The cottage industry emphasizes handcrafted goods made in small-scale, home-based settings, allowing artisans to maintain traditional skills and personalize each product. In contrast, the factory system relies on mass production with mechanized processes, increasing output efficiency but often sacrificing individual craftsmanship. While cottage industries promote sustainable and culturally rich products, factory systems drive large-scale distribution and lower costs.
Table of Comparison
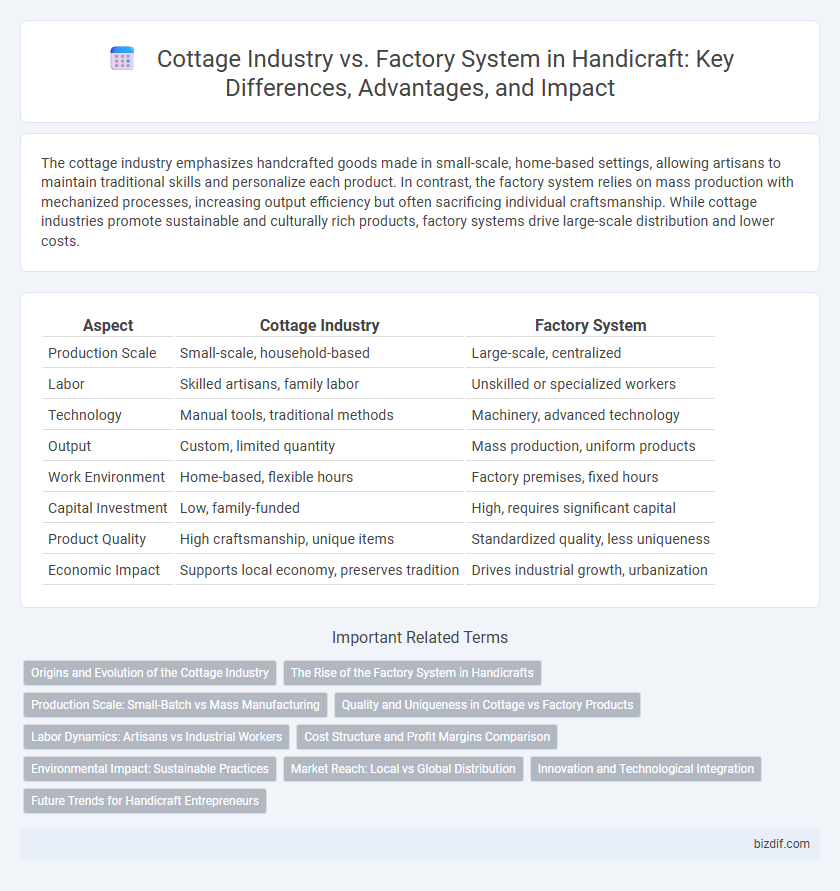
| Aspect | Cottage Industry | Factory System |
|---|---|---|
| Production Scale | Small-scale, household-based | Large-scale, centralized |
| Labor | Skilled artisans, family labor | Unskilled or specialized workers |
| Technology | Manual tools, traditional methods | Machinery, advanced technology |
| Output | Custom, limited quantity | Mass production, uniform products |
| Work Environment | Home-based, flexible hours | Factory premises, fixed hours |
| Capital Investment | Low, family-funded | High, requires significant capital |
| Product Quality | High craftsmanship, unique items | Standardized quality, less uniqueness |
| Economic Impact | Supports local economy, preserves tradition | Drives industrial growth, urbanization |
Origins and Evolution of the Cottage Industry
The cottage industry originated in the pre-industrial era, characterized by small-scale, home-based production where artisans crafted goods using manual tools and traditional techniques. This decentralized system allowed families to manage production within their homes, fostering community-based economies before mechanization. Over time, the evolution of the cottage industry faced significant transformation due to industrialization, which introduced factory systems that centralized production, increased output, and utilized machinery to replace manual labor.
The Rise of the Factory System in Handicrafts
The rise of the factory system in handicrafts revolutionized production by shifting from individual artisans to centralized manufacturing facilities, significantly increasing output and efficiency. Factories introduced mechanized tools and division of labor, reducing reliance on skilled craftsmanship and accelerating mass production. This transformation diminished the traditional cottage industry's role, leading to widespread economic and social changes in craft-based communities.
Production Scale: Small-Batch vs Mass Manufacturing
Cottage industry emphasizes small-batch production, allowing artisans to create unique, handcrafted items with high customization and attention to detail. In contrast, the factory system relies on mass manufacturing processes that produce large volumes of standardized products rapidly and cost-effectively. This difference in production scale significantly impacts product variety, quality, and economic efficiency within the handicraft sector.
Quality and Uniqueness in Cottage vs Factory Products
Cottage industry products are renowned for their exceptional quality and uniqueness, as skilled artisans use traditional techniques and personal attention in small-scale production. Factory system products prioritize mass production, often sacrificing individual craftsmanship and distinctiveness to achieve uniformity and efficiency. The inherent differences in production scale and methods result in cottage industry goods possessing greater aesthetic value and cultural authenticity compared to the standardized output of factories.
Labor Dynamics: Artisans vs Industrial Workers
Artisans in the cottage industry maintain control over their craftsmanship, working independently or in small family groups, which fosters skill specialization and personalized product quality. In contrast, industrial workers in factory systems perform segmented, repetitive tasks under strict supervision, leading to higher production efficiency but reduced individual creativity. The labor dynamics highlight a shift from autonomous, skill-driven work to regimented, volume-driven processes, impacting worker satisfaction and product uniqueness.
Cost Structure and Profit Margins Comparison
The cottage industry operates with low fixed costs due to minimal investment in machinery and reliance on manual labor, resulting in flexible but often variable profit margins influenced by product uniqueness and labor intensity. In contrast, the factory system requires significant capital investment in equipment and infrastructure, leading to higher fixed costs but benefiting from economies of scale that typically yield higher and more stable profit margins. Cost structures in the factory system favor mass production efficiency, while the cottage industry allows customization at a lower operational cost, affecting profitability in diverse market segments.
Environmental Impact: Sustainable Practices
Cottage industries prioritize sustainable practices by utilizing local materials and traditional methods that minimize waste and energy consumption, reducing their environmental footprint. Factory systems often rely on large-scale production processes that can lead to higher emissions, resource depletion, and waste generation, challenging environmental sustainability. Integrating eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient technologies in both systems can enhance environmental benefits and promote sustainable handicraft production.
Market Reach: Local vs Global Distribution
Cottage industries typically serve local markets, relying on handmade production and direct customer relationships to meet community-specific demands. In contrast, factory systems leverage mass production techniques and extensive distribution networks to achieve global market reach, enabling large-scale supply chains and international trade. The factory system's ability to scale output and standardize products efficiently broadens market access far beyond local boundaries.
Innovation and Technological Integration
Cottage industry relies heavily on manual skills and traditional techniques with minimal technological integration, fostering personalized craftsmanship but limiting large-scale innovation. Factory systems incorporate advanced machinery and automation, driving higher productivity and enabling continuous innovation through research and development. The shift towards factory systems has accelerated technological advancements, transforming production processes and optimizing efficiency in handicraft manufacturing.
Future Trends for Handicraft Entrepreneurs
Handicraft entrepreneurs are increasingly integrating digital technologies and e-commerce platforms to expand their market reach beyond traditional cottage industry confines. The factory system, with its automation and mass production, challenges artisans to innovate by blending handcrafted quality with scalable processes. Future trends indicate a growing demand for sustainable and customized products, positioning handicraft entrepreneurs to leverage authenticity and eco-conscious production methods.
Cottage Industry vs Factory System Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com