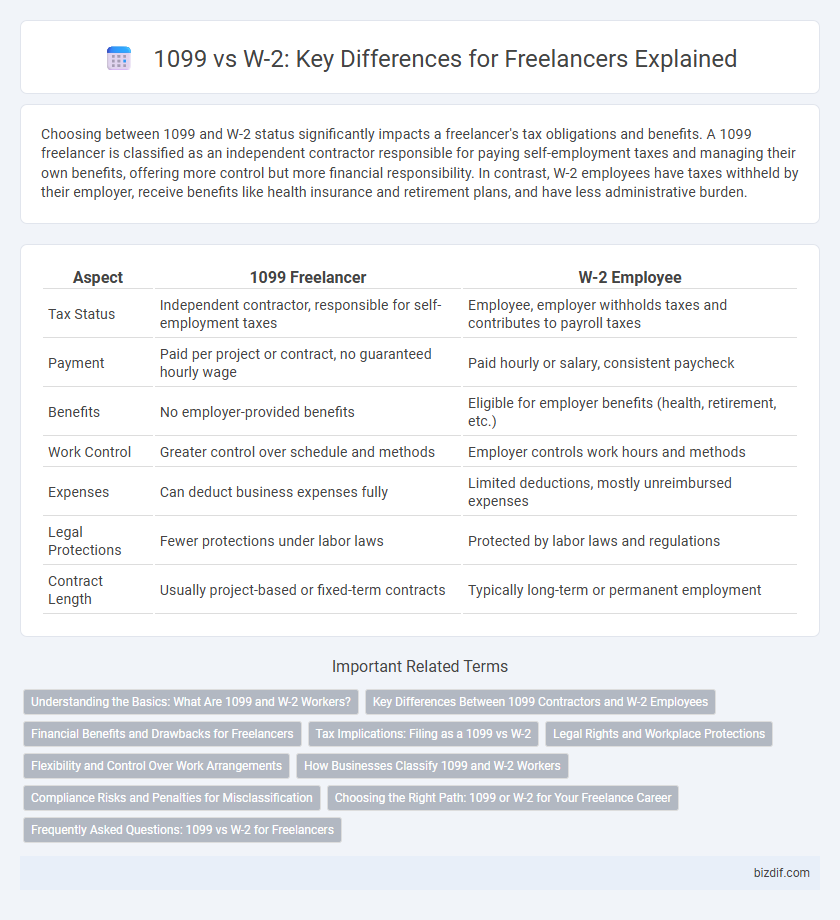
Choosing between 1099 and W-2 status significantly impacts a freelancer's tax obligations and benefits. A 1099 freelancer is classified as an independent contractor responsible for paying self-employment taxes and managing their own benefits, offering more control but more financial responsibility. In contrast, W-2 employees have taxes withheld by their employer, receive benefits like health insurance and retirement plans, and have less administrative burden.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | 1099 Freelancer | W-2 Employee |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Status | Independent contractor, responsible for self-employment taxes | Employee, employer withholds taxes and contributes to payroll taxes |
| Payment | Paid per project or contract, no guaranteed hourly wage | Paid hourly or salary, consistent paycheck |
| Benefits | No employer-provided benefits | Eligible for employer benefits (health, retirement, etc.) |
| Work Control | Greater control over schedule and methods | Employer controls work hours and methods |
| Expenses | Can deduct business expenses fully | Limited deductions, mostly unreimbursed expenses |
| Legal Protections | Fewer protections under labor laws | Protected by labor laws and regulations |
| Contract Length | Usually project-based or fixed-term contracts | Typically long-term or permanent employment |
Understanding the Basics: What Are 1099 and W-2 Workers?
1099 workers, often classified as independent contractors, receive a 1099-MISC form reporting income without tax withholding, making them responsible for estimating and paying their own taxes. W-2 workers are employees whose employers withhold income taxes, Social Security, and Medicare from their paychecks, typically offering benefits like health insurance and retirement plans. Understanding these distinctions is essential for freelancers to manage tax obligations and employment rights effectively.
