Literal translation preserves the exact wording and structure of the source text, maintaining its original meaning but sometimes resulting in awkward or unclear phrasing. Adapted translation prioritizes conveying the intended message and cultural nuances, ensuring the content resonates naturally with the target audience. Choosing between literal and adapted translation depends on the purpose of the translation and the desired impact on readers.
Table of Comparison
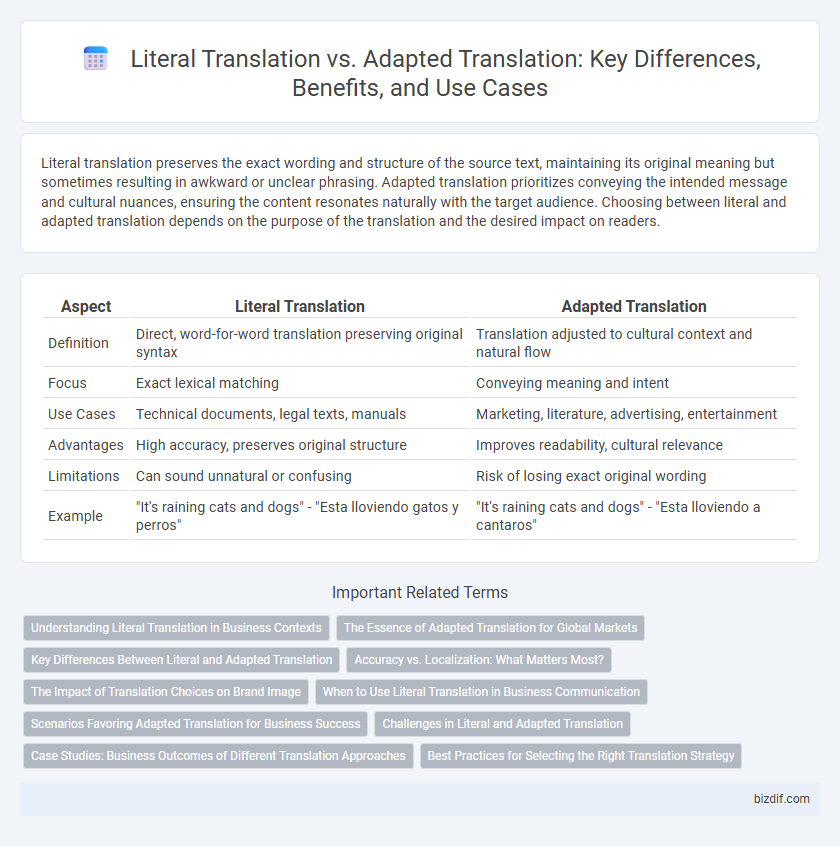
| Aspect | Literal Translation | Adapted Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct, word-for-word translation preserving original syntax | Translation adjusted to cultural context and natural flow |
| Focus | Exact lexical matching | Conveying meaning and intent |
| Use Cases | Technical documents, legal texts, manuals | Marketing, literature, advertising, entertainment |
| Advantages | High accuracy, preserves original structure | Improves readability, cultural relevance |
| Limitations | Can sound unnatural or confusing | Risk of losing exact original wording |
| Example | "It's raining cats and dogs" - "Esta lloviendo gatos y perros" | "It's raining cats and dogs" - "Esta lloviendo a cantaros" |
Understanding Literal Translation in Business Contexts
Literal translation in business contexts involves directly converting words from one language to another while maintaining the original sentence structure and vocabulary. This method preserves the precise terminology and technical details crucial for contracts, financial documents, and product specifications, ensuring legal and factual accuracy. However, it may lack cultural nuance and fluidity, potentially leading to misunderstandings in marketing materials or client communications.
The Essence of Adapted Translation for Global Markets
Adapted translation captures cultural nuances and context, ensuring the message resonates authentically with target audiences across global markets. Unlike literal translation, which translates word-for-word, adapted translation prioritizes meaning and tone to maintain relevance and emotional impact. This approach enhances brand engagement and communication effectiveness by tailoring content to local customs, idioms, and preferences.
Key Differences Between Literal and Adapted Translation
Literal translation preserves the exact words and structure of the source text, ensuring high fidelity to the original meaning but often resulting in awkward or unnatural phrasing. Adapted translation prioritizes cultural relevance and readability by modifying expressions, idioms, and references to suit the target audience while maintaining the intended message. Key differences include the balance between accuracy and localization, with literal translation favoring word-for-word accuracy and adapted translation emphasizing context and cultural adaptation.
Accuracy vs. Localization: What Matters Most?
Literal translation ensures accuracy by preserving the original text's exact meaning and structure, essential for technical documents or legal texts. Adapted translation prioritizes localization, tailoring content to cultural nuances and audience preferences, enhancing engagement and comprehension. The choice between accuracy and localization depends on the translation's purpose, with a balance often necessary for effective communication.
The Impact of Translation Choices on Brand Image
Literal translation preserves the original wording but can result in awkward or culturally irrelevant messages that dilute a brand's appeal. Adapted translation tailors content to resonate with the target audience's cultural norms and preferences, enhancing brand relatability and trust. Choosing between literal and adapted translation directly influences brand perception, market engagement, and customer loyalty.
When to Use Literal Translation in Business Communication
Literal translation is ideal in business communication when accuracy and clarity of technical terms, legal content, or financial data are crucial to avoid misunderstandings. It preserves the original message's exact meaning, making it suitable for contracts, reports, and product specifications where precise language matters. Use literal translation when the target audience requires a faithful representation of the source text without cultural or idiomatic alterations.
Scenarios Favoring Adapted Translation for Business Success
Adapted translation is crucial in marketing campaigns targeting diverse cultural markets, as it ensures messages resonate with local audiences by incorporating culturally relevant idioms and references. In product packaging and advertising, adapted translation helps avoid misinterpretations that could damage brand reputation or reduce consumer trust. Companies expanding into new international markets benefit from adapted translation to align their messaging with regional preferences, enhancing customer engagement and driving business growth.
Challenges in Literal and Adapted Translation
Literal translation often struggles with preserving idiomatic expressions and cultural nuances, leading to potential loss of meaning or unnatural phrasing. Adapted translation faces the challenge of balancing faithfulness to the source text with localization, risking distortion of the original intent. Both methods require deep linguistic and cultural knowledge to ensure accuracy and resonance in the target language.
Case Studies: Business Outcomes of Different Translation Approaches
Case studies reveal that literal translation often preserves original meanings but may fail to engage target audiences effectively in global markets, leading to lower customer retention rates. Adapted translation, by localizing content to cultural nuances and market expectations, drives higher conversion rates and brand loyalty across diverse regions. Businesses adopting adapted translation strategies report up to 30% revenue growth compared to those relying solely on literal translation methods.
Best Practices for Selecting the Right Translation Strategy
Selecting the right translation strategy involves evaluating the purpose, target audience, and cultural context of the content; literal translation preserves original structure and meaning for technical or legal texts where accuracy is paramount while adapted translation enhances relatability and engagement in marketing or literary works by localizing idiomatic expressions and cultural references. Best practices include conducting thorough audience analysis, consulting subject matter experts, and balancing fidelity with naturalness to maintain the text's intent and readability. Employing a hybrid approach often yields optimal results by integrating literal precision with cultural adaptation tailored to the specific translation goals.
Literal Translation vs Adapted Translation Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com