Typographical errors are simple mistakes in spelling, punctuation, or formatting that can often be detected by proofreading tools and spellcheckers. Factual errors involve incorrect information or data that require careful verification against reliable sources to ensure accuracy. Distinguishing between these two types of errors is crucial for maintaining the integrity and clarity of any written content.
Table of Comparison
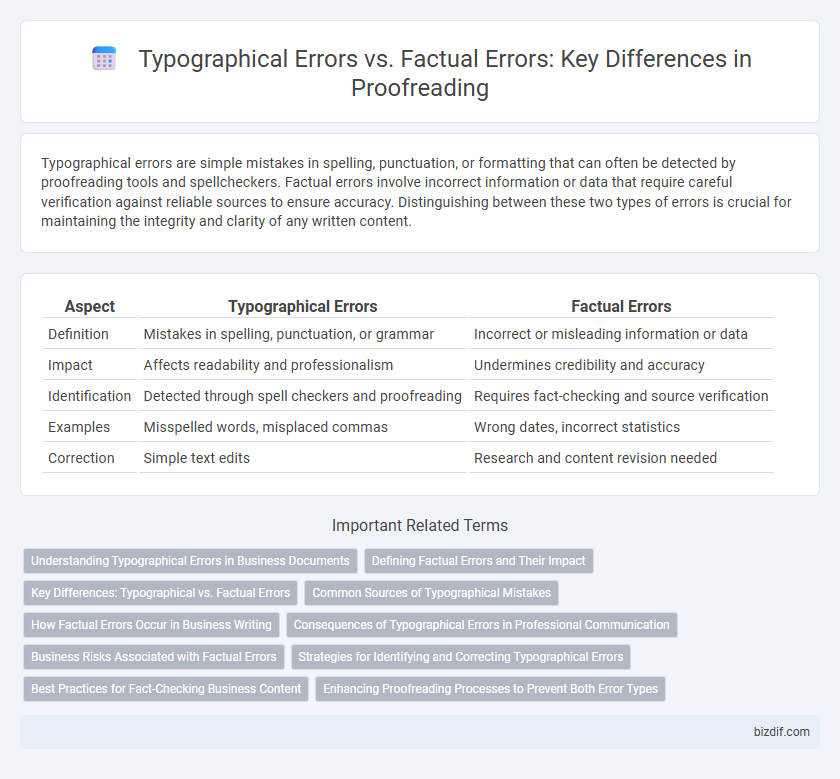
| Aspect | Typographical Errors | Factual Errors |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mistakes in spelling, punctuation, or grammar | Incorrect or misleading information or data |
| Impact | Affects readability and professionalism | Undermines credibility and accuracy |
| Identification | Detected through spell checkers and proofreading | Requires fact-checking and source verification |
| Examples | Misspelled words, misplaced commas | Wrong dates, incorrect statistics |
| Correction | Simple text edits | Research and content revision needed |
Understanding Typographical Errors in Business Documents
Typographical errors in business documents include misspellings, incorrect punctuation, and formatting inconsistencies that can undermine the professionalism of a text. These mistakes often result from oversight during typing or formatting processes and differ fundamentally from factual errors, which involve incorrect information or data. Identifying and correcting typographical errors ensures clarity, enhances the overall quality of the document, and maintains the credibility of the business communication.
Defining Factual Errors and Their Impact
Factual errors occur when incorrect information is presented, such as wrong dates, names, statistics, or data, undermining the credibility of the content. These errors disrupt the accuracy and reliability of a text, often leading to misinformation or misinterpretation. Correcting factual errors is essential to maintain trustworthiness and ensure the validity of the material.
Key Differences: Typographical vs. Factual Errors
Typographical errors are mistakes in the text's appearance, such as misspellings, incorrect punctuation, or formatting inconsistencies that do not alter the underlying facts. Factual errors involve inaccuracies in information, including incorrect dates, names, statistics, or data that compromise the truthfulness of content. Differentiating between these errors is crucial for effective proofreading, as typographical errors impact readability while factual errors affect content credibility and reliability.
Common Sources of Typographical Mistakes
Common sources of typographical errors include misplaced letters, repeated characters, and omitted punctuation marks, often resulting from fast typing or distractions. These mistakes differ from factual errors, which involve incorrect data or information rather than formatting issues. Identifying and correcting typographical errors enhances readability and professionalism in any written document.
How Factual Errors Occur in Business Writing
Factual errors in business writing often occur due to outdated information, misinterpretation of data, or insufficient research, leading to inaccuracies that can impact decision-making and credibility. Miscommunication between departments or reliance on incorrect sources further contributes to these errors, emphasizing the need for thorough fact-checking and verification. Unlike typographical errors that are primarily mechanical mistakes, factual errors undermine the integrity of the content and may cause legal or financial repercussions.
Consequences of Typographical Errors in Professional Communication
Typographical errors in professional communication can undermine credibility and create misunderstandings, potentially damaging business relationships and client trust. These mistakes often lead to misinterpretation of critical information, resulting in costly delays or errors in decision-making processes. Maintaining accuracy through thorough proofreading ensures clarity, professionalism, and effective information exchange.
Business Risks Associated with Factual Errors
Factual errors in business documents can lead to significant risks including financial losses, damaged reputation, and legal liabilities, whereas typographical errors primarily affect readability and professionalism. Misstated data or incorrect figures in contracts, reports, or marketing materials can result in misguided business decisions and loss of stakeholder trust. Ensuring accuracy through rigorous fact-checking minimizes exposure to compliance violations and potential disputes, safeguarding business integrity.
Strategies for Identifying and Correcting Typographical Errors
Typographical errors often involve misspellings, incorrect punctuation, or formatting mistakes that can be identified through meticulous proofreading techniques such as reading aloud, using spell Check tools, and focusing on one type of error at a time. Employing digital software like Grammarly or Microsoft Editor enhances detection accuracy by highlighting inconsistencies and common typos. Consistent practice of these strategies significantly reduces the likelihood of overlooked typographical errors before finalizing a document.
Best Practices for Fact-Checking Business Content
Typographical errors involve mistakes in spelling, punctuation, or formatting, while factual errors pertain to incorrect or misleading information within business content. Best practices for fact-checking business documents include verifying data against reliable sources, cross-referencing numerical figures and dates, and maintaining up-to-date knowledge of industry standards and terminology. Employing specialized software tools alongside manual reviews ensures accuracy and enhances the credibility of business communications.
Enhancing Proofreading Processes to Prevent Both Error Types
Enhancing proofreading processes requires integrating automated spell-check tools with rigorous fact-checking protocols to effectively identify typographical errors and factual inaccuracies. Leveraging AI-powered software like Grammarly or FactMata helps detect inconsistencies in spelling, grammar, and factual data within texts. Establishing multi-layered review systems combining human editors and machine learning algorithms significantly reduces the risk of both typographical and factual errors in published content.
Typographical Errors vs Factual Errors Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com