Localization adapts content to meet the cultural, linguistic, and functional needs of a specific target market, ensuring relevance and engagement. Globalization involves designing products and content from the outset to be easily adaptable across different regions and languages, fostering a unified brand experience. Both processes are critical for businesses aiming to expand internationally while maintaining local appeal and global consistency.
Table of Comparison
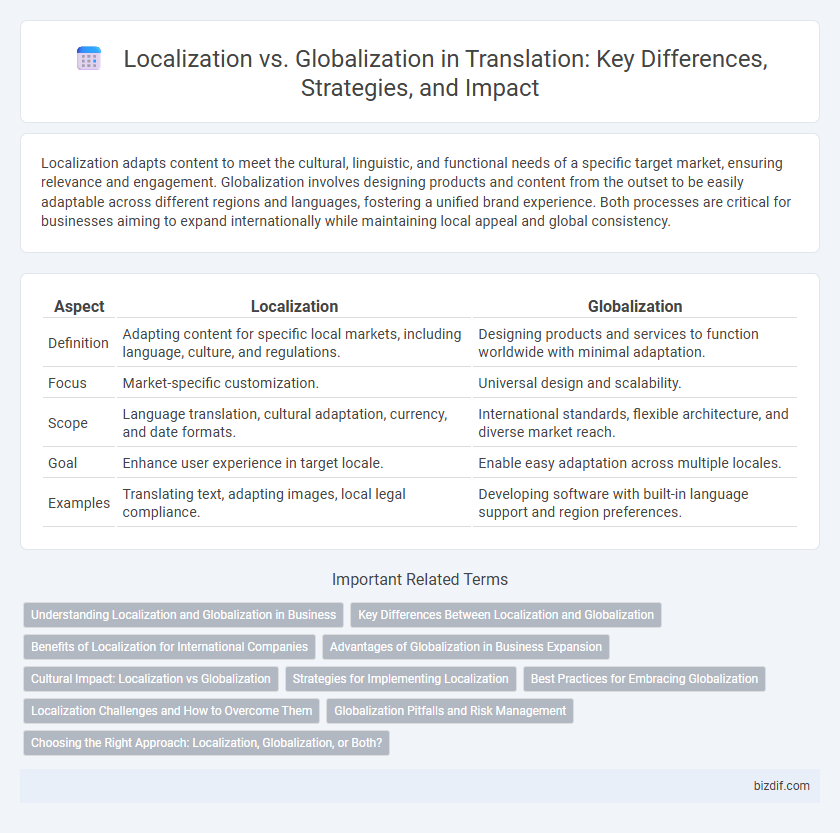
| Aspect | Localization | Globalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adapting content for specific local markets, including language, culture, and regulations. | Designing products and services to function worldwide with minimal adaptation. |
| Focus | Market-specific customization. | Universal design and scalability. |
| Scope | Language translation, cultural adaptation, currency, and date formats. | International standards, flexible architecture, and diverse market reach. |
| Goal | Enhance user experience in target locale. | Enable easy adaptation across multiple locales. |
| Examples | Translating text, adapting images, local legal compliance. | Developing software with built-in language support and region preferences. |
Understanding Localization and Globalization in Business
Localization customizes products and content to meet the specific linguistic, cultural, and regional preferences of target markets, enhancing user experience and engagement. Globalization involves creating products and strategies designed for seamless adaptation across multiple international markets, ensuring consistency and scalability on a global scale. Effective integration of localization within a broader globalization strategy drives business growth by expanding reach while respecting local nuances.
Key Differences Between Localization and Globalization
Localization customizes content to meet the cultural, linguistic, and regional preferences of a specific target market, improving user experience and relevance. Globalization involves designing products or content that can be easily adapted for multiple regions and languages without requiring significant rework. Key differences include localization's focus on adaptation for local markets versus globalization's emphasis on broad scalability and consistency across diverse markets.
Benefits of Localization for International Companies
Localization enhances user experience by adapting products and marketing materials to cultural preferences, increasing customer engagement and loyalty. It improves market penetration and competitive advantage through region-specific content, language, and legal compliance. This tailored approach boosts conversion rates and drives revenue growth in diverse international markets.
Advantages of Globalization in Business Expansion
Globalization enables businesses to access international markets, increasing revenue potential and brand recognition across diverse regions. It facilitates economies of scale by allowing companies to standardize products and streamline operations, reducing costs. Exposure to global competition drives innovation and improves product quality, enhancing competitiveness on a worldwide scale.
Cultural Impact: Localization vs Globalization
Localization adapts content to reflect the cultural norms, language nuances, and societal values of a target market, ensuring relevance and resonance with local audiences. Globalization emphasizes a unified brand message and consistent user experience across diverse regions, often prioritizing broad appeal over cultural specificity. Understanding the cultural impact of localization versus globalization is essential for businesses aiming to engage effectively with international markets.
Strategies for Implementing Localization
Effective localization strategies prioritize cultural adaptation and context-specific content to enhance user engagement across diverse markets. Incorporating regional dialects, localized idioms, and culturally relevant visuals ensures the message resonates authentically with target audiences. Leveraging advanced translation management systems (TMS) and collaboration with native linguistic experts optimizes accuracy and consistency throughout the localization process.
Best Practices for Embracing Globalization
Adopting best practices for globalization involves tailoring content to diverse cultural contexts while maintaining brand consistency across markets. Effective globalization strategies prioritize scalable translation workflows, use localization automation tools, and integrate continuous linguistic validation to ensure accuracy and cultural relevance. Incorporating global SEO techniques and culturally adapted marketing also enhances user engagement and expands international reach.
Localization Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Localization challenges often include cultural nuances, linguistic diversity, and maintaining brand consistency across different regions. Overcoming these obstacles requires in-depth cultural research, employing native linguists, and utilizing advanced translation management systems to ensure accuracy and relevance. Effective localization ensures that content resonates with local audiences while preserving the original message's intent.
Globalization Pitfalls and Risk Management
Globalization risks include cultural misunderstandings, inconsistent brand messaging, and regulatory non-compliance across diverse markets. Effective risk management requires thorough market research, adaptable localization strategies, and legal expertise to navigate varying international standards. Prioritizing scalable communication frameworks reduces errors and safeguards global brand reputation.
Choosing the Right Approach: Localization, Globalization, or Both?
Choosing the right approach between localization and globalization depends on a company's target markets and business goals, with localization focusing on adapting content, products, and services to specific cultural and linguistic contexts, while globalization aims to create universally applicable solutions that can be efficiently scaled across regions. Effective strategies often combine both approaches to balance global brand consistency with local relevance, leveraging tools such as multilingual content management systems and regional market analysis. Key performance indicators for success include user engagement metrics, market penetration rates, and customer satisfaction scores in localized versus globalized markets.
Localization vs Globalization Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com