Legal proofreading demands specialized knowledge to ensure accuracy in terminology, compliance with legal standards, and the avoidance of costly misinterpretations, unlike general proofreading which focuses on grammar, spelling, and basic clarity. It requires a keen eye for detail to verify citations, contract terms, and legal references, maintaining the document's integrity and enforceability. Precision in legal proofreading safeguards against errors that could lead to disputes or litigation, making it indispensable for legal professionals.
Table of Comparison
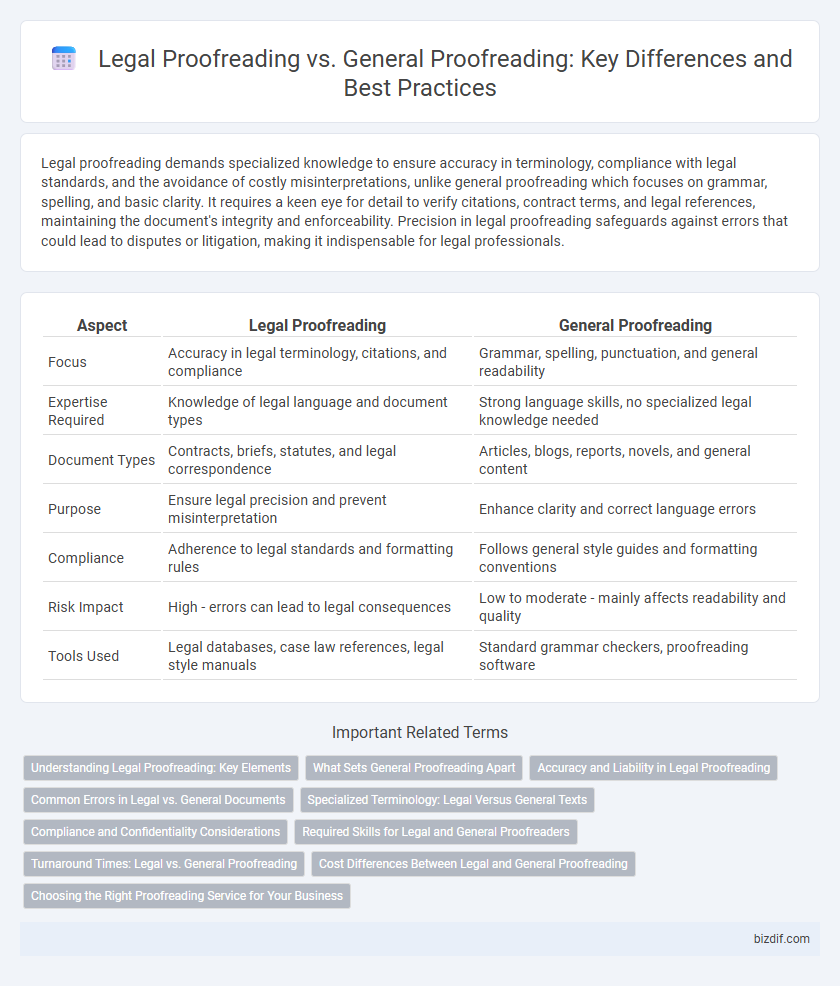
| Aspect | Legal Proofreading | General Proofreading |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Accuracy in legal terminology, citations, and compliance | Grammar, spelling, punctuation, and general readability |
| Expertise Required | Knowledge of legal language and document types | Strong language skills, no specialized legal knowledge needed |
| Document Types | Contracts, briefs, statutes, and legal correspondence | Articles, blogs, reports, novels, and general content |
| Purpose | Ensure legal precision and prevent misinterpretation | Enhance clarity and correct language errors |
| Compliance | Adherence to legal standards and formatting rules | Follows general style guides and formatting conventions |
| Risk Impact | High - errors can lead to legal consequences | Low to moderate - mainly affects readability and quality |
| Tools Used | Legal databases, case law references, legal style manuals | Standard grammar checkers, proofreading software |
Understanding Legal Proofreading: Key Elements
Legal proofreading requires a meticulous focus on terminology, statute references, and jurisdiction-specific language to ensure accuracy and compliance with legal standards. Unlike general proofreading, which addresses grammar, punctuation, and style, legal proofreading demands verification of legal citations, contract clauses, and court document formats to prevent costly errors. Familiarity with legal concepts and industry-specific jargon is essential to maintain the document's validity and credibility.
