Allergen-free baking prioritizes the exclusion of common allergens such as gluten, nuts, dairy, and eggs to ensure safe consumption for individuals with food sensitivities, using alternative ingredients like almond flour, coconut milk, and flax seeds. Standard baking typically relies on traditional ingredients like wheat flour, butter, and eggs, which provide familiar textures and flavors but pose risks to those with allergies. Choosing allergen-free baking methods enhances inclusivity and can inspire innovative recipes without compromising taste or quality.
Table of Comparison
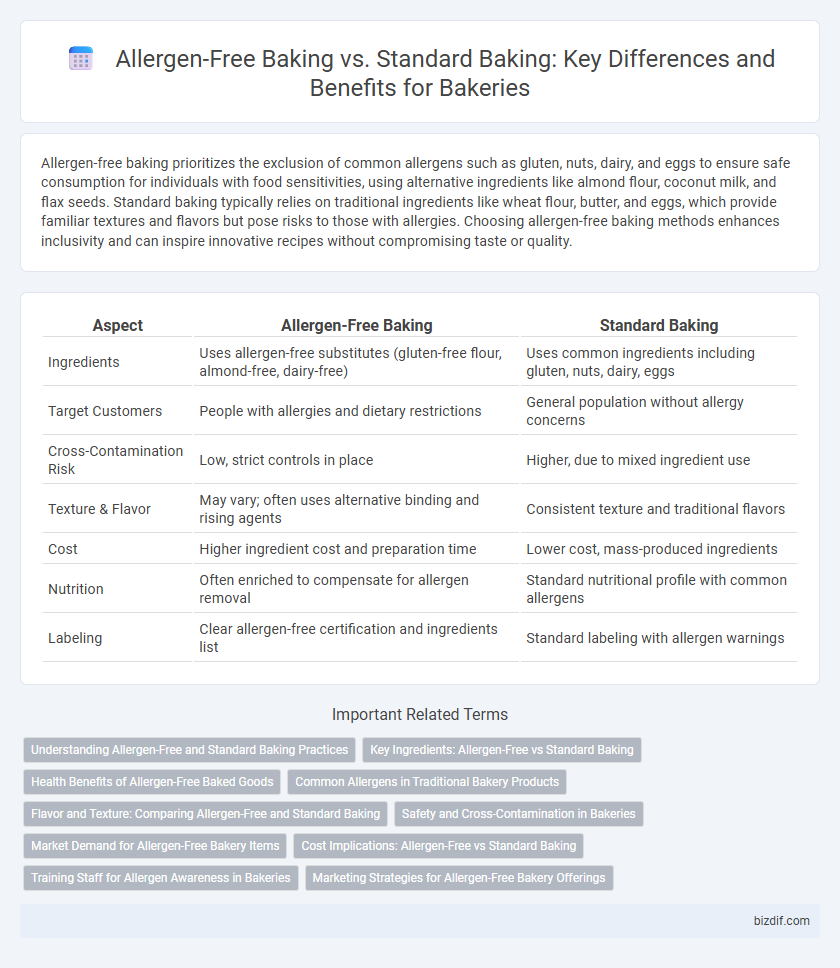
| Aspect | Allergen-Free Baking | Standard Baking |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | Uses allergen-free substitutes (gluten-free flour, almond-free, dairy-free) | Uses common ingredients including gluten, nuts, dairy, eggs |
| Target Customers | People with allergies and dietary restrictions | General population without allergy concerns |
| Cross-Contamination Risk | Low, strict controls in place | Higher, due to mixed ingredient use |
| Texture & Flavor | May vary; often uses alternative binding and rising agents | Consistent texture and traditional flavors |
| Cost | Higher ingredient cost and preparation time | Lower cost, mass-produced ingredients |
| Nutrition | Often enriched to compensate for allergen removal | Standard nutritional profile with common allergens |
| Labeling | Clear allergen-free certification and ingredients list | Standard labeling with allergen warnings |
Understanding Allergen-Free and Standard Baking Practices
Allergen-free baking involves using alternative ingredients such as almond flour, coconut milk, and flax eggs to avoid common allergens like gluten, dairy, nuts, and eggs, ensuring safe consumption for individuals with food allergies or sensitivities. Standard baking typically relies on traditional ingredients like wheat flour, butter, eggs, and milk, which may contain allergens and require careful management during preparation to prevent cross-contamination. Understanding these differences is crucial for bakeries to accommodate dietary restrictions, maintain food safety, and cater to a diverse customer base.
