API-first strategy enables scalable and flexible app development by prioritizing well-defined interfaces that facilitate seamless integration and faster iterations. Monolithic architecture, while simpler initially, can lead to rigidity and challenges in updating or scaling individual components. Prioritizing an API-first approach supports modular growth and better aligns with modern development workflows.
Table of Comparison
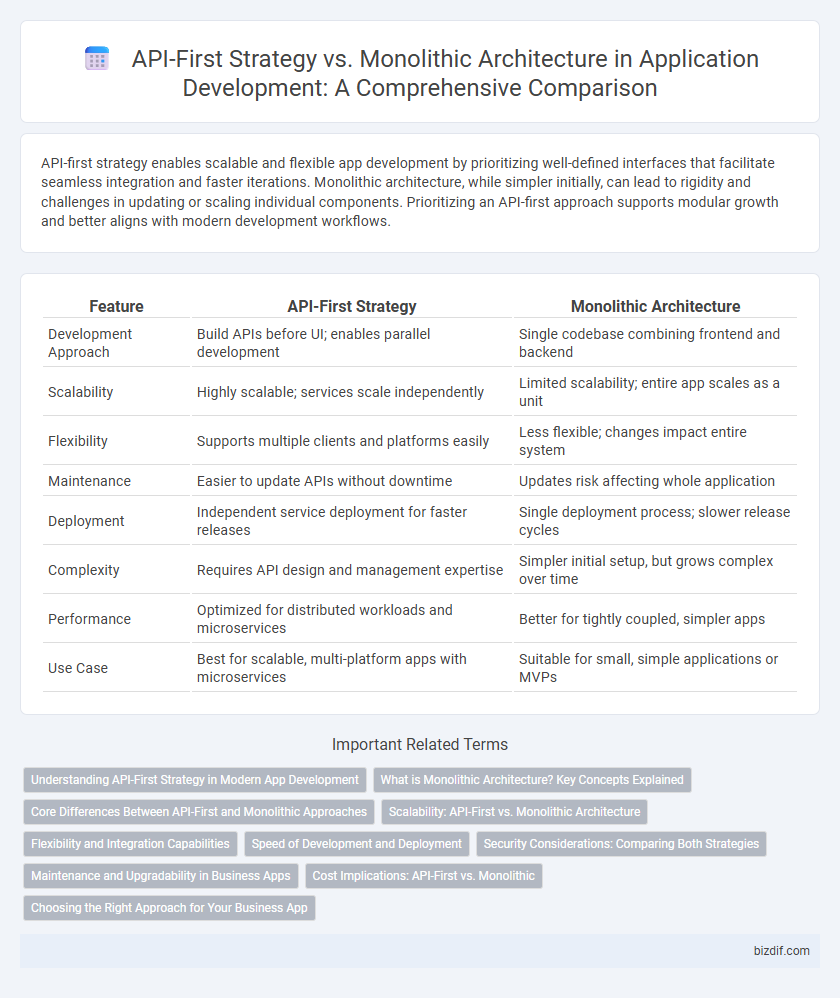
| Feature | API-First Strategy | Monolithic Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| Development Approach | Build APIs before UI; enables parallel development | Single codebase combining frontend and backend |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; services scale independently | Limited scalability; entire app scales as a unit |
| Flexibility | Supports multiple clients and platforms easily | Less flexible; changes impact entire system |
| Maintenance | Easier to update APIs without downtime | Updates risk affecting whole application |
| Deployment | Independent service deployment for faster releases | Single deployment process; slower release cycles |
| Complexity | Requires API design and management expertise | Simpler initial setup, but grows complex over time |
| Performance | Optimized for distributed workloads and microservices | Better for tightly coupled, simpler apps |
| Use Case | Best for scalable, multi-platform apps with microservices | Suitable for small, simple applications or MVPs |
Understanding API-First Strategy in Modern App Development
API-first strategy in modern app development emphasizes designing and building APIs before developing the user interface or other application components, ensuring seamless integration and scalability. This approach contrasts with monolithic architecture, where all components are tightly coupled, limiting flexibility and hindering continuous deployment. Prioritizing API design promotes modularity, accelerates development cycles, and enables easier maintenance and multi-platform support across web, mobile, and IoT devices.
