The SaaS model delivers fully functional applications accessible via the internet, eliminating the need for users to manage underlying infrastructure or platforms. In contrast, the PaaS model provides a development environment with tools and frameworks, enabling developers to build, deploy, and customize applications more flexibly. Choosing between SaaS and PaaS depends on the desired level of control, customization, and maintenance effort in app development projects.
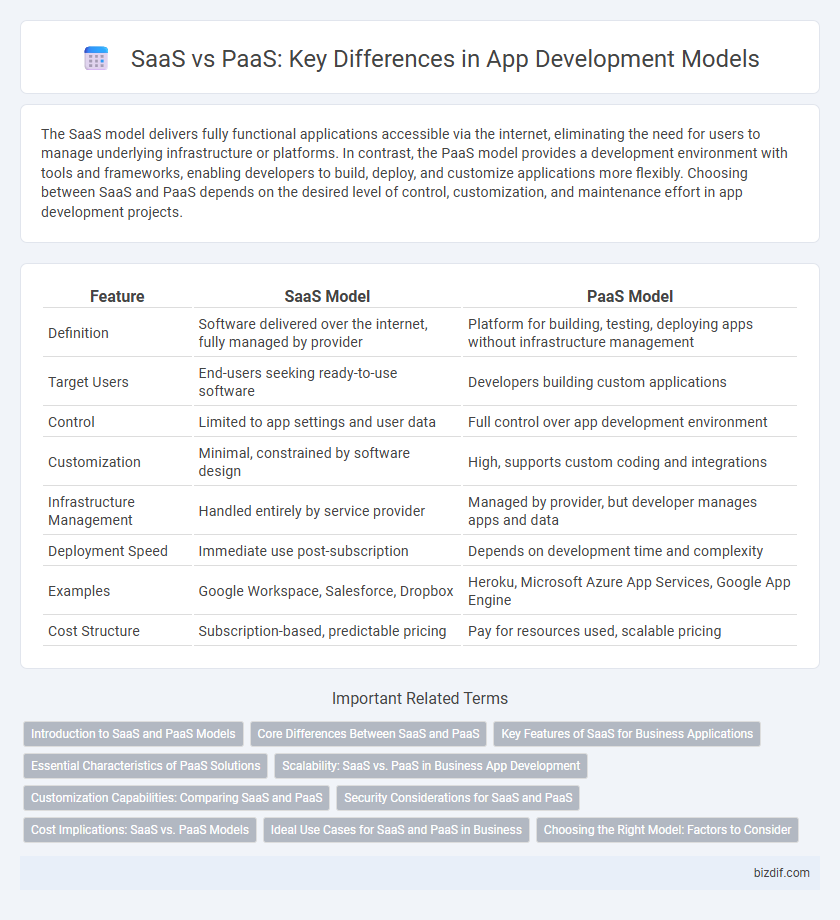
Table of Comparison
| Feature | SaaS Model | PaaS Model |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software delivered over the internet, fully managed by provider | Platform for building, testing, deploying apps without infrastructure management |
| Target Users | End-users seeking ready-to-use software | Developers building custom applications |
| Control | Limited to app settings and user data | Full control over app development environment |
| Customization | Minimal, constrained by software design | High, supports custom coding and integrations |
| Infrastructure Management | Handled entirely by service provider | Managed by provider, but developer manages apps and data |
| Deployment Speed | Immediate use post-subscription | Depends on development time and complexity |
| Examples | Google Workspace, Salesforce, Dropbox | Heroku, Microsoft Azure App Services, Google App Engine |
| Cost Structure | Subscription-based, predictable pricing | Pay for resources used, scalable pricing |
Introduction to SaaS and PaaS Models
SaaS (Software as a Service) provides fully developed applications accessible via the internet, eliminating the need for local installation or maintenance. PaaS (Platform as a Service) offers a development environment with tools, frameworks, and infrastructure, enabling developers to build, deploy, and manage apps without handling underlying hardware. Both models streamline app development and deployment but cater to different stages: SaaS delivers ready-to-use software, while PaaS supports custom app creation and scaling.
