Test-Driven Development (TDD) emphasizes writing tests before code to ensure functionality meets technical specifications, fostering reliable, bug-free app development. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) extends TDD by focusing on user behavior and collaboration between developers, testers, and non-technical stakeholders, enhancing communication and aligning features with real user needs. Choosing between TDD and BDD impacts app quality, development efficiency, and stakeholder involvement throughout the development lifecycle.
Table of Comparison
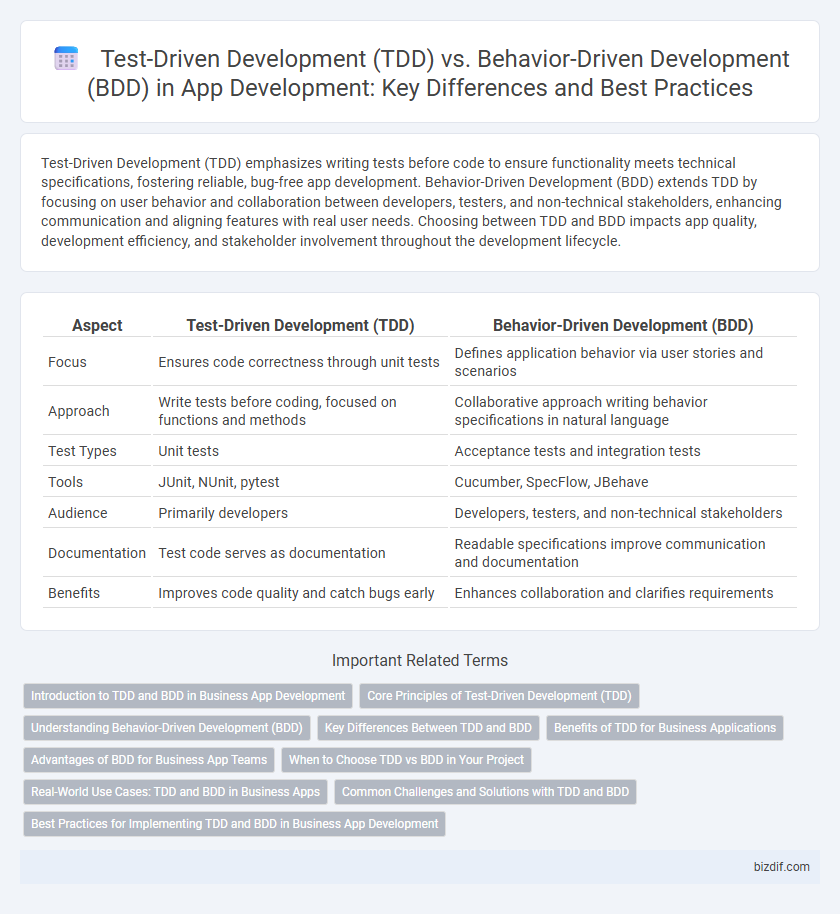
| Aspect | Test-Driven Development (TDD) | Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Ensures code correctness through unit tests | Defines application behavior via user stories and scenarios |
| Approach | Write tests before coding, focused on functions and methods | Collaborative approach writing behavior specifications in natural language |
| Test Types | Unit tests | Acceptance tests and integration tests |
| Tools | JUnit, NUnit, pytest | Cucumber, SpecFlow, JBehave |
| Audience | Primarily developers | Developers, testers, and non-technical stakeholders |
| Documentation | Test code serves as documentation | Readable specifications improve communication and documentation |
| Benefits | Improves code quality and catch bugs early | Enhances collaboration and clarifies requirements |
Introduction to TDD and BDD in Business App Development
Test-Driven Development (TDD) in business app development emphasizes writing unit tests before coding, ensuring robust functionality and early bug detection. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) expands on TDD by incorporating user stories and collaboration between developers, testers, and stakeholders to align software behavior with business requirements. Both methodologies improve code quality and project clarity but prioritize different aspects of the development lifecycle.
