Document editing ensures clarity, consistency, and proper formatting for business, legal, or academic texts, while manuscript editing focuses on refining narrative flow, character development, and plot coherence for creative writing. Manuscript editing often involves in-depth feedback on style, tone, and pacing to enhance the storytelling experience. Both types of editing improve the overall quality but target different goals and audiences.
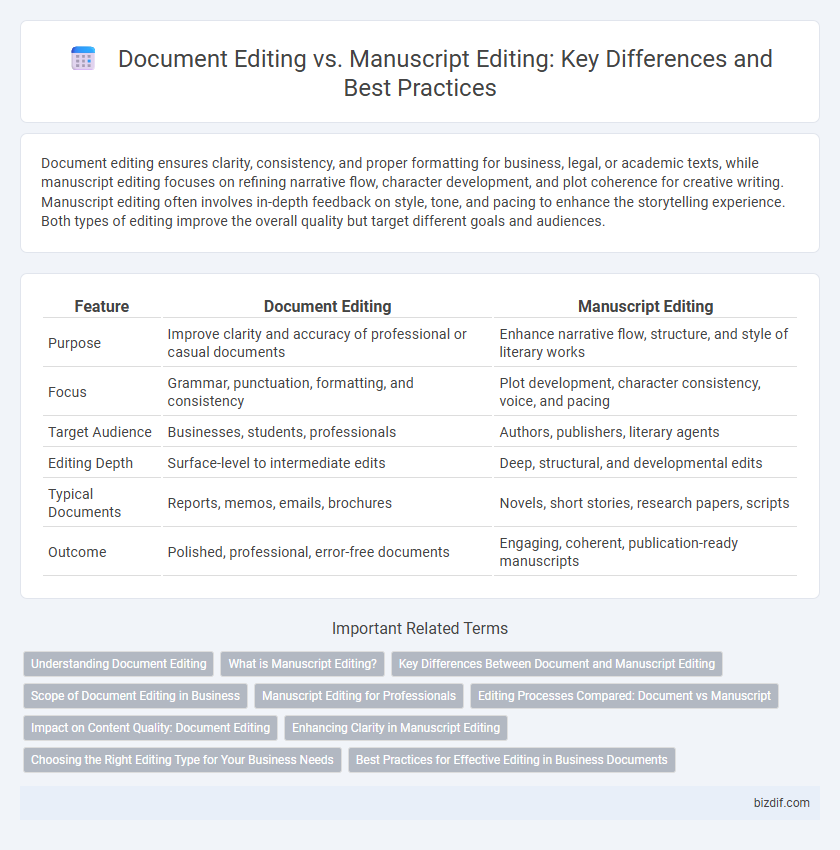
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Document Editing | Manuscript Editing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Improve clarity and accuracy of professional or casual documents | Enhance narrative flow, structure, and style of literary works |
| Focus | Grammar, punctuation, formatting, and consistency | Plot development, character consistency, voice, and pacing |
| Target Audience | Businesses, students, professionals | Authors, publishers, literary agents |
| Editing Depth | Surface-level to intermediate edits | Deep, structural, and developmental edits |
| Typical Documents | Reports, memos, emails, brochures | Novels, short stories, research papers, scripts |
| Outcome | Polished, professional, error-free documents | Engaging, coherent, publication-ready manuscripts |
Understanding Document Editing
Document editing involves refining content for clarity, grammar, and overall coherence across a variety of formats, including reports, articles, and business communications. It ensures consistency in style, tone, and structure, making the text accessible and professional for its intended audience. Unlike manuscript editing, which focuses deeply on narrative flow and developmental aspects, document editing prioritizes precision and clarity tailored to specific document types.
What is Manuscript Editing?
Manuscript editing involves a comprehensive review designed to prepare a manuscript for publication by addressing structure, clarity, grammar, and style while ensuring the author's voice remains intact. This process targets academic papers, books, or articles, focusing on substantive content improvement, flow enhancement, and error correction. Manuscript editors often collaborate closely with authors to refine arguments, improve readability, and meet specific formatting and submission guidelines.
Key Differences Between Document and Manuscript Editing
Document editing typically involves refining shorter texts such as reports, memos, or business correspondence, focusing on clarity, grammar, and formatting consistency. Manuscript editing addresses longer, complex works like novels or academic papers, emphasizing structural coherence, narrative flow, and adherence to genre-specific conventions. The key differences lie in the depth of content revision and the specialized knowledge required to enhance the manuscript's thematic and stylistic elements versus the document's concise communication needs.
Scope of Document Editing in Business
Document editing in business primarily focuses on refining reports, proposals, presentations, and correspondence to ensure clarity, professionalism, and accuracy. This scope includes grammar correction, formatting consistency, tone adjustment, and alignment with corporate style guides. Unlike manuscript editing, which emphasizes narrative flow and creative elements, document editing aims to enhance readability and effectiveness for decision-making and communication within corporate environments.
Manuscript Editing for Professionals
Manuscript editing for professionals involves a comprehensive review of structure, content, and language to ensure clarity, coherence, and adherence to publication standards. Unlike basic document editing, manuscript editing addresses deeper issues such as narrative flow, argument development, and scholarly tone essential for academic or literary success. Expert manuscript editors provide targeted feedback that enhances the work's impact, preparing it for submission to journals or publishers with rigorous quality expectations.
Editing Processes Compared: Document vs Manuscript
Document editing primarily involves refining grammar, punctuation, formatting, and clarity to ensure professional presentation, often for business reports or academic papers. Manuscript editing delves deeper, focusing on structure, plot consistency, character development, and thematic elements, essential for preparing novels or scholarly works for publication. The editing process for manuscripts is typically more extensive, iterative, and collaborative, requiring multiple revisions to enhance narrative flow and coherence compared to the more straightforward, concise nature of document editing.
Impact on Content Quality: Document Editing
Document editing significantly enhances content quality by refining clarity, coherence, and overall readability, ensuring the message is effectively communicated to the target audience. It involves correcting grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors, as well as improving sentence structure and flow without altering the core content. This process maintains the original intent while elevating the professionalism and accuracy of the document.
Enhancing Clarity in Manuscript Editing
Manuscript editing prioritizes enhancing clarity by refining the author's voice and ensuring the narrative flows seamlessly for readers in academic, fiction, or non-fiction contexts. Unlike basic document editing, it involves deeper analysis of structure, content coherence, and stylistic consistency to elevate the manuscript's overall quality. This process helps authors communicate complex ideas effectively while maintaining engagement and readability throughout the text.
Choosing the Right Editing Type for Your Business Needs
Document editing targets clarity, grammar, and formatting for business reports, proposals, or presentations, ensuring professional and error-free communication. Manuscript editing delves deeper into structure, content coherence, and style, essential for authors preparing books, articles, or academic papers for publication. Assessing your objective--whether polished internal documents or refined publishable manuscripts--guides the selection of the appropriate editing service tailored to your business goals.
Best Practices for Effective Editing in Business Documents
Document editing focuses on clarity, consistency, and professionalism to ensure business communications convey the intended message effectively. Manuscript editing involves deeper structural adjustments, tone refinement, and adherence to publication standards, which are essential for academic or literary submissions. Implementing best practices such as thorough proofreading, using style guides, and incorporating feedback loops enhances the precision and impact of both document and manuscript editing processes.
Document Editing vs Manuscript Editing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com