Core Differences Between SaaS and PaaS
SaaS (Software as a Service) delivers fully functional software applications accessible via the internet, enabling users to perform tasks without managing underlying infrastructure or platform details. PaaS (Platform as a Service) provides a cloud-based platform with tools for developers to build, deploy, and manage custom applications, offering greater control over application development environments. Core differences include SaaS focusing on end-user software consumption, while PaaS targets developers by supplying the frameworks and services necessary for app creation and lifecycle management.
Key Features of SaaS for Business Applications
SaaS (Software as a Service) offers businesses scalable, subscription-based access to software applications hosted in the cloud, eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure and complex installations. Key features include automatic updates and maintenance, seamless integration with various third-party services, and real-time collaboration capabilities that enhance productivity. The SaaS model enables rapid deployment, cost-effective scalability, and accessibility from any device with internet connectivity, making it ideal for dynamic business environments.
Essential Characteristics of PaaS Solutions
PaaS solutions offer essential characteristics such as integrated development environments, pre-built middleware, and scalable infrastructure that streamline app development and deployment. These platforms provide automated updates, seamless collaboration tools, and extensive APIs that enhance developer productivity. Unlike SaaS, PaaS delivers customizable backend services allowing for flexible application customization and rapid prototyping.
Scalability: SaaS vs. PaaS in Business App Development
SaaS models offer ready-to-use applications that scale effortlessly with user demand, minimizing infrastructure management for businesses. PaaS platforms provide developers with customizable environments and tools, enabling scalable application development tailored to specific business needs. Choosing between SaaS and PaaS impacts how companies handle growth, resource allocation, and deployment flexibility in app development strategies.
Customization Capabilities: Comparing SaaS and PaaS
SaaS models offer limited customization, typically allowing users to adjust settings within predefined parameters, making them ideal for standardized applications with quick deployment needs. PaaS models provide extensive customization capabilities by enabling developers to build, modify, and deploy applications using various tools, frameworks, and programming languages tailored to specific business requirements. Customization in PaaS supports complex workflows and integrations, whereas SaaS customization is generally constrained to user interface and feature adjustments.
Security Considerations for SaaS and PaaS
SaaS models often face heightened security risks due to multi-tenant architecture, exposing data to potential breaches if access controls are weak, whereas PaaS platforms provide developers with customizable security layers to better protect applications during development and deployment. Encryption standards, identity and access management (IAM), and compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA are critical security considerations for both models, but PaaS allows more granular control over these elements. Regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and secure API management are essential practices to mitigate risks inherent in SaaS and PaaS environments.
Cost Implications: SaaS vs. PaaS Models
SaaS models typically offer lower upfront costs as they provide ready-to-use applications hosted on the vendor's infrastructure, eliminating the need for extensive development or hardware investments. PaaS models, while requiring higher initial development expenses, enable greater customization and scalability by providing a platform for building, testing, and deploying applications. Cost implications for businesses depend on factors like application complexity, maintenance, and long-term scalability needs, with SaaS favoring quicker deployments and PaaS supporting tailored solutions and innovation.
Ideal Use Cases for SaaS and PaaS in Business
SaaS models are ideal for businesses seeking ready-to-use software solutions with minimal upfront investment and maintenance, such as customer relationship management (CRM), email services, and collaboration tools. PaaS models suit companies that require customizable application development environments, enabling developers to build, test, and deploy apps efficiently without managing the underlying infrastructure. Enterprises aiming for scalability and rapid development benefit from PaaS, while those focused on straightforward access to software services without development overhead opt for SaaS.
Choosing the Right Model: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right app development model depends on factors such as customization needs, scalability requirements, and budget constraints. SaaS offers ready-to-use applications with minimal maintenance, ideal for businesses seeking quick deployment and low upfront costs. PaaS provides a flexible development environment for building custom apps, suitable for organizations needing greater control over features and integration.
SaaS Model vs PaaS Model Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com