Core Principles of Test-Driven Development (TDD)
Test-Driven Development (TDD) centers on writing automated test cases before coding functionality, ensuring that each new feature passes predefined tests. This approach follows a strict Red-Green-Refactor cycle that promotes minimal working code, leading to higher code quality and fewer bugs. Core principles include iterative development, continuous testing, and immediate feedback, which collectively improve software reliability and maintainability in app development.
Understanding Behavior-Driven Development (BDD)
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) enhances collaboration between developers, testers, and business stakeholders by using natural language to define application behavior, which improves communication and reduces misunderstandings. BDD frameworks like Cucumber and SpecFlow enable automated testing based on user stories, promoting clearer requirements and more reliable software outcomes. Emphasizing user-centric scenarios, BDD bridges the gap between technical implementation and business needs, leading to higher-quality app development.
Key Differences Between TDD and BDD
Test-Driven Development (TDD) centers on writing unit tests before code implementation to ensure functional correctness, emphasizing internal component behavior. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) expands on TDD by focusing on system behavior and user scenarios, using natural language specifications to improve communication between developers, testers, and stakeholders. BDD frameworks like Cucumber and SpecFlow enable automated acceptance testing aligned with business requirements, while TDD relies primarily on unit testing frameworks such as JUnit or NUnit.
Benefits of TDD for Business Applications
Test-Driven Development (TDD) enhances code quality and reduces bugs in business applications by enforcing rigorous unit testing before implementation. This approach accelerates development cycles and lowers maintenance costs through early defect detection and clearer code structure. TDD also improves collaboration between developers and stakeholders by providing immediate feedback and ensuring alignment with business requirements.
Advantages of BDD for Business App Teams
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) enhances collaboration between business stakeholders and development teams by using shared, natural language scenarios that clarify requirements and reduce misunderstandings. BDD's emphasis on executable specifications ensures that business rules and user behaviors are accurately captured and tested, leading to higher-quality apps aligned with customer needs. This approach accelerates feedback loops and improves communication, enabling teams to deliver more reliable and user-centric business applications.
When to Choose TDD vs BDD in Your Project
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is ideal for projects requiring precise unit tests and internal code quality, emphasizing developer-centric validation through writing tests before code implementation. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) suits projects needing clear collaboration among developers, testers, and non-technical stakeholders by focusing on user behavior and acceptance criteria with readable scenarios. Choose TDD when the priority is code correctness and refactoring ease, while select BDD to ensure shared understanding of requirements and facilitate communication across cross-functional teams.
Real-World Use Cases: TDD and BDD in Business Apps
Test-Driven Development (TDD) focuses on writing unit tests before code implementation, ensuring robust and error-resistant business application modules such as payment processing and user authentication. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) emphasizes defining application behavior through collaboration between developers and stakeholders, enhancing clarity in real-world scenarios like customer onboarding and workflow automation. Both methodologies improve software quality but serve different phases of app development with TDD targeting code correctness and BDD fostering communication and requirement validation.
Common Challenges and Solutions with TDD and BDD
Test-Driven Development (TDD) and Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) both face challenges such as maintaining test coverage and managing evolving requirements during app development. TDD struggles with writing overly granular unit tests that can increase maintenance overhead, while BDD often encounters difficulties in clearly defining behavior specifications that align with stakeholder expectations. Implementing robust collaboration tools and adopting clear documentation standards can effectively address these challenges, ensuring that tests remain relevant and actionable throughout the development lifecycle.
Best Practices for Implementing TDD and BDD in Business App Development
Implementing Test-Driven Development (TDD) and Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) in business app development requires clear definition of test cases and behaviors aligned with user requirements to ensure robust code quality and enhanced collaboration. Best practices include writing minimal tests before code in TDD to drive design, using ubiquitous language in BDD scenarios to improve communication between developers and stakeholders, and continuously refactoring code to maintain flexibility and scalability. Integrating automated testing tools such as JUnit for TDD and Cucumber for BDD optimizes the development workflow and accelerates delivery of reliable business applications.
Test-Driven Development (TDD) vs Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com