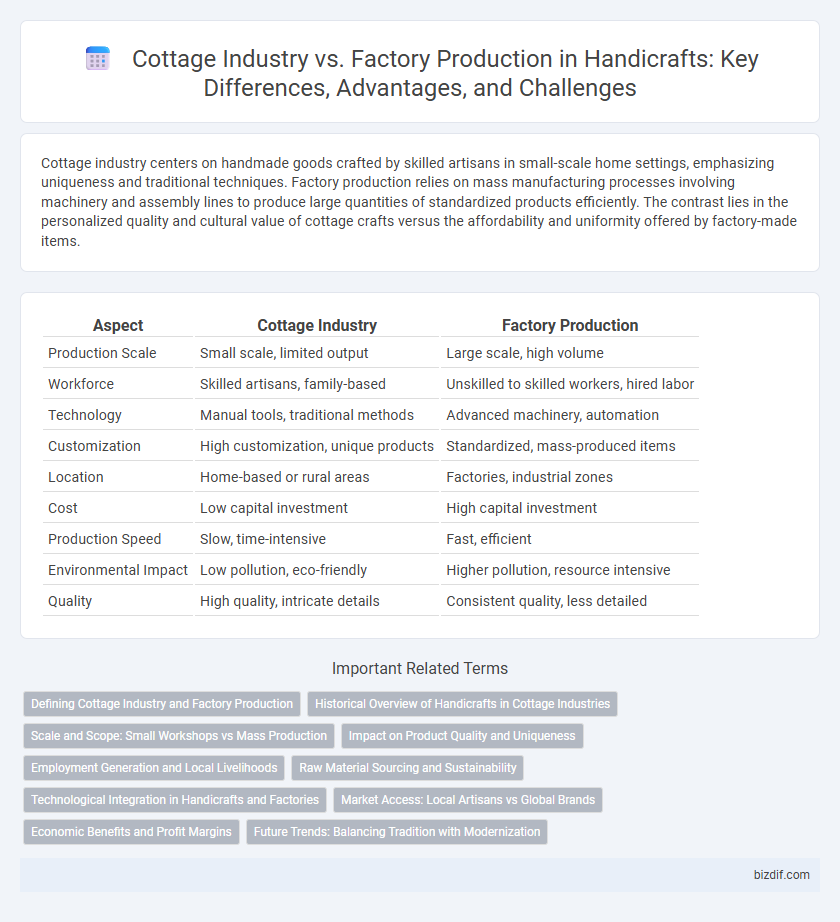
Cottage industry centers on handmade goods crafted by skilled artisans in small-scale home settings, emphasizing uniqueness and traditional techniques. Factory production relies on mass manufacturing processes involving machinery and assembly lines to produce large quantities of standardized products efficiently. The contrast lies in the personalized quality and cultural value of cottage crafts versus the affordability and uniformity offered by factory-made items.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cottage Industry | Factory Production |
|---|---|---|
| Production Scale | Small scale, limited output | Large scale, high volume |
| Workforce | Skilled artisans, family-based | Unskilled to skilled workers, hired labor |
| Technology | Manual tools, traditional methods | Advanced machinery, automation |
| Customization | High customization, unique products | Standardized, mass-produced items |
| Location | Home-based or rural areas | Factories, industrial zones |
| Cost | Low capital investment | High capital investment |
| Production Speed | Slow, time-intensive | Fast, efficient |
| Environmental Impact | Low pollution, eco-friendly | Higher pollution, resource intensive |
| Quality | High quality, intricate details | Consistent quality, less detailed |
Defining Cottage Industry and Factory Production
Cottage industry refers to small-scale, home-based production where artisans or families create handcrafted goods using traditional techniques, often with minimal machinery. Factory production involves large-scale manufacturing in centralized facilities, utilizing advanced machinery and assembly lines to produce standardized products efficiently. While cottage industries emphasize craftsmanship and customization, factory production prioritizes high volume and uniform quality.
Historical Overview of Handicrafts in Cottage Industries
Cottage industries have historically dominated handicraft production, allowing artisans to create goods with intricate, personalized designs using traditional techniques passed down through generations. This decentralized model fostered local economies and preserved cultural heritage by emphasizing manual skills over mechanization. In contrast, factory production, emerging during the Industrial Revolution, centralized manufacturing, increasing output but often at the cost of craftsmanship and individual artistic expression.
Scale and Scope: Small Workshops vs Mass Production
Cottage industry thrives on small workshops where artisans produce handcrafted goods, emphasizing unique designs and limited quantities. Factory production leverages mass production techniques to create large volumes of standardized products with greater efficiency. The scale of cottage industries remains localized and small-scale, while factories operate on a global scale with extensive product scopes.
Impact on Product Quality and Uniqueness
Cottage industry handicrafts typically exhibit higher product quality and uniqueness due to meticulous handcrafting techniques and personalized attention. Factory production emphasizes mass output, often compromising individual craftsmanship and resulting in standardized, less distinctive goods. The artisanal nature of cottage industry products fosters cultural heritage preservation, unlike the uniformity driven by factory manufacturing.
Employment Generation and Local Livelihoods
Cottage industries play a crucial role in employment generation by providing self-employment and job opportunities to rural artisans, thereby supporting local livelihoods and preserving traditional skills. Factory production, while capable of generating large-scale employment, often leads to urban migration and can marginalize small-scale producers by centralizing production. The growth of cottage industries sustains local economies through decentralized production, enhancing community resilience and cultural heritage.
Raw Material Sourcing and Sustainability
Cottage industries often source raw materials locally, promoting sustainable practices and reducing carbon footprints through minimal transportation. In contrast, factory production relies on large-scale, often global supply chains that may prioritize cost over environmental impact, leading to increased resource depletion and waste. Emphasizing sustainable raw material sourcing in cottage industries supports ethical consumption and preserves traditional craftsmanship.
Technological Integration in Handicrafts and Factories
Cottage industry handicrafts emphasize manual skill and traditional techniques with minimal technological integration, preserving cultural heritage and unique craftsmanship. Factory production incorporates advanced machinery and automation, significantly increasing output, consistency, and efficiency in manufacturing processes. The technological integration in factories allows for mass production while cottage industries maintain artisanal value and customization.
Market Access: Local Artisans vs Global Brands
Cottage industry handicraft thrives on local market access, allowing artisans to maintain cultural authenticity and personalized customer connections. Factory production enables global brands to mass-produce goods with uniform quality, expanding reach through international distribution networks. Local artisans face challenges competing with global brands' economies of scale, but niche markets and online platforms are bridging gaps in market access.
Economic Benefits and Profit Margins
Cottage industries offer higher profit margins by minimizing overhead costs and utilizing skilled artisan labor, fostering local economic growth through direct community employment. Factory production benefits from economies of scale, enabling mass production and lower per-unit costs that drive competitive pricing and increased market reach. While factories generate substantial revenue through volume sales, cottage industries sustain niche markets with personalized, high-value products that enhance economic diversity.
Future Trends: Balancing Tradition with Modernization
Cottage industry in handicrafts preserves artisanal skills and cultural heritage by emphasizing handcrafted quality, while factory production leverages automation for mass output and consistency. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach where advanced technology enhances traditional techniques, enabling customized products at scale without sacrificing authenticity. Integrating digital tools and sustainable practices will drive innovation, ensuring that handicraft industries remain economically viable and culturally relevant.
Cottage industry vs Factory production Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com