of proofreading focuses on identifying and correcting obvious errors such as spelling mistakes, grammar issues, and punctuation. The second pass delves deeper into sentence structure, coherence, and consistency to ensure the text flows smoothly and maintains a professional tone. Combining both passes enhances the overall quality and clarity of the document.
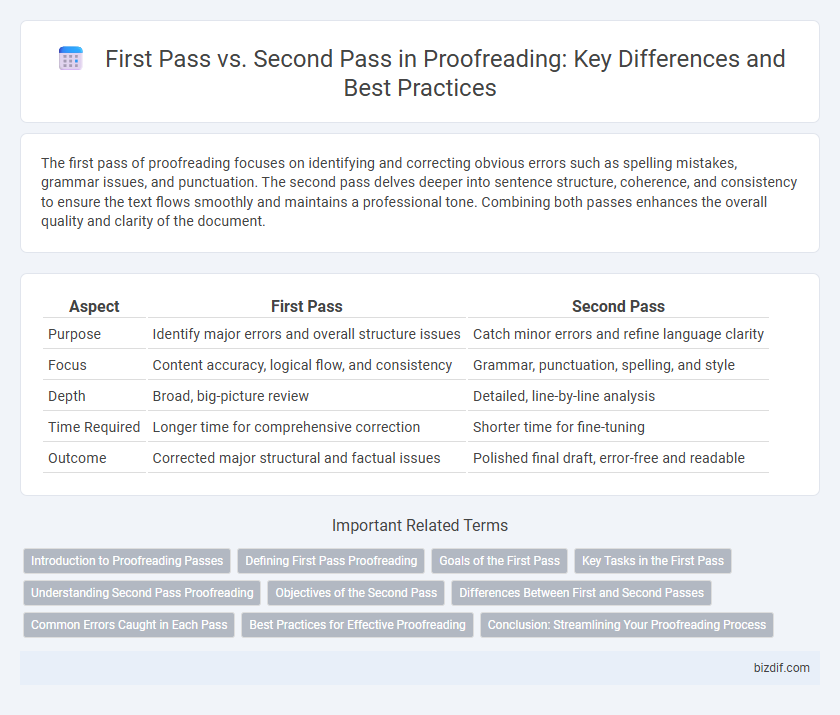
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | First Pass | Second Pass |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify major errors and overall structure issues | Catch minor errors and refine language clarity |
| Focus | Content accuracy, logical flow, and consistency | Grammar, punctuation, spelling, and style |
| Depth | Broad, big-picture review | Detailed, line-by-line analysis |
| Time Required | Longer time for comprehensive correction | Shorter time for fine-tuning |
| Outcome | Corrected major structural and factual issues | Polished final draft, error-free and readable |
Introduction to Proofreading Passes
Proofreading involves multiple passes to ensure accuracy and clarity, with the first pass focusing on identifying obvious errors such as spelling, punctuation, and grammar mistakes. The second pass goes deeper by reviewing sentence structure, word choice, and overall flow to enhance readability and coherence. Each pass targets different error types, making the proofreading process more thorough and effective.
Defining First Pass Proofreading
First pass proofreading involves an initial comprehensive review aimed at identifying and correcting obvious errors such as spelling mistakes, grammatical issues, and punctuation inconsistencies. This stage focuses on ensuring the text's basic accuracy and coherence before deeper, more detailed editing. Mastering first pass proofreading significantly enhances the overall quality and readability of written content.
Goals of the First Pass
The first pass in proofreading aims to identify and correct major errors in grammar, punctuation, and spelling to ensure overall text clarity. This initial review focuses on structural consistency and eliminating obvious mistakes that disrupt the flow and comprehension. Establishing a strong foundation during the first pass streamlines the subsequent second pass, which targets finer stylistic and contextual refinements.
Key Tasks in the First Pass
The first pass in proofreading focuses on identifying and correcting major errors such as spelling mistakes, grammatical issues, and punctuation inconsistencies. This stage ensures that the foundational aspects of the text meet clarity and correctness standards before moving on to finer stylistic or formatting adjustments. Concentrating on key tasks like verifying sentence structure and word choice sets the groundwork for a smoother second pass focused on detailed refinement.
Understanding Second Pass Proofreading
Second pass proofreading involves a detailed review focusing on correcting overlooked spelling errors, punctuation, and grammar mistakes missed during the first pass. It emphasizes consistency in style, formatting, and adherence to the style guide, enhancing the overall quality of the document. This thorough examination reduces the risk of residual errors and improves the readability and professionalism of the final text.
Objectives of the Second Pass
The second pass in proofreading aims to identify and correct more subtle errors missed during the first pass, such as inconsistencies in tone, style, and complex grammatical issues. It ensures the overall coherence and accuracy of the text by focusing on sentence flow, punctuation precision, and formatting alignment. This stage enhances the document's professionalism and readability prior to final approval or publication.
Differences Between First and Second Passes
The first pass in proofreading primarily focuses on catching glaring errors such as spelling mistakes, punctuation issues, and basic grammatical problems. The second pass involves a deeper review, concentrating on sentence structure, consistency, style, and clarity to ensure overall coherence and polish. Together, these two passes create a comprehensive approach that enhances both mechanical accuracy and textual refinement.
Common Errors Caught in Each Pass
First pass proofreading typically catches spelling mistakes, incorrect punctuation, and typographical errors, ensuring basic text accuracy. Second pass proofreading focuses on grammatical inconsistencies, sentence structure, and context flow, enhancing overall readability and coherence. Combining both passes significantly reduces errors and improves the quality of the final document.
Best Practices for Effective Proofreading
First pass proofreading targets glaring errors such as spelling mistakes, punctuation issues, and formatting inconsistencies to ensure a clean foundation. The second pass involves a detailed review for subtle grammatical errors, tone, clarity, and flow to enhance overall readability. Employing separate passes improves error detection rates and maintains objectivity throughout the proofreading process.
Conclusion: Streamlining Your Proofreading Process
Streamlining your proofreading process involves differentiating between the first pass and second pass stages to enhance efficiency and accuracy. The first pass focuses on catching major errors like typos and structural issues, while the second pass targets finer details such as grammar, punctuation, and consistency. Implementing this two-tiered approach reduces oversight and improves the overall quality of the final document.
First pass vs Second pass Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com