What is Monolithic Architecture? Key Concepts Explained
Monolithic architecture is a traditional software design where all components and functionalities are integrated into a single, unified codebase, enabling straightforward development and deployment processes. This approach often leads to tightly coupled modules, making updates and scaling more challenging compared to modular alternatives like API-first strategies. Key concepts include a single executable, shared memory space, and direct communication between components without intermediary layers.
Core Differences Between API-First and Monolithic Approaches
API-first strategy emphasizes building discrete, reusable services designed for interoperability and scalability through well-defined endpoints, enhancing flexibility in app development and integration. Monolithic architecture consolidates all functions into a single, unified codebase, which often results in tighter coupling and challenges in scaling specific components independently. Core differences include modularity, deployment agility, and ease of continuous integration, where API-first supports rapid iteration and diverse client access, whereas monolithic systems tend to require full-stack updates for any change.
Scalability: API-First vs. Monolithic Architecture
API-first strategy enhances scalability by enabling modular development and independent deployment of services, facilitating rapid updates and seamless integration with third-party platforms. Monolithic architecture often faces scalability challenges due to tightly coupled components that require extensive modifications and redeployments to accommodate growth. Organizations seeking flexible scaling solutions and faster time-to-market benefit significantly from adopting API-first approaches over monolithic systems.
Flexibility and Integration Capabilities
API-first strategy enhances flexibility by enabling modular development and seamless integration with diverse third-party services, fostering scalable and adaptable applications. Monolithic architecture often limits integration capabilities due to tightly coupled components, making updates and expansions more challenging. Prioritizing API-first design accelerates innovation and supports dynamic ecosystems compared to the rigid structure of monolithic systems.
Speed of Development and Deployment
API-first strategy accelerates development and deployment by enabling parallel work on frontend and backend components, reducing dependencies and integration delays. In contrast, monolithic architecture often results in slower release cycles due to tightly coupled systems requiring comprehensive testing for each change. Adopting an API-first approach increases agility, allowing faster iterations and more frequent updates in app development.
Security Considerations: Comparing Both Strategies
API-first strategy enhances security by isolating services, enabling granular access controls and reducing attack surfaces through modular endpoints. In contrast, monolithic architecture consolidates functions in a single codebase, increasing vulnerability risks since a breach can compromise the entire system. Strong authentication, rigorous input validation, and continuous monitoring are essential in both architectures, but API-first allows more targeted and scalable security implementations.
Maintenance and Upgradability in Business Apps
API-first strategy enhances maintenance and upgradability in business apps by enabling modular development, which allows independent updates without disrupting the entire system. In contrast, monolithic architecture often results in complex, tightly coupled codebases that increase the risk and effort required for maintenance and upgrades. Prioritizing API-first design reduces downtime and accelerates feature deployment, fostering greater agility in evolving business requirements.
Cost Implications: API-First vs. Monolithic
API-first strategy reduces long-term costs by enabling reusable, scalable services and faster integration with third-party tools, minimizing development and maintenance expenses. Monolithic architecture often incurs higher upfront costs due to tightly coupled components and limited flexibility, requiring more resources for updates and scaling. Choosing API-first can optimize operational budgets through modular deployment and easier iteration, leading to better cost-efficiency over time.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Business App
API-first strategy enables scalable and flexible app development by prioritizing modular services and seamless third-party integrations, which accelerates innovation and improves user experience. In contrast, monolithic architecture offers simplicity and faster initial deployment but can hinder scalability and complicate maintenance as the app grows. Selecting the right approach depends on your business goals, desired agility, and long-term scalability requirements.
API-first strategy vs Monolithic architecture Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com