Monolithic app development involves building a single, unified codebase where all components are interconnected, leading to simpler deployment but limited scalability. Microservices architecture breaks an application into smaller, independent services that communicate through APIs, enabling better flexibility, scalability, and easier maintenance. Choosing between monolithic and microservices depends on factors such as project size, team expertise, and the need for rapid updates or scalability.
Table of Comparison
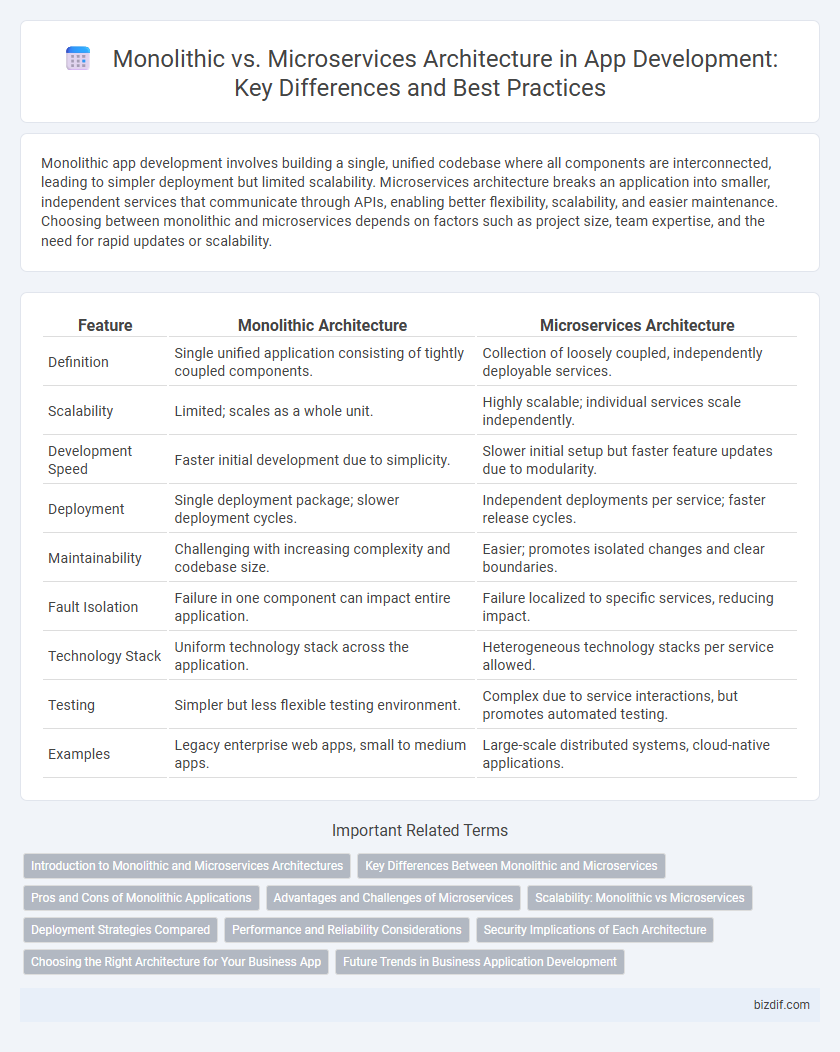
| Feature | Monolithic Architecture | Microservices Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single unified application consisting of tightly coupled components. | Collection of loosely coupled, independently deployable services. |
| Scalability | Limited; scales as a whole unit. | Highly scalable; individual services scale independently. |
| Development Speed | Faster initial development due to simplicity. | Slower initial setup but faster feature updates due to modularity. |
| Deployment | Single deployment package; slower deployment cycles. | Independent deployments per service; faster release cycles. |
| Maintainability | Challenging with increasing complexity and codebase size. | Easier; promotes isolated changes and clear boundaries. |
| Fault Isolation | Failure in one component can impact entire application. | Failure localized to specific services, reducing impact. |
| Technology Stack | Uniform technology stack across the application. | Heterogeneous technology stacks per service allowed. |
| Testing | Simpler but less flexible testing environment. | Complex due to service interactions, but promotes automated testing. |
| Examples | Legacy enterprise web apps, small to medium apps. | Large-scale distributed systems, cloud-native applications. |
Introduction to Monolithic and Microservices Architectures
Monolithic architecture integrates all components of an application into a single unified codebase, enabling straightforward development but often limiting scalability and flexibility. Microservices architecture decomposes an application into independent, loosely coupled services that communicate via APIs, enhancing modularity and facilitating continuous deployment. Choosing between these architectures depends on factors like application complexity, team structure, and scalability requirements.
