Sustainable handicraft practices prioritize eco-friendly materials, reduce waste, and support fair trade, contrasting with conventional methods that often rely on mass-produced, non-renewable resources and contribute to environmental degradation. Artisans using sustainable techniques preserve traditional skills while promoting biodiversity and reducing carbon footprints. Embracing sustainability in handicrafts fosters ethical consumerism and long-term cultural and ecological balance.
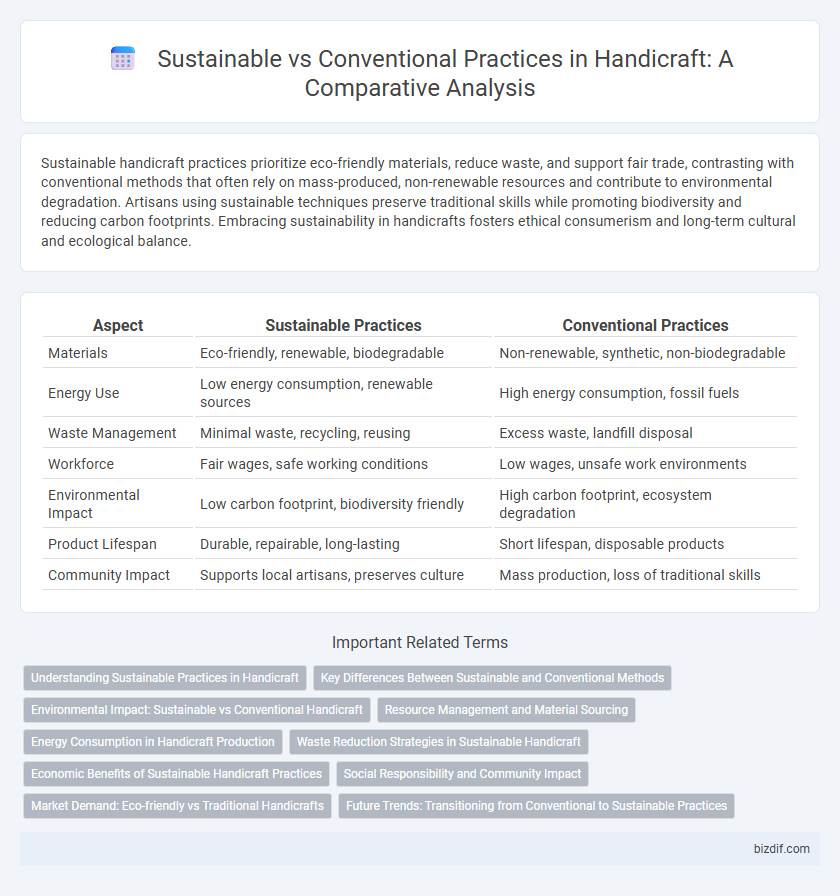
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sustainable Practices | Conventional Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Eco-friendly, renewable, biodegradable | Non-renewable, synthetic, non-biodegradable |
| Energy Use | Low energy consumption, renewable sources | High energy consumption, fossil fuels |
| Waste Management | Minimal waste, recycling, reusing | Excess waste, landfill disposal |
| Workforce | Fair wages, safe working conditions | Low wages, unsafe work environments |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodiversity friendly | High carbon footprint, ecosystem degradation |
| Product Lifespan | Durable, repairable, long-lasting | Short lifespan, disposable products |
| Community Impact | Supports local artisans, preserves culture | Mass production, loss of traditional skills |
Understanding Sustainable Practices in Handicraft
Sustainable practices in handicraft emphasize using eco-friendly materials, such as organic fibers and natural dyes, which reduce environmental impact compared to conventional synthetic alternatives. These methods promote waste minimization through recycling and upcycling, conserving resources and supporting local ecosystems. Embracing sustainability ensures the preservation of traditional techniques while fostering social responsibility and economic benefits for artisan communities.
