White-labeling allows freelancers to deliver services under another company's brand, enhancing client trust and expanding reach without direct client interaction. Subcontracting involves outsourcing specific tasks to other freelancers, enabling project scalability and specialized expertise while maintaining overall project control. Both strategies optimize workflow but differ in client relationship dynamics and brand representation.
Table of Comparison
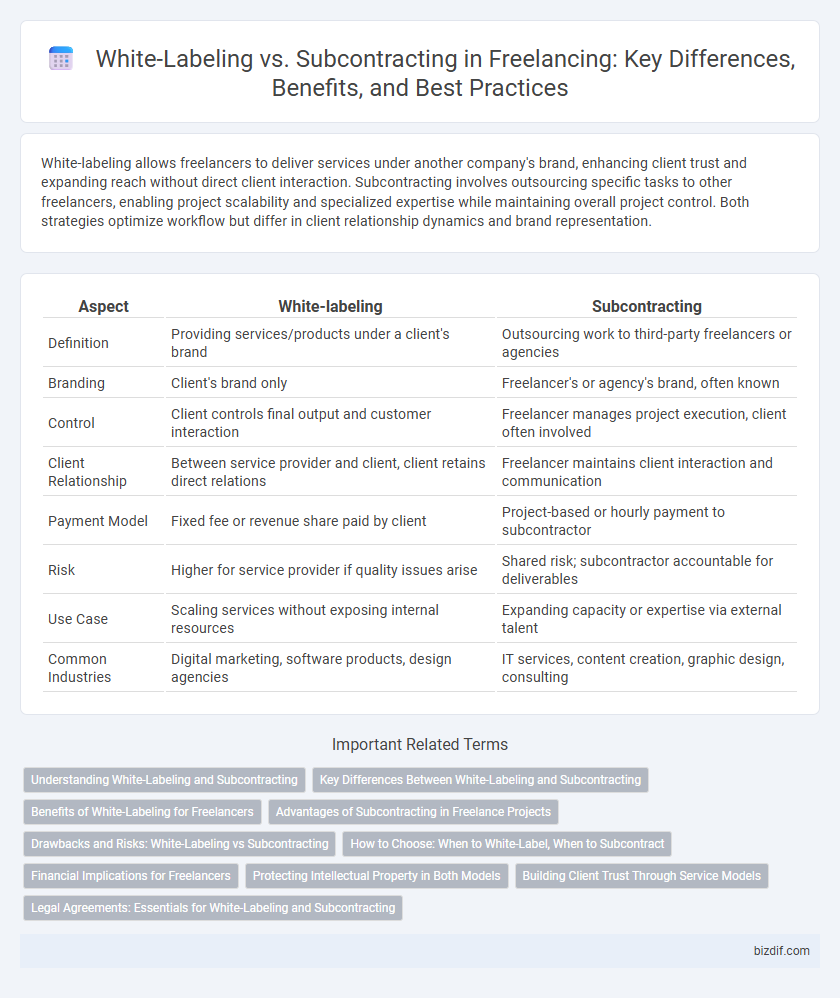
| Aspect | White-labeling | Subcontracting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Providing services/products under a client's brand | Outsourcing work to third-party freelancers or agencies |
| Branding | Client's brand only | Freelancer's or agency's brand, often known |
| Control | Client controls final output and customer interaction | Freelancer manages project execution, client often involved |
| Client Relationship | Between service provider and client, client retains direct relations | Freelancer maintains client interaction and communication |
| Payment Model | Fixed fee or revenue share paid by client | Project-based or hourly payment to subcontractor |
| Risk | Higher for service provider if quality issues arise | Shared risk; subcontractor accountable for deliverables |
| Use Case | Scaling services without exposing internal resources | Expanding capacity or expertise via external talent |
| Common Industries | Digital marketing, software products, design agencies | IT services, content creation, graphic design, consulting |
Understanding White-Labeling and Subcontracting
White-labeling in freelancing involves delivering services under another company's brand, allowing the client to resell without revealing the original provider. Subcontracting refers to hiring another freelancer or agency to complete parts of a project, maintaining transparency about the workflow. Understanding these models helps freelancers choose between maintaining brand identity and efficiently managing workloads.