Key Differences Between Monolithic and Microservices
Monolithic applications consist of a single, unified codebase where all components are tightly integrated, making deployment straightforward but scaling and updating more complex. Microservices architecture breaks down an application into loosely coupled, independently deployable services, enabling greater scalability, flexibility, and fault isolation. Key differences include deployment flexibility, scalability options, and maintenance complexity, with microservices offering superior modularity and technology diversity compared to monolithic systems.
Pros and Cons of Monolithic Applications
Monolithic applications offer the advantage of simplified deployment and straightforward development due to their unified codebase, making them easier to manage for small to medium-sized projects. However, they often face challenges with scalability and flexibility, as any change requires redeploying the entire application, which can slow down updates and hinder the adoption of new technologies. Maintenance becomes increasingly complex as the application grows, potentially leading to longer development cycles and reduced agility compared to microservices architectures.
Advantages and Challenges of Microservices
Microservices architecture enables independent deployment, scalability, and improved fault isolation, enhancing agility in app development. This approach allows teams to develop, test, and deploy services independently, accelerating innovation and reducing time-to-market. Challenges include increased complexity in service orchestration, data management, and the need for robust DevOps practices to handle distributed systems effectively.
Scalability: Monolithic vs Microservices
Monolithic applications often face scalability challenges because scaling requires duplicating the entire application, which can be resource-intensive and inefficient. Microservices architecture allows independent scaling of specific components based on demand, optimizing resource use and improving performance. This granular scalability makes microservices a preferred choice for complex, high-traffic applications requiring flexible growth.
Deployment Strategies Compared
Monolithic applications require deploying the entire codebase as a single unit, which can result in longer deployment times and increased risk of downtime. Microservices architecture enables independent deployment of individual services, allowing for faster updates and more granular scaling. Container orchestration tools like Kubernetes optimize microservices deployment by automating scaling, load balancing, and recovery processes.
Performance and Reliability Considerations
Monolithic architectures often provide faster initial performance due to tightly integrated components but can suffer from scalability bottlenecks under heavy load. Microservices enhance reliability by isolating failures within individual services, allowing other components to operate uninterrupted, and enable independent scaling to optimize resource use. Performance tuning in microservices requires addressing network latency and inter-service communication overhead, which can impact response times compared to monolithic systems.
Security Implications of Each Architecture
Monolithic architectures centralize code in a single executable, simplifying security management but increasing risk from a single vulnerability compromising the entire system. Microservices distribute functionality across independent services, enhancing isolation and limiting attack surfaces, yet complicating security due to the need for inter-service authentication, encrypted communication, and consistent policy enforcement. Effective security in microservices demands robust identity management, API gateway controls, and continuous monitoring to mitigate risks from the increased network exposure and complexity.
Choosing the Right Architecture for Your Business App
Monolithic architecture consolidates all components into a single codebase, offering simplicity and ease of deployment for small to medium-sized business apps with limited scalability demands. Microservices architecture divides apps into independent, loosely coupled services, enhancing flexibility, scalability, and fault isolation suited for complex, large-scale business applications. The choice depends on factors like development speed, team expertise, expected user load, and long-term maintenance strategies.
Future Trends in Business Application Development
Future trends in business application development indicate a growing shift from monolithic architectures to microservices, driven by the need for scalability, flexibility, and faster deployment cycles. Microservices enable independent service updates and improved fault isolation, which align with DevOps practices and cloud-native environments. Businesses adopting containerization technologies like Kubernetes are better positioned to leverage microservices for continuous integration and continuous delivery pipelines.
Monolithic vs Microservices Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com