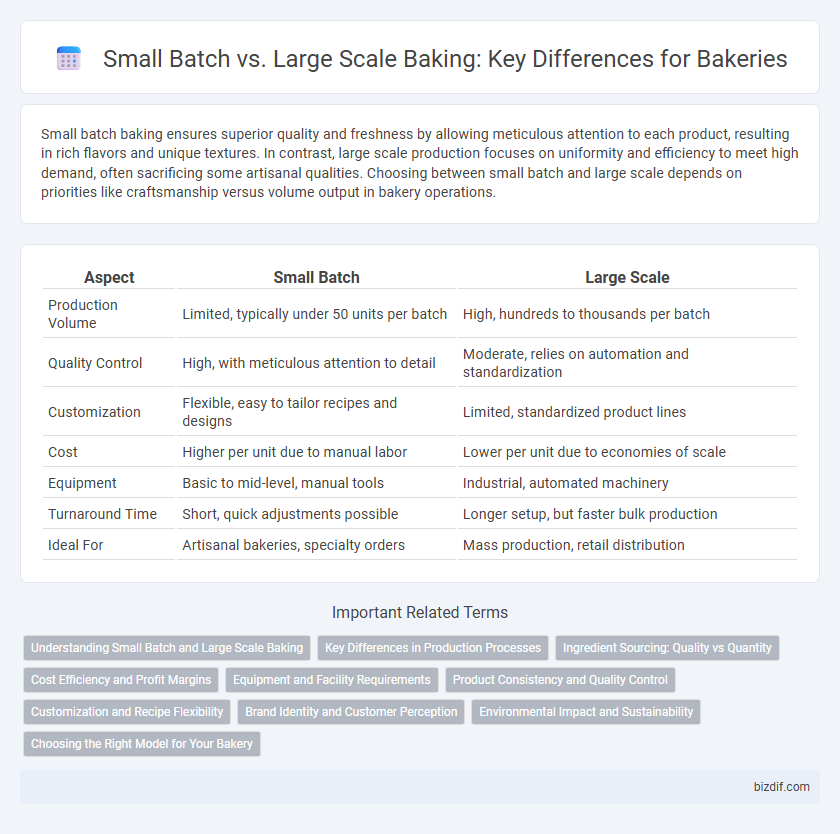
Small batch baking ensures superior quality and freshness by allowing meticulous attention to each product, resulting in rich flavors and unique textures. In contrast, large scale production focuses on uniformity and efficiency to meet high demand, often sacrificing some artisanal qualities. Choosing between small batch and large scale depends on priorities like craftsmanship versus volume output in bakery operations.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Small Batch | Large Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Production Volume | Limited, typically under 50 units per batch | High, hundreds to thousands per batch |
| Quality Control | High, with meticulous attention to detail | Moderate, relies on automation and standardization |
| Customization | Flexible, easy to tailor recipes and designs | Limited, standardized product lines |
| Cost | Higher per unit due to manual labor | Lower per unit due to economies of scale |
| Equipment | Basic to mid-level, manual tools | Industrial, automated machinery |
| Turnaround Time | Short, quick adjustments possible | Longer setup, but faster bulk production |
| Ideal For | Artisanal bakeries, specialty orders | Mass production, retail distribution |
Understanding Small Batch and Large Scale Baking
Small batch baking focuses on producing limited quantities of baked goods, ensuring higher quality control and the ability to experiment with unique recipes. Large scale baking prioritizes mass production, utilizing automated processes and industrial ovens to meet high demand efficiently. Understanding the differences between small batch and large scale baking helps bakers optimize their operations for quality, consistency, and volume.
Key Differences in Production Processes
Small batch bakery production emphasizes artisanal techniques, shorter production cycles, and frequent quality checks, resulting in fresh, handcrafted products with unique flavors. Large scale production relies on automated machinery, consistent ingredient sourcing, and extended batch sizes to maximize efficiency and uniformity across high volumes. Key differences include scalability, customization potential, and control over ingredient quality, which significantly affect product texture and taste.
Ingredient Sourcing: Quality vs Quantity
Small batch bakeries prioritize ingredient sourcing with a focus on quality, often selecting artisanal, organic, or locally-sourced components to enhance flavor and texture. Large scale bakeries emphasize quantity and cost-efficiency, sourcing bulk ingredients from industrial suppliers to meet high production demands. This difference impacts not only product consistency but also the overall taste and consumer perception of freshness.
Cost Efficiency and Profit Margins
Small batch baking often results in higher production costs due to limited economies of scale and increased labor intensity, impacting overall cost efficiency. Large-scale bakeries benefit from bulk purchasing and automated processes, significantly lowering ingredient and operational expenses to maximize profit margins. Balancing batch size directly influences profitability by determining material costs, waste reduction, and pricing strategies in bakery operations.
Equipment and Facility Requirements
Small batch baking requires specialized, smaller-scale equipment such as countertop mixers, compact proofers, and limited oven space, allowing for greater control over product quality and ingredient customization. Large-scale baking demands industrial-grade machinery, including high-capacity mixers, automated dough dividers, and conveyor ovens, to efficiently handle high production volumes within expansive facilities. Facility design for large-scale operations must incorporate extensive storage, workflow optimization, and compliance with food safety regulations, whereas small batch bakeries can operate in more flexible, smaller environments.
Product Consistency and Quality Control
Small batch baking ensures superior product consistency and quality control by allowing bakers to closely monitor ingredient ratios, fermentation times, and baking temperatures, resulting in uniform texture and flavor. Large-scale operations face challenges maintaining this consistency due to the volume and speed of production, often relying on automated processes that may sacrifice artisanal quality. Emphasizing small batch techniques enhances freshness, precision, and overall product excellence, which can be difficult to replicate on a mass scale without compromising quality standards.
Customization and Recipe Flexibility
Small batch baking enables greater customization and recipe flexibility, allowing bakers to experiment with unique ingredients and tailor products to specific customer preferences. In contrast, large scale production prioritizes efficiency and consistency, often limiting the ability to modify recipes or create personalized offerings. Small batch methods support artisanal quality and innovation, while large scale operations optimize volume and standardized taste.
Brand Identity and Customer Perception
Small batch baking enhances brand identity by emphasizing artisanal quality and craftsmanship, creating a unique customer perception of exclusivity and freshness. Large scale production often prioritizes consistency and availability, which can strengthen brand reliability but may dilute the perceived authenticity of the products. Customers associate small batch bakeries with personalized care, while large scale operations attract those seeking convenience and predictable taste.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Small batch baking minimizes environmental impact by reducing energy consumption and food waste through precise ingredient use, promoting sustainability in artisanal production. Large scale operations often demand significant water and energy resources, contributing to higher carbon footprints and increased packaging waste. Sustainable bakery practices prioritize small batch methods to enhance resource efficiency and support eco-friendly supply chains.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Bakery
Choosing the right model for your bakery depends on factors like production volume, ingredient freshness, and customer demand. Small batch baking ensures higher quality, customization, and reduced waste, ideal for artisanal bakeries or those focusing on niche markets. Large scale production offers cost efficiency, consistent output, and faster fulfillment, suitable for bakeries targeting broad distribution and high sales volume.
Small Batch vs Large Scale Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com