What Sets General Proofreading Apart
General proofreading primarily involves checking for grammar, spelling, punctuation, and typographical errors across a wide range of documents such as articles, essays, and business communications. Unlike legal proofreading, which requires a deep understanding of legal terminology, statutes, and case law to ensure accuracy and compliance, general proofreading focuses on clarity, consistency, and readability without needing specialized knowledge. This broader scope makes general proofreading essential for enhancing overall communication quality in diverse contexts.
Accuracy and Liability in Legal Proofreading
Legal proofreading demands a higher level of accuracy due to the critical nature of legal documents, where even minor errors can lead to significant liability issues. Proofreaders must thoroughly verify legal terminology, citations, and statutory references to ensure compliance with jurisdictional standards. In contrast, general proofreading primarily focuses on grammar, punctuation, and style without the same stringent consequences tied to inaccuracies.
Common Errors in Legal vs. General Documents
Legal proofreading requires meticulous attention to terminology accuracy, citation formats, and compliance with legal standards, while general proofreading often focuses on grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. Common errors in legal documents include misinterpretation of statutes, incorrect legal references, and inconsistent use of legal terms, which can lead to significant consequences. In contrast, general documents frequently contain typographical mistakes, sentence structure issues, and stylistic inconsistencies that affect readability but rarely have legal repercussions.
Specialized Terminology: Legal Versus General Texts
Legal proofreading demands meticulous attention to specialized terminology, including complex jargon, statutes, and case law references, which differ significantly from general text proofreading. Mistakes in legal terms can lead to misinterpretation of contracts, legal documents, or court filings, emphasizing the necessity of expertise in legal language nuances. General proofreading typically focuses on grammar, syntax, and style without the added layer of domain-specific language critical in legal contexts.
Compliance and Confidentiality Considerations
Legal proofreading demands strict adherence to compliance with industry regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA to protect sensitive client information. Confidentiality considerations are paramount, requiring rigorous protocols to prevent unauthorized disclosure of privileged documents. General proofreading lacks the same legal constraints, focusing more broadly on grammar and style without intensive compliance obligations.
Required Skills for Legal and General Proofreaders
Legal proofreading demands specialized knowledge of legal terminology, contract language, and the ability to identify inconsistencies within complex legal documents. General proofreading requires a strong grasp of grammar, punctuation, and style across various content types but lacks the necessity for legal expertise. Precision, attention to detail, and familiarity with industry-specific guidelines are critical skills distinguishing legal proofreaders from their general counterparts.
Turnaround Times: Legal vs. General Proofreading
Legal proofreading typically requires faster turnaround times due to strict court deadlines and regulatory compliance, often demanding completion within 24 to 48 hours. General proofreading projects allow more flexible timelines, ranging from a few days to a week depending on the document's complexity and client requirements. Efficient legal proofreading prioritizes accuracy under time constraints, whereas general proofreading balances speed with thoroughness over longer periods.
Cost Differences Between Legal and General Proofreading
Legal proofreading typically costs more than general proofreading due to the specialized knowledge required to accurately review complex legal terminology, documents, and compliance standards. General proofreading involves editing a broad range of content types with less need for subject-matter expertise, resulting in lower fees. The price disparity reflects the higher demand for precision and risk mitigation in legal texts, often leading to charges that are 30-50% higher than standard proofreading rates.
Choosing the Right Proofreading Service for Your Business
Legal proofreading requires specialized knowledge of legal terminology, compliance standards, and document formatting, ensuring contracts, briefs, and regulations are error-free and legally sound. General proofreading focuses on grammar, spelling, punctuation, and clarity across various content types, but may overlook critical legal nuances. Selecting the right proofreading service for your business depends on the document type, industry requirements, and the need for precision in legal language versus general content accuracy.
legal proofreading vs general proofreading Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com