Key Differences Between 1099 Contractors and W-2 Employees
1099 contractors operate as independent workers responsible for managing their own taxes, including self-employment tax, while W-2 employees have taxes withheld by their employer. Unlike W-2 employees, 1099 contractors do not receive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, or paid time off. Employers have more control over W-2 employees' work schedules and processes, whereas 1099 contractors maintain greater autonomy over how and when they complete tasks.
Financial Benefits and Drawbacks for Freelancers
Freelancers receiving a 1099 form retain control over tax deductions like business expenses, which can significantly reduce taxable income but require careful record-keeping and quarterly estimated tax payments. W-2 employees benefit from employer-covered payroll taxes and consistent income, reducing tax filing complexity but limiting deductible expense opportunities. Choosing between 1099 and W-2 impacts financial flexibility, tax liability, and benefits access, making it crucial for freelancers to weigh autonomy against administrative responsibilities.
Tax Implications: Filing as a 1099 vs W-2
Filing taxes as a 1099 freelancer requires reporting income as an independent contractor, subjecting earnings to self-employment tax which covers Social Security and Medicare contributions. W-2 employees have taxes withheld by employers, including income tax and half of Social Security and Medicare taxes, simplifying the filing process. Understanding the differences in tax liabilities and deductions between 1099 and W-2 forms helps freelancers optimize tax savings and ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
Legal Rights and Workplace Protections
Freelancers receiving a 1099 form are classified as independent contractors, which limits their access to legal rights and workplace protections such as minimum wage, overtime pay, and unemployment benefits. W-2 employees benefit from labor laws that guarantee rights including workers' compensation, anti-discrimination protections, and employer-provided benefits. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for freelancers to ensure proper classification and to seek appropriate legal safeguards in the gig economy.
Flexibility and Control Over Work Arrangements
1099 freelancers enjoy greater flexibility and control over their work arrangements, choosing projects, hours, and clients independently without employer-imposed schedules. W-2 employees have less autonomy, adhering to set work hours, direct supervision, and company policies that limit their ability to modify assignments or workload. This distinction impacts daily routines, work-life balance, and the extent of personal decision-making in professional roles.
How Businesses Classify 1099 and W-2 Workers
Businesses classify 1099 workers as independent contractors who manage their own taxes and benefits, allowing companies to avoid payroll taxes and provide more project-based work. W-2 workers are classified as employees, subject to employer withholding taxes, benefits, and labor protections under federal and state laws. Correct classification impacts compliance, tax obligations, and eligibility for unemployment and workers' compensation benefits.
Compliance Risks and Penalties for Misclassification
Misclassifying workers as independent contractors (1099) instead of employees (W-2) can lead to significant compliance risks including back taxes, penalties, and legal fees imposed by the IRS and Department of Labor. The IRS imposes fines up to 20% of wages for intentional misclassification, along with liability for unpaid payroll taxes and employee benefits. Businesses may also face class-action lawsuits from misclassified workers seeking wage and hour protections under state and federal labor laws.
Choosing the Right Path: 1099 or W-2 for Your Freelance Career
Choosing between 1099 and W-2 classification significantly impacts tax obligations, benefits, and control over your freelance career. As a 1099 independent contractor, you handle self-employment taxes and have greater flexibility but lack employer-provided benefits like health insurance and retirement plans. W-2 employees receive consistent paychecks, tax withholding, and access to benefits, often with less autonomy but increased financial stability and legal protections.
Frequently Asked Questions: 1099 vs W-2 for Freelancers
Freelancers often ask about the differences between 1099 and W-2 classifications, with 1099 indicating independent contractor status and W-2 representing employee status. Understanding tax implications is crucial, as 1099 freelancers handle their own tax payments, including self-employment tax, while W-2 employees have taxes withheld by employers. Benefits, job control, and legal protections also differ significantly, making the choice between 1099 and W-2 essential for freelancing tax strategy and career planning.
1099 vs W-2 Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com