Gluten-free bakeries specialize in products made without wheat, barley, or rye, catering to individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. Traditional bakeries use conventional flours, offering a wider variety of textures and flavors but may not accommodate dietary restrictions. Choosing between the two depends on dietary needs and taste preferences, with gluten-free bakeries prioritizing health-conscious recipes and traditional bakeries focusing on classic baking techniques.
Table of Comparison
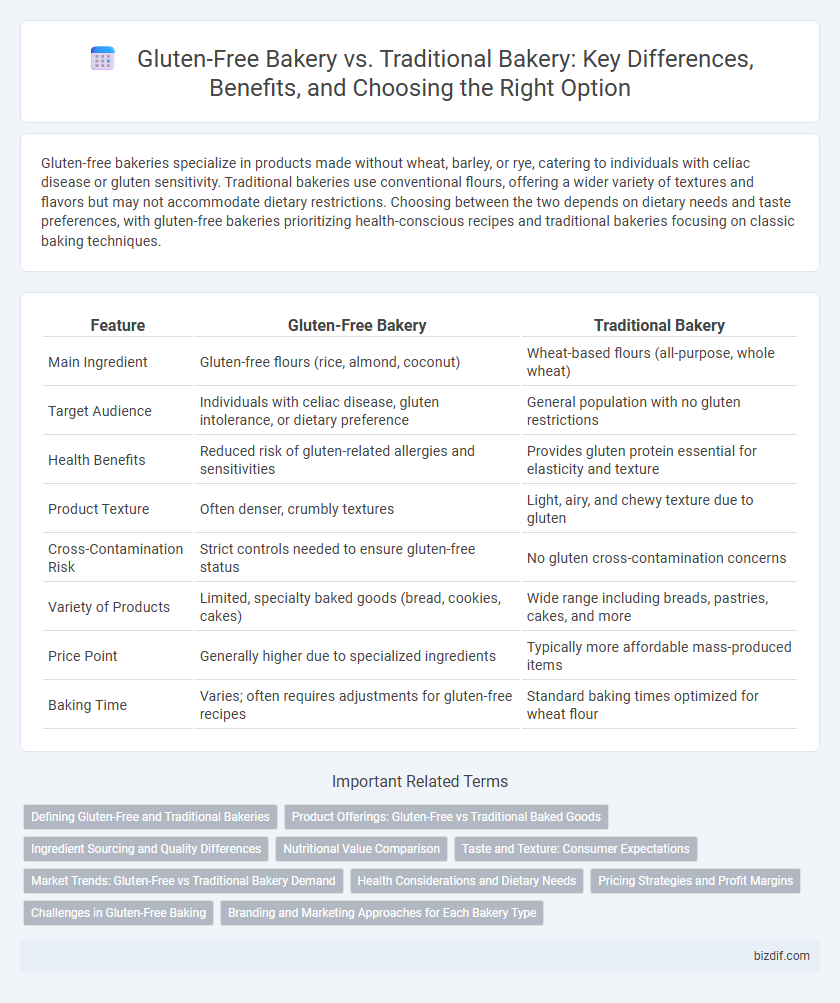
| Feature | Gluten-Free Bakery | Traditional Bakery |
|---|---|---|
| Main Ingredient | Gluten-free flours (rice, almond, coconut) | Wheat-based flours (all-purpose, whole wheat) |
| Target Audience | Individuals with celiac disease, gluten intolerance, or dietary preference | General population with no gluten restrictions |
| Health Benefits | Reduced risk of gluten-related allergies and sensitivities | Provides gluten protein essential for elasticity and texture |
| Product Texture | Often denser, crumbly textures | Light, airy, and chewy texture due to gluten |
| Cross-Contamination Risk | Strict controls needed to ensure gluten-free status | No gluten cross-contamination concerns |
| Variety of Products | Limited, specialty baked goods (bread, cookies, cakes) | Wide range including breads, pastries, cakes, and more |
| Price Point | Generally higher due to specialized ingredients | Typically more affordable mass-produced items |
| Baking Time | Varies; often requires adjustments for gluten-free recipes | Standard baking times optimized for wheat flour |
Defining Gluten-Free and Traditional Bakeries
Gluten-free bakeries specialize in products made without wheat, barley, rye, or other gluten-containing grains, catering to individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. Traditional bakeries use conventional ingredients like wheat flour, which contains gluten, contributing to the texture and rise of baked goods. The fundamental difference lies in ingredient selection, affecting texture, flavor, and dietary suitability.
