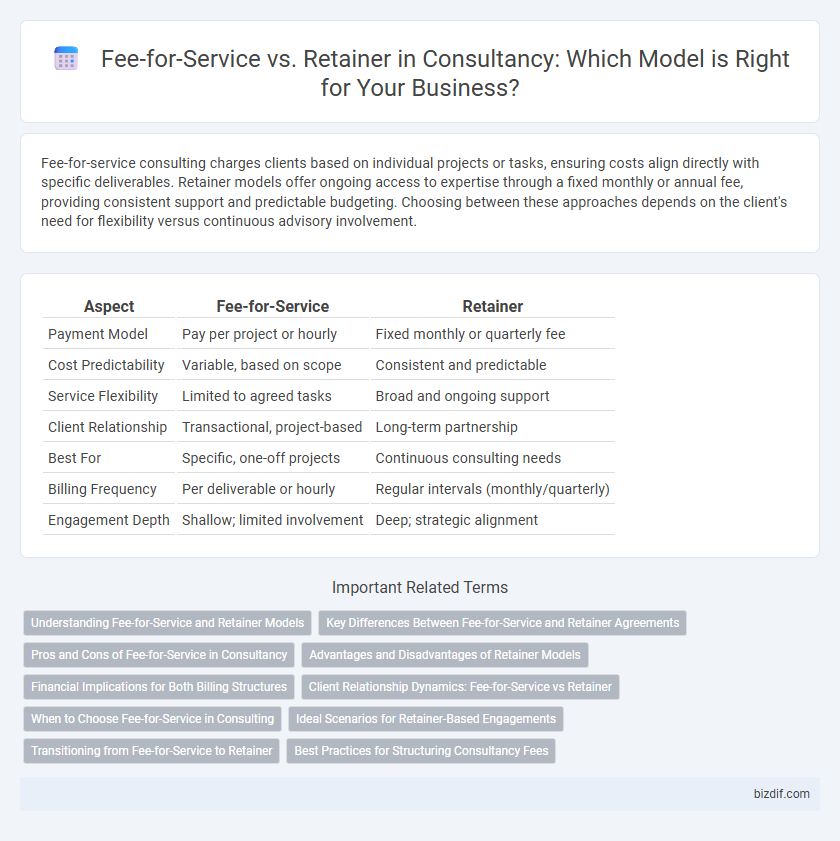
Fee-for-service consulting charges clients based on individual projects or tasks, ensuring costs align directly with specific deliverables. Retainer models offer ongoing access to expertise through a fixed monthly or annual fee, providing consistent support and predictable budgeting. Choosing between these approaches depends on the client's need for flexibility versus continuous advisory involvement.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fee-for-Service | Retainer |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Model | Pay per project or hourly | Fixed monthly or quarterly fee |
| Cost Predictability | Variable, based on scope | Consistent and predictable |
| Service Flexibility | Limited to agreed tasks | Broad and ongoing support |
| Client Relationship | Transactional, project-based | Long-term partnership |
| Best For | Specific, one-off projects | Continuous consulting needs |
| Billing Frequency | Per deliverable or hourly | Regular intervals (monthly/quarterly) |
| Engagement Depth | Shallow; limited involvement | Deep; strategic alignment |
Understanding Fee-for-Service and Retainer Models
Fee-for-Service consulting charges clients based on individual services rendered, offering flexibility and transparency in billing, while retainer models involve clients paying a fixed fee for ongoing access to consultancy expertise, ensuring consistent support and prioritization. Fee-for-Service suits projects with well-defined scopes and clear deliverables, whereas retainer agreements benefit clients needing continuous advisory and strategic guidance. Understanding these models helps businesses align consultancy expenses with their operational needs and resource planning.
Key Differences Between Fee-for-Service and Retainer Agreements
Fee-for-service agreements charge clients based on individual projects or tasks, offering flexibility and clear cost allocation for specific deliverables. Retainer agreements involve a fixed ongoing fee, providing continuous access to consultancy services and fostering long-term client relationships. Key differences include billing structure, predictability of expenses, and the scope of services covered under each contract type.
Pros and Cons of Fee-for-Service in Consultancy
Fee-for-Service consultancy offers clear cost transparency by charging clients based on specific tasks or hours worked, allowing precise budgeting and flexibility to engage consultants as needed. This model may lead to unpredictable expenses since consultants' work volumes can vary, potentially increasing overall costs without guaranteed sustained service. Lack of continuous engagement can limit strategic alignment and long-term value creation compared to retainer agreements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Retainer Models
Retainer models offer consistent revenue streams and foster long-term client relationships, ensuring ongoing support and strategic alignment. They may limit flexibility, as clients commit to fixed fees regardless of fluctuating service needs, potentially leading to underutilization or perceived value concerns. Retainers facilitate deeper client engagement but require clear scope definitions to prevent scope creep and maintain profitability.
Financial Implications for Both Billing Structures
Fee-for-service billing provides clear, upfront costs tied directly to specific deliverables, enabling clients to pay only for utilized services but may result in unpredictable expenses. Retainer agreements offer steady, predictable revenue streams for consultancies and fixed monthly fees for clients, ensuring budget stability while potentially leading to underutilization or overpayment risks. Evaluating cash flow impact, client commitment, and resource allocation is essential when choosing between these financial models.
Client Relationship Dynamics: Fee-for-Service vs Retainer
Fee-for-service models create transactional client relationships driven by specific project deliverables and clear cost boundaries, promoting flexibility but potentially limiting long-term engagement. Retainer agreements foster ongoing partnerships with predictable revenue streams, enabling deeper strategic collaboration and enhanced trust through consistent support. Clients on retainers typically experience prioritized access and tailored advice, while fee-for-service clients benefit from customized solutions without long-term commitment.
When to Choose Fee-for-Service in Consulting
Fee-for-Service consulting is ideal when projects have clearly defined deliverables, fixed scopes, or short-term needs, allowing clients to pay only for specific services rendered. This model suits businesses seeking flexibility and control over consulting expenses without long-term commitments. Choosing Fee-for-Service enables precise budgeting and accountability, essential for episodic or experimental consulting engagements.
Ideal Scenarios for Retainer-Based Engagements
Retainer-based engagements are ideal for clients seeking consistent advisory support with ongoing strategic needs or requiring continuous access to specialized expertise. This model suits projects with evolving scopes, where flexibility and rapid response are critical, such as digital transformation or regulatory compliance consulting. Organizations prioritizing long-term partnerships benefit from predictable budgeting and enhanced consultant familiarity with internal processes, driving more tailored and impactful recommendations.
Transitioning from Fee-for-Service to Retainer
Transitioning from a fee-for-service model to a retainer-based consultancy enhances financial predictability and strengthens client relationships through ongoing engagement. Consultants benefit from stable revenue streams and reduced administrative overhead, while clients receive continuous access to expertise and strategic support. Effective communication and clear scope definition are critical to ensure a smooth shift and mutual understanding of value in retainer agreements.
Best Practices for Structuring Consultancy Fees
Effective consultancy fee structuring balances client needs with business sustainability by clearly defining the scope and deliverables under Fee-for-Service agreements, ensuring transparency and measurability of outcomes. Retainer models foster long-term client relationships by providing predictable revenue streams and ongoing access to expertise, optimized through regular review and adjustment of service levels to match evolving client demands. Tailoring fee structures with clear contracts, milestone-based payments, and performance metrics enhances trust and aligns consultant incentives with client success.
Fee-for-Service vs Retainer Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com