Key Differences Between Sustainable and Conventional Methods
Sustainable handicraft practices prioritize using eco-friendly materials, minimizing waste, and supporting fair labor conditions, whereas conventional methods often rely on mass-produced, synthetic materials with higher environmental impact and less emphasis on ethical production. Sustainable artisans frequently adopt traditional techniques that enhance durability and cultural heritage, contrasting with conventional processes that focus on speed and cost-efficiency. The key differences lie in environmental responsibility, social equity, and the preservation of craftsmanship versus mass production and resource depletion.
Environmental Impact: Sustainable vs Conventional Handicraft
Sustainable handicraft practices significantly reduce environmental impact by utilizing natural, renewable materials and minimizing waste through eco-friendly production methods. Conventional handicraft processes often rely on synthetic materials and chemical treatments, leading to higher pollution and resource depletion. Adopting sustainable techniques helps preserve biodiversity, lowers carbon emissions, and supports circular economy principles within the handicraft industry.
Resource Management and Material Sourcing
Sustainable practices in handicraft emphasize renewable resource management and ethically sourced materials, reducing environmental impact compared to conventional practices that often rely on non-renewable inputs and mass-produced components. Artisans adopting sustainable methods prioritize local, biodegradable, and recycled materials, minimizing waste and fostering biodiversity conservation. These approaches ensure long-term ecological balance while supporting fair trade and community well-being.
Energy Consumption in Handicraft Production
Sustainable practices in handicraft production significantly reduce energy consumption by utilizing natural materials, manual tools, and solar-powered equipment, contrasting with conventional methods that rely heavily on electricity and fossil fuels. Traditional handicraft techniques often incorporate low-energy processes, minimizing the carbon footprint compared to industrialized manufacturing. Emphasizing energy-efficient practices not only conserves resources but also supports eco-friendly craftsmanship and long-term environmental sustainability.
Waste Reduction Strategies in Sustainable Handicraft
Sustainable handicraft employs innovative waste reduction strategies such as upcycling scrap materials, utilizing natural dyes, and adopting zero-waste design techniques to minimize environmental impact. These methods contrast with conventional practices that often generate significant textile and material waste through mass production and synthetic chemical use. Emphasizing waste minimization not only conserves resources but also enhances the artistic value and cultural significance of handcrafted goods.
Economic Benefits of Sustainable Handicraft Practices
Sustainable handicraft practices generate long-term economic benefits by utilizing locally sourced, renewable materials that reduce production costs and minimize environmental impact. Craft communities adopting eco-friendly techniques often access niche markets willing to pay premium prices for ethically made products, enhancing artisans' income stability. Furthermore, sustainable methods promote resource efficiency and waste reduction, lowering operational expenses compared to conventional practices reliant on synthetic inputs and mass production.
Social Responsibility and Community Impact
Sustainable practices in handicraft emphasize social responsibility by ensuring fair wages, safe working conditions, and community empowerment, contrasting with conventional methods that often exploit labor and ignore local welfare. By prioritizing eco-friendly materials and traditional skills, sustainable handicrafts foster economic growth and cultural preservation within communities, enhancing social cohesion and resilience. These practices reduce environmental harm while promoting ethical consumerism, driving long-term positive impacts on artisan livelihoods and regional development.
Market Demand: Eco-friendly vs Traditional Handicrafts
Sustainable practices in handicraft emphasize eco-friendly materials and processes, meeting the growing market demand for environmentally responsible products. Consumers increasingly prefer handmade goods that minimize environmental impact, boosting the popularity of organic fibers, natural dyes, and recycled materials. Traditional handicrafts, while valued for cultural authenticity, face declining market share as awareness of sustainability influences purchasing decisions globally.
Future Trends: Transitioning from Conventional to Sustainable Practices
The shift from conventional to sustainable practices in handicrafts emphasizes eco-friendly materials, renewable energy use, and waste reduction techniques to minimize environmental impact. Future trends include integrating digital tools for efficient resource management and adopting circular economy models to enhance product lifecycle sustainability. Artisans' growing commitment to transparency and ethical sourcing drives consumer demand for sustainable handcrafted goods.
Sustainable Practices vs Conventional Practices Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com