Key Ingredients: Allergen-Free vs Standard Baking
Allergen-free baking replaces common allergens like wheat, dairy, and eggs with alternative ingredients such as gluten-free flours (rice, almond, or coconut flour), plant-based milk, and flaxseed or chia seeds as egg substitutes. Standard baking typically uses ingredients like all-purpose flour, butter, cow's milk, and eggs, which provide structure, moisture, and leavening but may trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Using allergen-free key ingredients ensures safe consumption for people with allergies while maintaining texture and flavor through specialized substitutes.
Health Benefits of Allergen-Free Baked Goods
Allergen-free baked goods eliminate common triggers such as gluten, nuts, dairy, and eggs, significantly reducing the risk of allergic reactions and improving overall digestive health for sensitive individuals. These products often use alternative ingredients that promote better nutrient absorption and reduce inflammation, contributing to enhanced immune function. Choosing allergen-free options supports inclusive dietary needs and fosters safer consumption for people with food allergies and intolerances.
Common Allergens in Traditional Bakery Products
Traditional bakery products often contain common allergens such as wheat, eggs, milk, peanuts, tree nuts, soy, and gluten, posing risks for individuals with allergies or intolerances. Allergen-free baking replaces these ingredients with alternatives like gluten-free flours, plant-based milks, and egg substitutes to ensure safety and inclusivity. Understanding the prevalence of allergens in standard baked goods highlights the importance of allergen-free options for health-conscious consumers.
Flavor and Texture: Comparing Allergen-Free and Standard Baking
Allergen-free baking often requires alternative ingredients such as almond flour, coconut oil, or flaxseed to replace common allergens like gluten, dairy, and eggs, influencing both flavor and texture significantly compared to standard baking. Standard baking typically relies on wheat flour, butter, and eggs, which contribute to the familiar moistness and rich taste of traditional baked goods. While allergen-free products can achieve comparable texture using innovative binders and leavening agents, subtle differences in crumb structure and taste profiles remain noticeable to discerning palates.
Safety and Cross-Contamination in Bakeries
Allergen-free baking prioritizes strict ingredient control and dedicated equipment to prevent cross-contamination with common allergens like nuts, gluten, and dairy, ensuring consumer safety for individuals with food allergies. Standard baking operations often face challenges in avoiding allergen exposure due to shared preparation areas and utensils, increasing the risk of allergic reactions. Implementing rigorous cleaning protocols and allergen segregation is essential to maintain a safe environment in bakeries catering to allergen-sensitive customers.
Market Demand for Allergen-Free Bakery Items
The market demand for allergen-free bakery items is growing rapidly due to increasing awareness of food allergies and dietary restrictions. Consumers seeking gluten-free, nut-free, and dairy-free options drive the expansion of this niche within the broader bakery industry. Bakeries offering allergen-free products benefit from tapping into a loyal customer base focused on health and safety, making allergen-free baking a profitable and essential segment in today's market.
Cost Implications: Allergen-Free vs Standard Baking
Allergen-free baking requires specialized ingredients such as gluten-free flour, nut-free alternatives, and dairy substitutes, which often come at a higher cost compared to standard baking ingredients. The need for dedicated equipment and strict contamination controls further increases operational expenses in allergen-free baking. These factors contribute to higher production costs that are typically reflected in the final price of allergen-free baked goods.
Training Staff for Allergen Awareness in Bakeries
Training staff for allergen awareness in bakeries is essential to prevent cross-contamination and ensure customer safety. Comprehensive programs cover ingredient identification, proper cleaning protocols, and emergency response for allergic reactions. Regular refresher courses and clear labeling practices strengthen commitment to allergen-free baking standards compared to standard baking processes.
Marketing Strategies for Allergen-Free Bakery Offerings
Marketing strategies for allergen-free bakery offerings emphasize transparency and trust by clearly labeling ingredients and certifications such as gluten-free or nut-free. Targeted digital campaigns leverage social media platforms and influencer partnerships to reach health-conscious consumers and those with dietary restrictions. Collaborations with health professionals and participation in allergy awareness events further enhance brand credibility and customer loyalty.
Allergen-free Baking vs Standard Baking Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com