Key Differences Between White-Labeling and Subcontracting
White-labeling involves delivering a product or service under another company's brand, allowing the hiring firm to maintain client relationships while outsourcing production. Subcontracting entails hiring an external freelancer or agency to complete specific tasks or projects without transferring branding rights, where the subcontractor directly impacts project execution. The key difference lies in ownership of the client relationship and brand representation, with white-labeling emphasizing invisible outsourcing and subcontracting focusing on collaborative task fulfillment.
Benefits of White-Labeling for Freelancers
White-labeling offers freelancers increased brand control by allowing them to deliver services under their own name, enhancing client trust and loyalty. It enables higher profit margins as freelancers can set their own pricing without intermediaries, unlike subcontracting. White-labeling also fosters long-term client relationships through consistent quality and direct communication, positioning freelancers as reliable industry experts.
Advantages of Subcontracting in Freelance Projects
Subcontracting in freelance projects offers increased flexibility by allowing freelancers to delegate specialized tasks and manage larger workloads efficiently, leading to faster project completion. It enhances scalability, enabling freelancers to take on multiple projects simultaneously without compromising quality. Outsourcing to reliable subcontractors also reduces risk by distributing responsibilities and leveraging diverse expertise.
Drawbacks and Risks: White-Labeling vs Subcontracting
White-labeling risks include loss of direct client relationships and potential brand dilution, which can undermine long-term business reputation. Subcontracting drawbacks involve reduced control over project quality and timelines, increasing the chance of missed deadlines and client dissatisfaction. Both models carry confidentiality risks, but subcontracting often requires stricter agreements to protect intellectual property and sensitive information.
How to Choose: When to White-Label, When to Subcontract
Choosing between white-labeling and subcontracting depends on your control preferences and client relationships. Opt for white-labeling when you want to maintain direct client interaction and brand your service as your own, ensuring a seamless, branded experience. Subcontracting is preferable when you aim to delegate specialized tasks to experts without altering your brand, allowing efficient project scaling while focusing on core competencies.
Financial Implications for Freelancers
White-labeling offers freelancers consistent income by allowing them to sell services under another company's brand, often with fixed pricing but limited profit margins. Subcontracting typically involves variable pay rates based on project scope, which can lead to higher earnings but less financial stability. Freelancers must weigh steady, lower-risk income against potential for greater, yet unpredictable, revenue streams when choosing between these models.
Protecting Intellectual Property in Both Models
White-labeling involves delivering services under a client's brand, requiring clear contracts that define ownership of intellectual property (IP) to prevent disputes and ensure the freelancer retains rights to their original work. Subcontracting demands explicit agreements outlining IP transfer or licensing terms, protecting both the primary contractor's and subcontractor's innovations. Effective IP protection in both models hinges on well-drafted contracts specifying usage, rights, and confidentiality obligations.
Building Client Trust Through Service Models
White-labeling offers freelancers the advantage of delivering branded services that clients can present as their own, significantly enhancing trust through consistent quality and seamless integration. Subcontracting involves handling specific tasks for primary contractors, which can build trust by demonstrating reliability and expertise within a defined scope. Choosing between these service models depends on the freelancer's ability to maintain transparency, meet deadlines, and uphold high standards that reinforce client confidence.
Legal Agreements: Essentials for White-Labeling and Subcontracting
Legal agreements for white-labeling and subcontracting in freelancing define intellectual property rights, confidentiality, and liability to protect both parties. White-label contracts typically emphasize branding ownership and client anonymity, while subcontracting agreements focus on work scope, deadlines, and payment terms. Clear clauses on dispute resolution and service quality standards ensure smooth collaboration and legal compliance.
White-labeling vs Subcontracting Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com