Product Offerings: Gluten-Free vs Traditional Baked Goods
Gluten-free bakeries specialize in products made without wheat, barley, or rye, offering alternatives like almond flour bread, coconut flour muffins, and gluten-free pastries that cater to individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. Traditional bakeries focus on classic baked goods such as wheat-based bread, croissants, and cakes, utilizing gluten-containing ingredients to achieve texture and flavor. The distinction in product offerings emphasizes health concerns and dietary restrictions in gluten-free options, while traditional bakeries prioritize texture, taste, and variety rooted in gluten's structural properties.
Ingredient Sourcing and Quality Differences
Gluten-free bakeries prioritize sourcing certified gluten-free ingredients such as rice flour, almond flour, and tapioca starch to prevent cross-contamination, ensuring safety for celiac and gluten-sensitive customers. Traditional bakeries commonly use wheat-based flours like all-purpose and bread flour, which provide gluten's elasticity and structure, contributing to classic texture and rise. Quality differences emerge as gluten-free ingredients often require additional binders like xanthan gum to mimic gluten's properties, affecting the bread's chewiness and moisture retention.
Nutritional Value Comparison
Gluten-free bakeries often use alternative flours like almond, coconut, or rice flour, which can increase fiber and protein content compared to traditional wheat-based baked goods. Traditional bakeries typically offer a higher gluten content that supports dough elasticity but may have fewer nutrients like vitamins and minerals present in whole grain flours. Consumers seeking enhanced nutritional benefits often prefer gluten-free options due to lower carbohydrate levels and the absence of gluten, which may affect digestive health in sensitive individuals.
Taste and Texture: Consumer Expectations
Gluten-free bakeries prioritize alternative flours such as almond, rice, or coconut, creating products with a denser texture and slightly different mouthfeel compared to traditional wheat-based baked goods. Traditional bakeries typically deliver a softer crumb and chewier texture due to gluten's elasticity, meeting many consumers' expectations for classic taste and structure. Consumers seeking gluten-free options often look for improved flavor profiles and textures that closely mimic traditional bakery items without compromising dietary restrictions.
Market Trends: Gluten-Free vs Traditional Bakery Demand
The gluten-free bakery market has experienced a significant rise in consumer demand, driven by growing awareness of gluten intolerance and health-conscious lifestyles, leading to a market growth rate of over 10% annually. Traditional bakeries, while maintaining a strong presence, face challenges in capturing this emerging segment as preferences shift towards specialty diets and allergen-free options. Market trends indicate that gluten-free products are increasingly integrated into mainstream bakery offerings, signaling a notable shift in consumer purchasing behavior.
Health Considerations and Dietary Needs
Gluten-free bakeries cater specifically to individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease by eliminating wheat, barley, and rye from their recipes, reducing the risk of adverse reactions and digestive issues. Traditional bakeries typically use gluten-containing grains, which may pose health challenges for those with gluten sensitivity but provide essential nutrients like fiber and B vitamins to the general population. Understanding these dietary distinctions is crucial for selecting baked goods that align with individual health requirements and nutritional goals.
Pricing Strategies and Profit Margins
Gluten-free bakeries often implement premium pricing strategies due to higher ingredient costs and specialized production processes, which can lead to lower profit margins compared to traditional bakeries. Traditional bakeries benefit from economies of scale with bulk purchasing of standard ingredients, enabling competitive pricing and often healthier profit margins. Market demand for gluten-free products allows niche bakeries to maintain profitability despite higher prices, but traditional bakeries typically sustain steadier revenue streams due to broader customer bases.
Challenges in Gluten-Free Baking
Gluten-free baking faces significant challenges due to the absence of gluten, a protein that provides structure and elasticity in traditional bakery products. Achieving the same texture, moisture, and rise as in conventional breads and pastries requires specialized ingredients like xanthan gum, guar gum, or alternative flours such as almond, rice, or tapioca flour. Managing cross-contamination risks and ensuring consistent product quality further complicate gluten-free bakery operations compared to traditional bakeries.
Branding and Marketing Approaches for Each Bakery Type
Gluten-free bakeries emphasize health-conscious branding and target niche markets through social media campaigns showcasing allergen-free ingredients and certifications, attracting customers with dietary restrictions. Traditional bakeries rely on heritage branding, promoting artisanal craftsmanship and freshness, often leveraging local partnerships and in-store experiences to build trust and brand loyalty. Marketing strategies for gluten-free bakeries focus on transparency and education, whereas traditional bakeries highlight authenticity and sensory appeal to engage broader audiences.
Gluten-free bakery vs Traditional bakery Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com